SNOSAZ6C August 2008 – November 2015 LMV831 , LMV832 , LMV834
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
At TA = 25°C, RL = 10 kΩ, V+ = 3.3 V, V− = 0 V, Unless otherwise specified.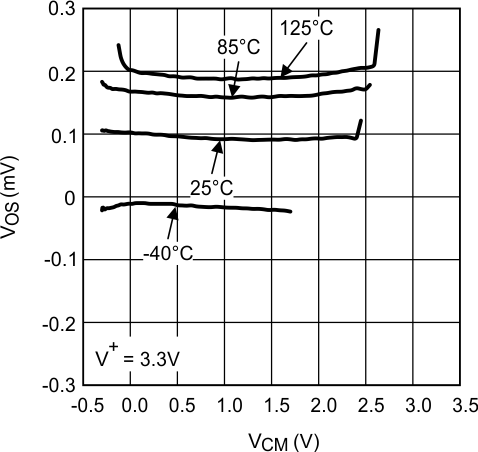 Figure 1. VOS vs VCM at V+ = 3.3 V
Figure 1. VOS vs VCM at V+ = 3.3 V
 Figure 3. VOS vs Supply Voltage
Figure 3. VOS vs Supply Voltage
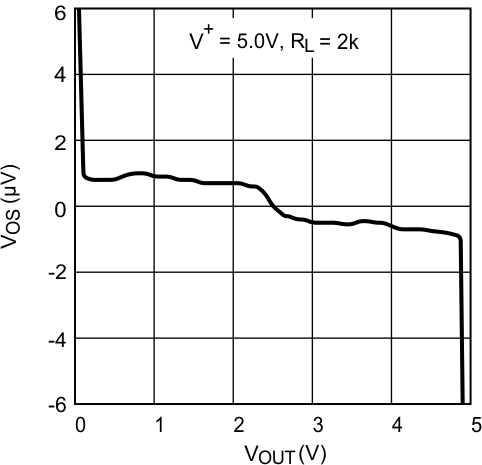 Figure 5. VOS vs VOUT
Figure 5. VOS vs VOUT
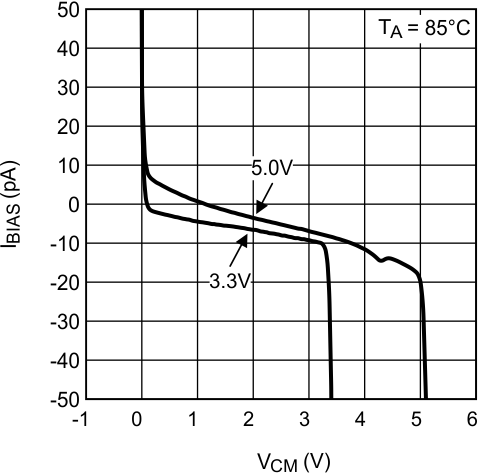 Figure 7. Input Bias Current vs VCM at 85°C
Figure 7. Input Bias Current vs VCM at 85°C
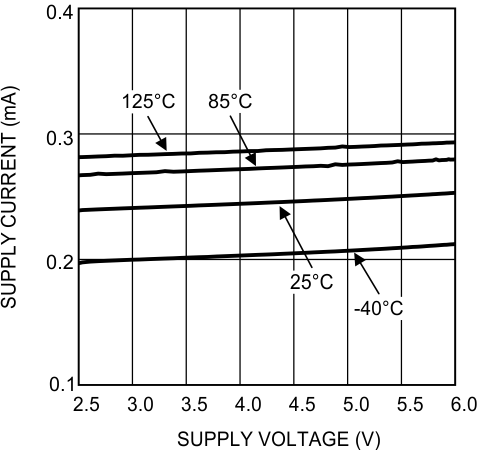 Figure 9. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Single LMV831
Figure 9. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Single LMV831
