SNVS496F January 2007 – May 2021 LM5002
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Peak MOSFET Current
The peak MOSFET current is determined with Equation 9.
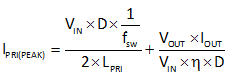
where:
- fsw is the switching frequency
- ƞ is the efficiency of the converter
The maximum peak MOSFET current occurs when VIN is at its minimum specified voltage. Equation 9 is used to calculate the peak MOSFET current. Assuming η is 90% the peak MOSFET current is calculated as 430 mA.
The internal power MOSFET must withstand the input voltage plus the output voltage multiplied by the turns ratio during the off-time. This is determined with Equation 10.
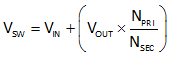
In addition, any leakage inductance of the transformer causes a turnoff voltage spike in addition to Equation 10. This voltage spike is related to the MOSFET drain-to-source capacitance as well as other parasitic capacitances. To limit the spike magnitude, use a RCD termination or a Diode-Zener clamp.