SCPS200E July 2009 – April 2019 TCA9555
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.5.4 Control Register and Command Byte
Following the successful acknowledgment of the address byte, the bus master sends a command byte shown in Table 3, that is stored in the control register in the TCA9555. Three bits of this data byte state the operation (read or write) and the internal register (input, output, polarity inversion, or configuration) that is affected. This register can be written or read through the I2C bus. The command byte is sent only during a write transmission.
When a command byte has been sent, the register that was addressed continues to be accessed by reads until a new command byte has been sent. Figure 33 shows the control register bits.
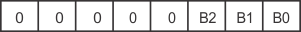 Figure 33. Control Register Bits
Figure 33. Control Register Bits Table 3. Command Byte
| CONTROL REGISTER BITS | COMMAND
BYTE (HEX) |
REGISTER | PROTOCOL | POWER-UP
DEFAULT |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | B1 | B0 | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x00 | Input Port 0 | Read byte | xxxx xxxx |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0x01 | Input Port 1 | Read byte | xxxx xxxx |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0x02 | Output Port 0 | Read-write byte | 1111 1111 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0x03 | Output Port 1 | Read-write byte | 1111 1111 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0x04 | Polarity Inversion Port 0 | Read-write byte | 0000 0000 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0x05 | Polarity Inversion Port 1 | Read-write byte | 0000 0000 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x06 | Configuration Port 0 | Read-write byte | 1111 1111 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0x07 | Configuration Port 1 | Read-write byte | 1111 1111 |