 Figure 11. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Quad LMV834
Figure 11. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Quad LMV834
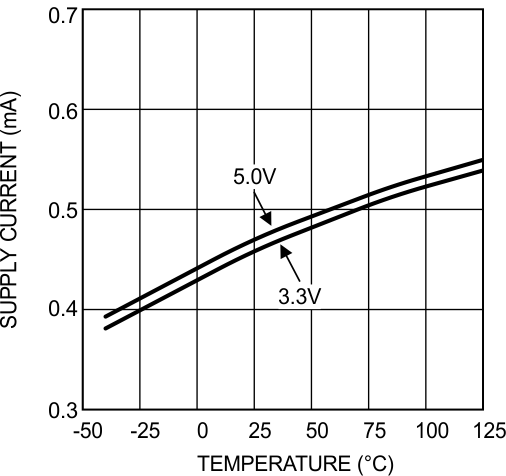 Figure 13. Supply Current vs Temperature Dual LMV832
Figure 13. Supply Current vs Temperature Dual LMV832
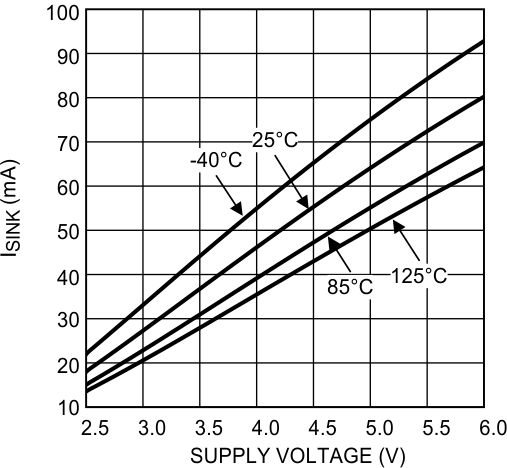 Figure 15. Sinking Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 15. Sinking Current vs Supply Voltage

RL = 2 kΩ
Figure 17. Output Swing High vs Supply Voltage

RL = 2 kΩ
Figure 19. Output Swing Low vs Supply Voltage
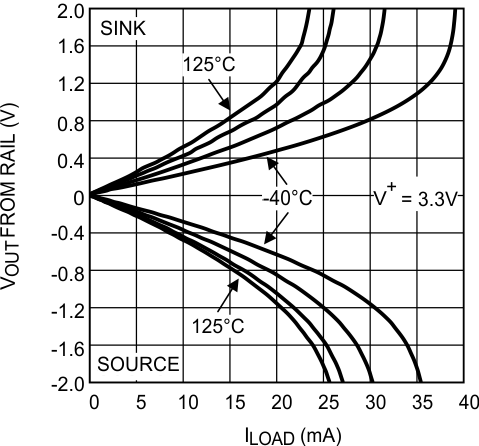 Figure 21. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Current at V+ = 3.3 V
Figure 21. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Current at V+ = 3.3 V
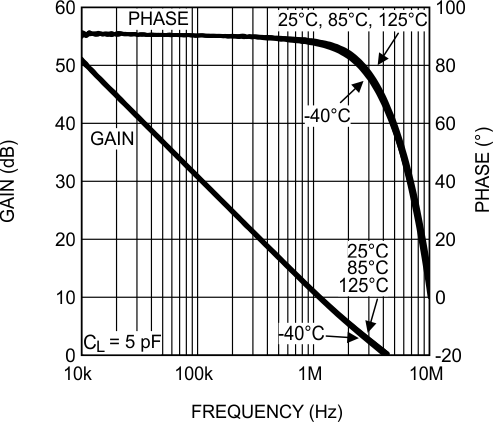 Figure 23. Open-Loop Frequency Response vs Temperature
