SLASE58E February 2016 – December 2019 MSP430FR2310 , MSP430FR2311
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5 Active Mode Supply Current Per MHz
- 5.6 Low-Power Mode LPM0 Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.7 Low-Power Mode LPM3 and LPM4 Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.8 Low-Power Mode LPMx.5 Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.9 Production Distribution of LPM Supply Currents
- 5.10 Typical Characteristics – Current Consumption Per Module
- 5.11 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.12
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.12.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.12.2 Reset Timing
- 5.12.3 Clock Specifications
- 5.12.4 Digital I/Os
- 5.12.5 VREF+ Built-in Reference
- 5.12.6 Timer_B
- 5.12.7
eUSCI
- Table 5-14 eUSCI (UART Mode) Clock Frequency
- Table 5-15 eUSCI (UART Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-16 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Clock Frequency
- Table 5-17 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-18 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-19 eUSCI (I2C Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 5.12.8 ADC
- 5.12.9 Enhanced Comparator (eCOMP)
- 5.12.10 Smart Analog Combo (SAC)
- 5.12.11 Transimpedance Amplifier (TIA)
- 5.12.12 FRAM
- 5.12.13 Emulation and Debug
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 CPU
- 6.3 Operating Modes
- 6.4 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 6.5 Memory Organization
- 6.6 Bootloader (BSL)
- 6.7 JTAG Standard Interface
- 6.8 Spy-Bi-Wire Interface (SBW)
- 6.9 FRAM
- 6.10 Memory Protection
- 6.11
Peripherals
- 6.11.1 Power-Management Module (PMM) and On-chip Reference Voltages
- 6.11.2 Clock System (CS) and Clock Distribution
- 6.11.3 General-Purpose Input/Output Port (I/O)
- 6.11.4 Watchdog Timer (WDT)
- 6.11.5 System Module (SYS)
- 6.11.6 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 6.11.7 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI_A0, eUSCI_B0)
- 6.11.8 Timers (Timer0_B3, Timer1_B3)
- 6.11.9 Backup Memory (BAKMEM)
- 6.11.10 Real-Time Clock (RTC) Counter
- 6.11.11 10-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 6.11.12 eCOMP0
- 6.11.13 SAC0
- 6.11.14 TIA0
- 6.11.15 eCOMP0, SAC0, TIA0, and ADC in SOC Interconnection
- 6.11.16 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM)
- 6.11.17 Peripheral File Map
- 6.12 Input/Output Diagrams
- 6.13 Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 6.14 Identification
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGY|16
Orderable Information
6.11.8 Timers (Timer0_B3, Timer1_B3)
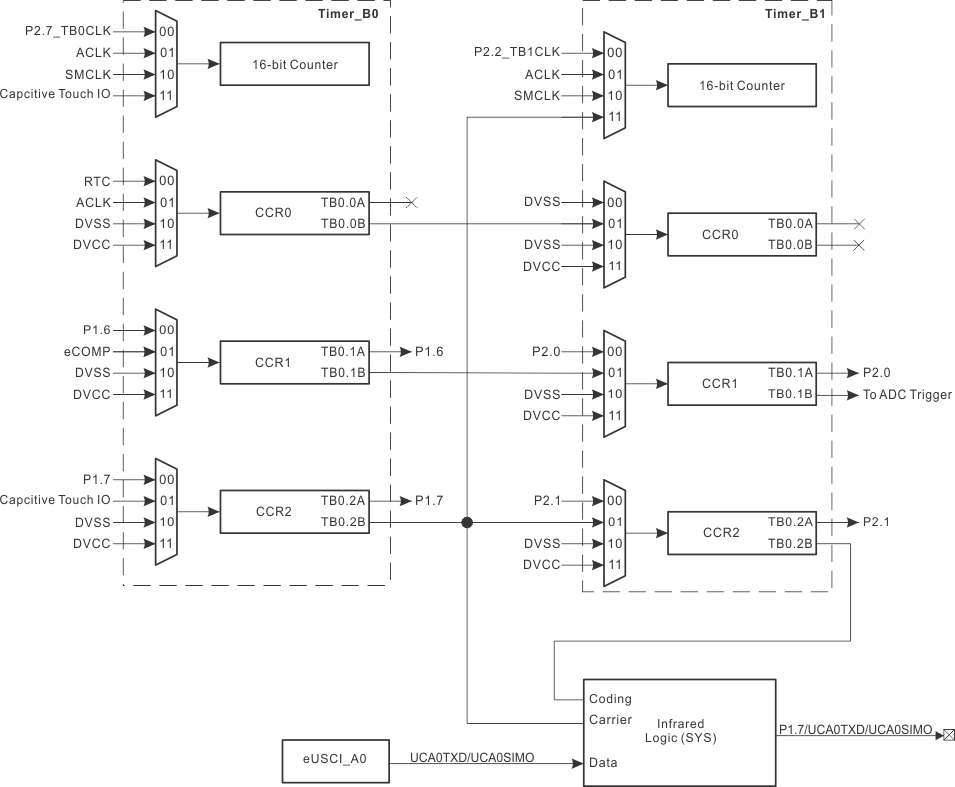
The Timer0_B3 and Timer1_B3 modules are 16-bit timers and counters with three capture/compare registers each. Each can support multiple captures or compares, PWM outputs, and interval timing (see Table 6-13 and Table 6-14). Each has extensive interrupt capabilities. Interrupts may be generated from the counter on overflow conditions and from each of the capture/compare registers. The CCR0 registers on TB0 and TB1 are not externally connected and can be used only for hardware period timing and interrupt generation. In Up mode, they can set the overflow value of the counter.