Figure 23. Open-Loop Frequency Response vs Temperature
 Figure 25. Phase Margin vs Capacitive Load
Figure 25. Phase Margin vs Capacitive Load
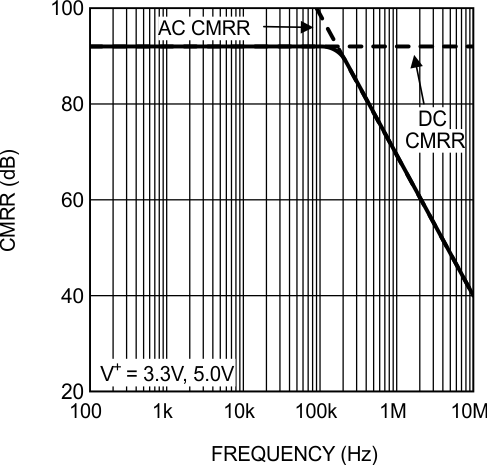 Figure 27. CMRR vs Frequency
Figure 27. CMRR vs Frequency
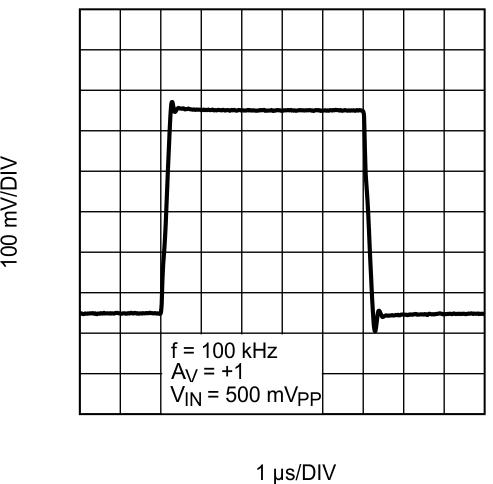 Figure 29. Large Signal Step Response With Gain = 1
Figure 29. Large Signal Step Response With Gain = 1
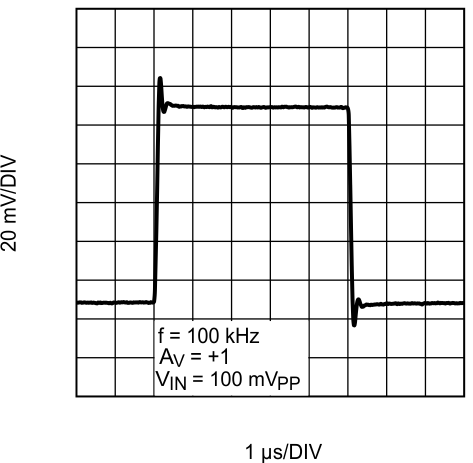 Figure 31. Small Signal Step Response With Gain = 1
Figure 31. Small Signal Step Response With Gain = 1
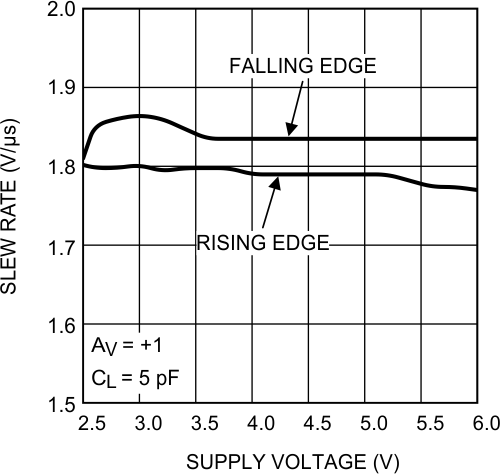 Figure 33. Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage
Figure 33. Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage
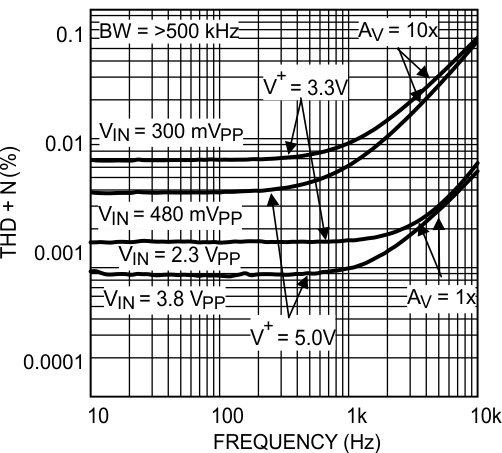 Figure 35. THD+N vs Frequency
Figure 35. THD+N vs Frequency
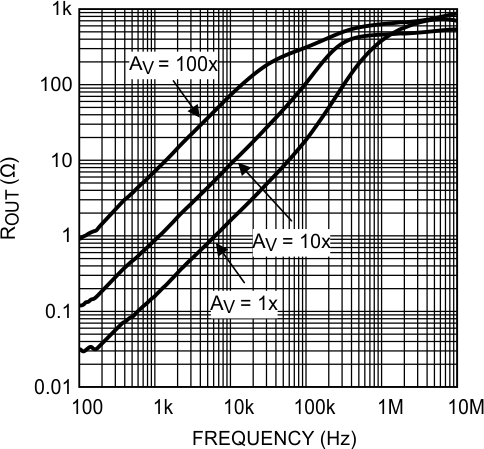 Figure 37. ROUT vs Frequency
Figure 37. ROUT vs Frequency
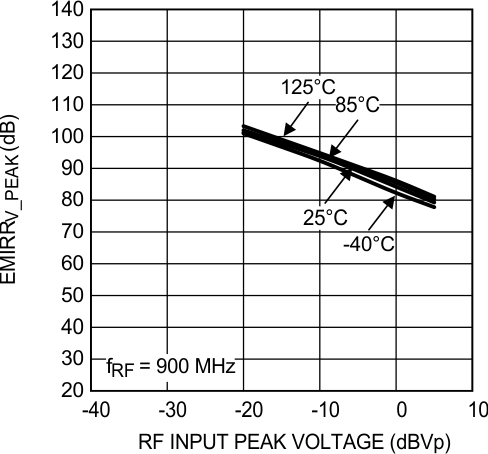 Figure 39. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 900 MHz
Figure 39. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 900 MHz
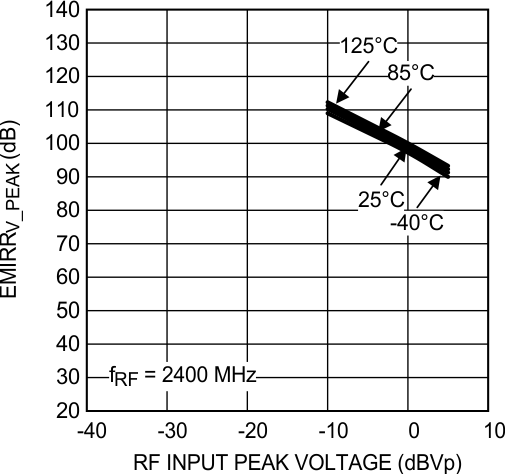 Figure 41. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 2400 MHz
Figure 41. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 2400 MHz
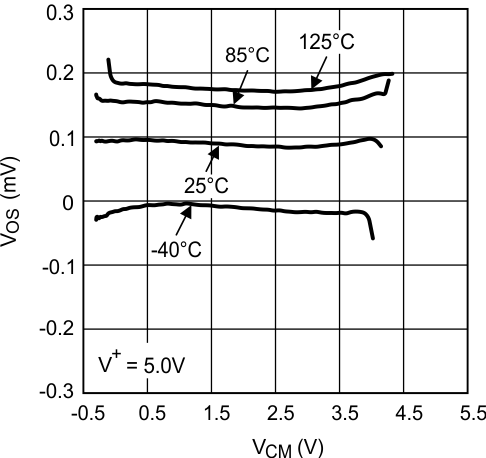 Figure 2. VOS vs VCM at V+ = 5 V
Figure 2. VOS vs VCM at V+ = 5 V
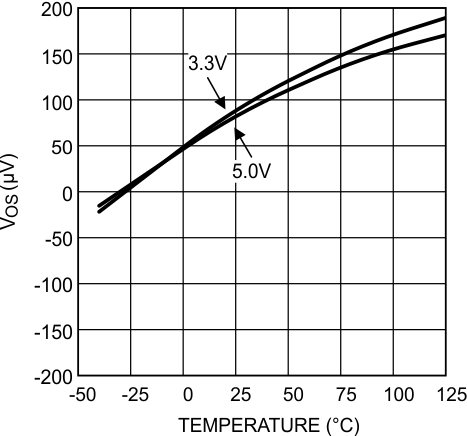 Figure 4. VOS vs Temperature
Figure 4. VOS vs Temperature
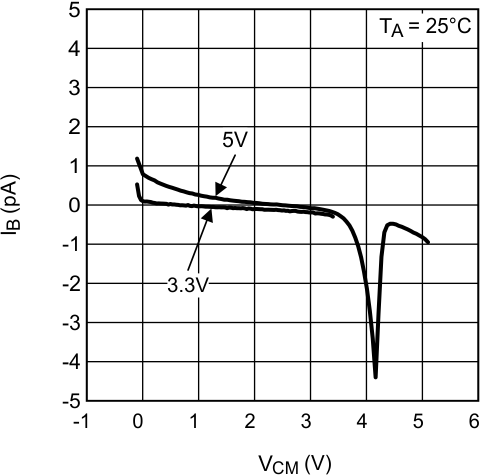 Figure 6. Input Bias Current vs VCM at 25°C
Figure 6. Input Bias Current vs VCM at 25°C