The interconnection of Timer0_B3 and Timer1_B3 can modulate the eUSCI_A pin of UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO in either ASK or FSK mode, with which a user can easily acquire a modulated infrared command for directly driving an external IR diode (see Figure 6-2). The IR functions are fully controlled by the SYS configuration registers including IREN (enable), IRPSEL (polarity select), IRMSEL (mode select), IRDSSEL (data select), and IRDATA (data) bits. For more information, see the System Resets, Interrupts, and Operating Modes, System Control Module (SYS) chapter in the MSP430FR4xx and MSP430FR2xx Family User's Guide.
Table 6-13 Timer0_B3 Signal Connections
| PORT PIN | DEVICE INPUT SIGNAL | MODULE INPUT NAME | MODULE BLOCK | MODULE OUTPUT SIGNAL | DEVICE OUTPUT SIGNAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2.7 | TB0CLK | TBCLK | Timer | N/A | |
| ACLK (internal) | ACLK | ||||
| SMCLK (internal) | SMCLK | ||||
| From Capacitive Touch I/O (internal) | INCLK | ||||
| From RTC (internal) | CCI0A | CCR0 | TB0 | ||
| ACLK (internal) | CCI0B | Timer1_B3 CCI0B input | |||
| DVSS | GND | ||||
| DVCC | VCC | ||||
| P1.6 | TB0.1 | CCI1A | CCR1 | TB1 | TB0.1 |
| From eCOMP (internal) | CCI1B | Timer1_B3 CCI1B input | |||
| DVSS | GND | ||||
| DVCC | VCC | ||||
| P1.7 | TB0.2 | CCI2A | CCR2 | TB2 | TB0.2 |
| From Capacitive Touch I/O (internal) | CCI2B | Timer1_B3 INCLK
Timer1_B3 CCI2B input, IR input |
|||
| DVSS | GND | ||||
| DVCC | VCC |
Table 6-14 Timer1_B3 Signal Connections
| PORT PIN | DEVICE INPUT SIGNAL | MODULE INPUT NAME | MODULE BLOCK | MODULE OUTPUT SIGNAL | DEVICE OUTPUT SIGNAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2.2 | TB1CLK | TBCLK | Timer | N/A | |
| ACLK (internal) | ACLK | ||||
| SMCLK (internal) | SMCLK | ||||
| Timer0_B3 CCR2B output (internal) | INCLK | ||||
| DVSS | CCI0A | CCR0 | TB0 | ||
| Timer0_B3 CCR0B output (internal) | CCI0B | ||||
| DVSS | GND | ||||
| DVCC | VCC | ||||
| P2.0 | TB1.1 | CCI1A | CCR1 | TB1 | TB1.1 |
| Timer0_B3 CCR1B output (internal) | CCI1B | To ADC trigger | |||
| DVSS | GND | ||||
| DVCC | VCC | ||||
| P2.1 | TB1.2 | CCI2A | CCR2 | TB2 | TB1.2 |
| Timer0_B3 CCR2B output (internal) | CCI2B | IR input | |||
| DVSS | GND | ||||
| DVCC | VCC |
The Timer_B module includes a feature that puts all Timer_B outputs into a high-impedance state when the selected source is triggered. The source can be selected from an external pin or an internal signal, and it is controlled by TBxTRG in SYS. For more information, see the System Resets, Interrupts, and Operating Modes, System Control Module (SYS) chapter in the MSP430FR4xx and MSP430FR2xx Family User's Guide.
Table 6-15 lists the Timer_B high-impedance trigger source selections.
Table 6-15 TBxOUTH
| TBxTRGSEL | TBxOUTH TRIGGER SOURCE SELECTION | Timer_B PAD OUTPUT HIGH IMPEDANCE |
|---|---|---|
| TB0TRGSEL = 0 | eCOMP0 output (internal) | P1.6, P1.7 |
| TB0TRGSEL= 1 | P1.2 | |
| TB1TRGSEL = 0 | eCOMP0 output (internal) | P2.0, P2.1 |
| TB1TRGSEL = 1 | P2.3 |