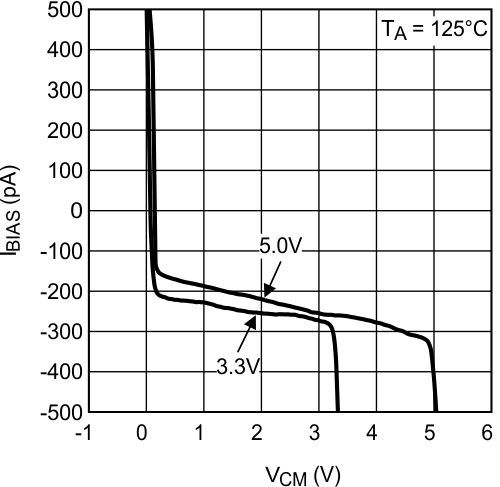 Figure 8. Input Bias Current vs VCM at 125°C
Figure 8. Input Bias Current vs VCM at 125°C
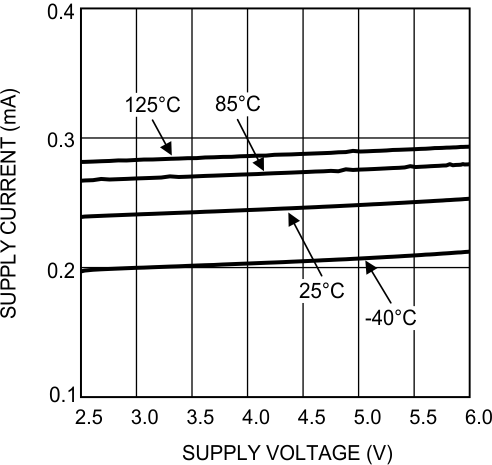 Figure 10. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Dual LMV832
Figure 10. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Dual LMV832
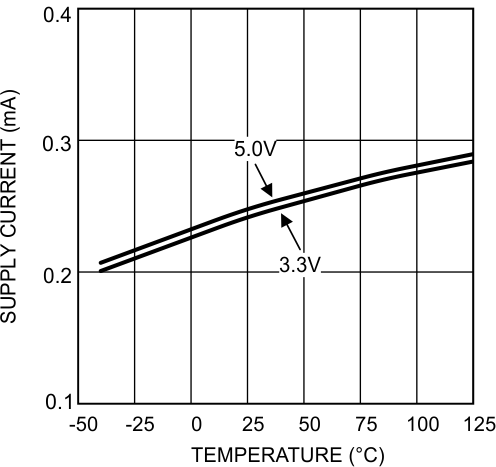 Figure 12. Supply Current vs Temperature Single LMV831
Figure 12. Supply Current vs Temperature Single LMV831
 Figure 14. Supply Current vs Temperature Quad LMV834
Figure 14. Supply Current vs Temperature Quad LMV834
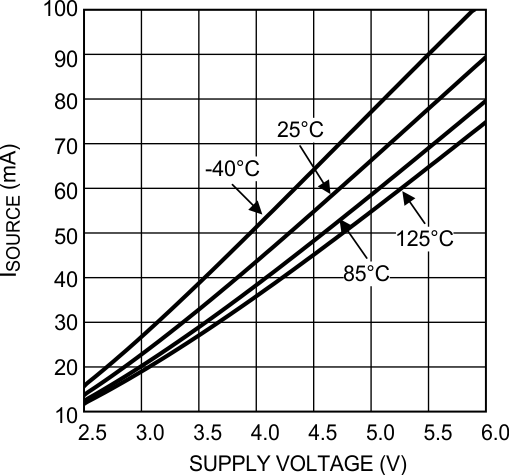 Figure 16. Sourcing Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 16. Sourcing Current vs Supply Voltage
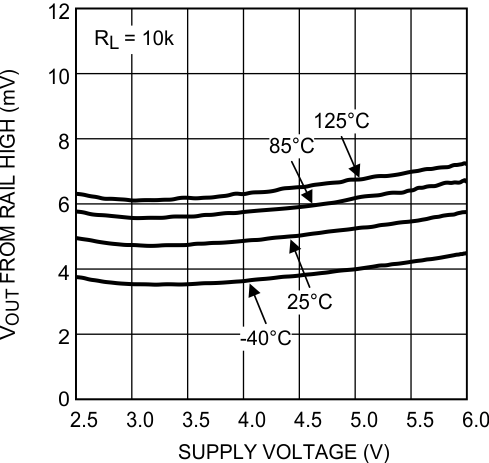
RL = 10 kΩ
Figure 18. Output Swing High vs Supply Voltage

RL = 10 kΩ
Figure 20. Output Swing Low vs Supply Voltage
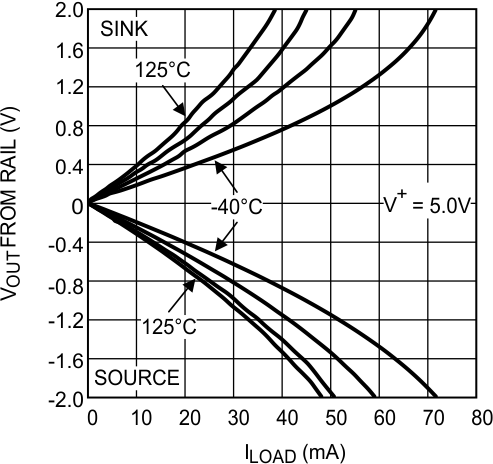 Figure 22. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Current at V+ = 5 V
Figure 22. Output Voltage Swing vs Load Current at V+ = 5 V
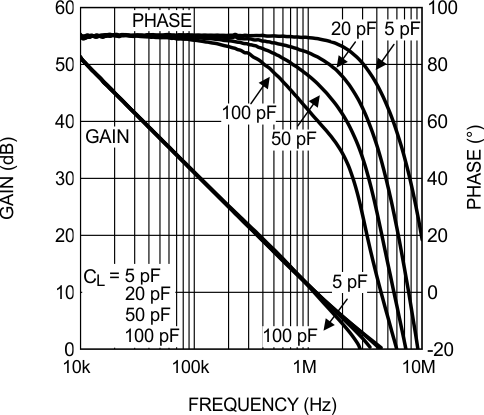 Figure 24. Open-Loop Frequency Response vs Load Conditions
Figure 24. Open-Loop Frequency Response vs Load Conditions
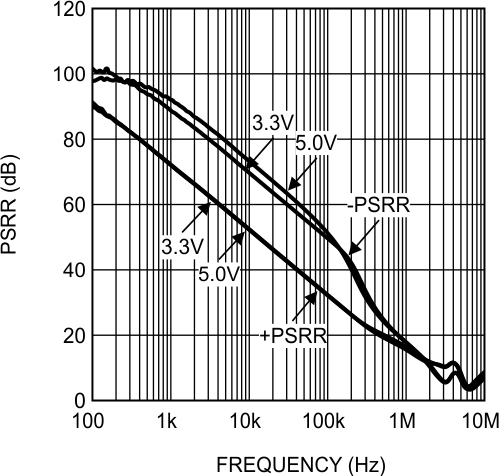 Figure 26. PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 26. PSRR vs Frequency
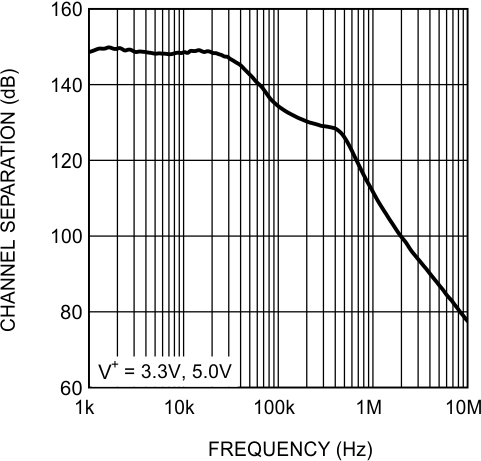 Figure 28. Channel Separation vs Frequency
Figure 28. Channel Separation vs Frequency
 Figure 30. Large Signal Step Response With Gain = 10
Figure 30. Large Signal Step Response With Gain = 10
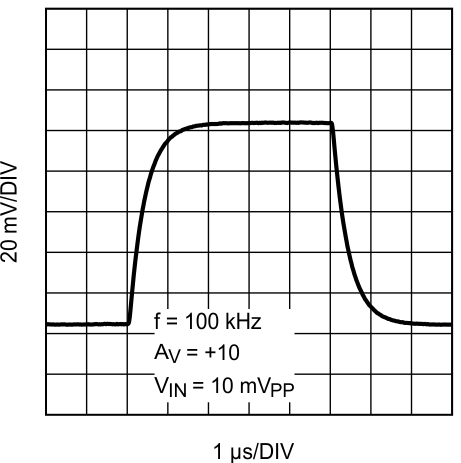 Figure 32. Small Signal Step Response With Gain = 10
Figure 32. Small Signal Step Response With Gain = 10
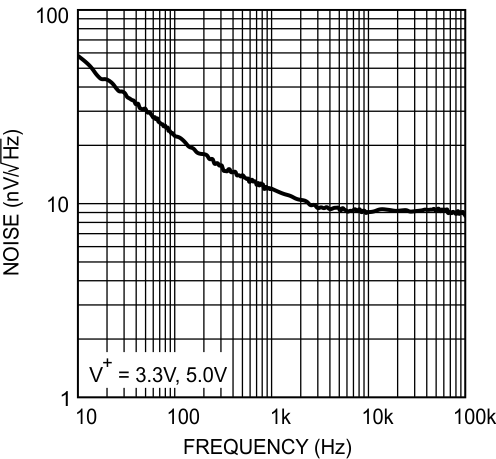 Figure 34. Input Voltage Noise vs Frequency
Figure 34. Input Voltage Noise vs Frequency
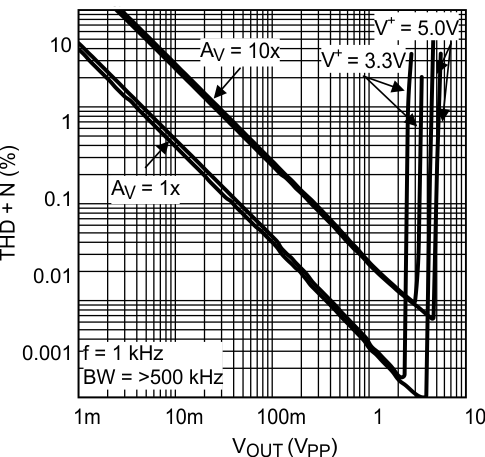 Figure 36. THD+N vs Amplitude
Figure 36. THD+N vs Amplitude
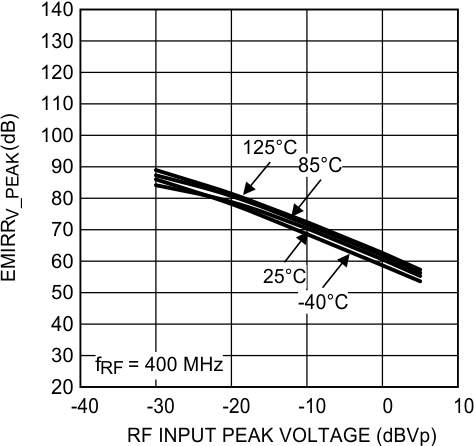 Figure 38. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 400 MHz
Figure 38. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 400 MHz
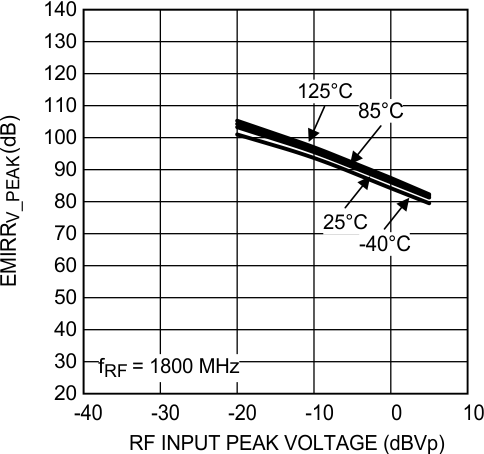 Figure 40. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 1800 MHz
Figure 40. EMIRR IN+ vs Power at 1800 MHz
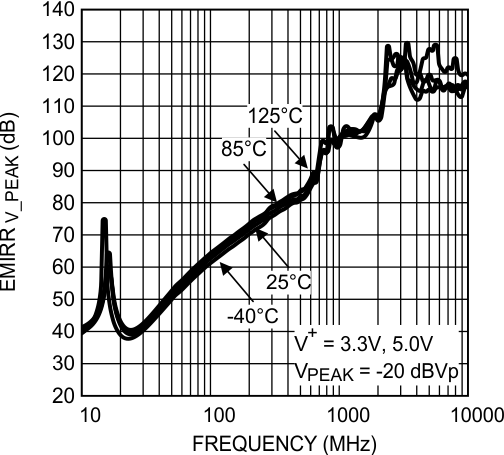 Figure 42. EMIRR IN+ vs Frequency
Figure 42. EMIRR IN+ vs Frequency