SLVS543R August 2004 – October 2023 TL431 , TL432
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Thermal Information
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics, TL431C, TL432C
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics, TL431I, TL432I
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics, TL431Q, TL432Q
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics, TL431AC, TL432AC
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics, TL431AI, TL432AI
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics, TL431AQ, TL432AQ
- 7.11 Electrical Characteristics, TL431BC, TL432BC
- 7.12 Electrical Characteristics, TL431BI, TL432BI
- 7.13 Electrical Characteristics, TL431BQ, TL432BQ
- 7.14 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- PW|8
- PK|3
- LP|3
- PS|8
- DCK|6
- DBV|5
- P|8
- DBZ|3
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.14 Typical Characteristics
Data at high and low temperatures are applicable only within the recommended operating free-air temperature ranges of the various devices.
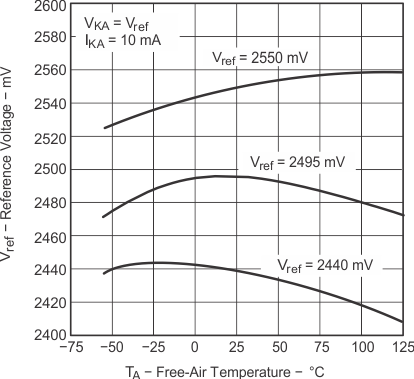 Figure 7-1 Reference Voltage vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 7-1 Reference Voltage vs Free-Air Temperature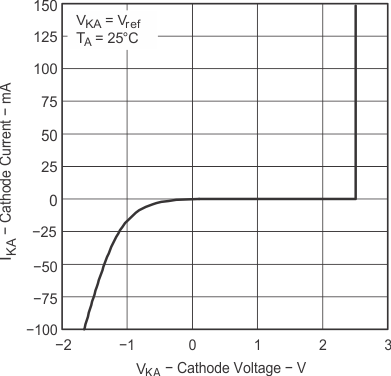 Figure 7-3 Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage
Figure 7-3 Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage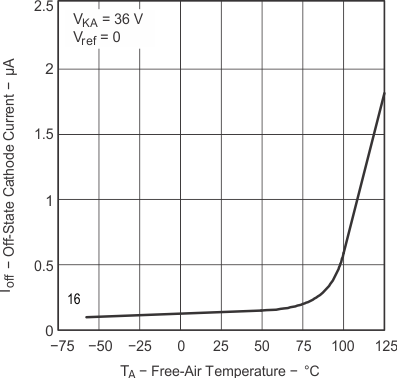 Figure 7-5 Off-State Cathode Current vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 7-5 Off-State Cathode Current vs Free-Air Temperature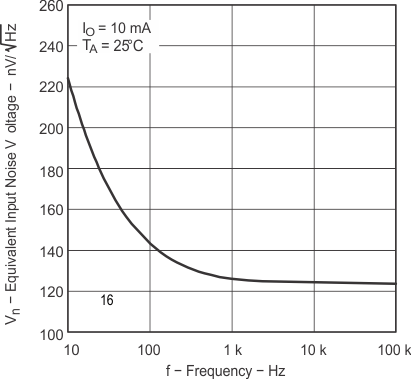 Figure 7-7 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage vs Frequency
Figure 7-7 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage vs Frequency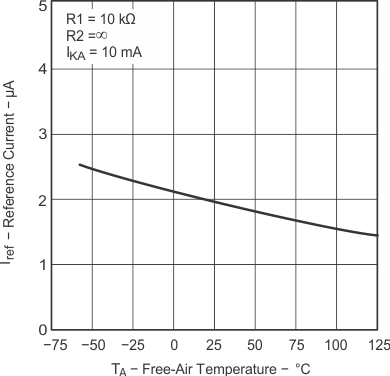 Figure 7-2 Reference Current vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 7-2 Reference Current vs Free-Air Temperature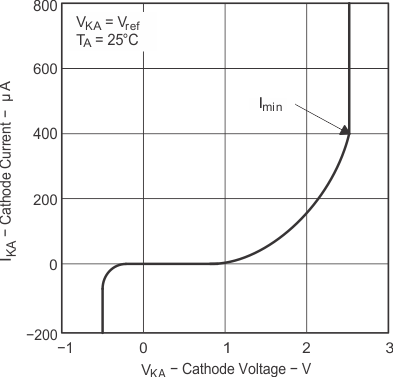 Figure 7-4 Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage
Figure 7-4 Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage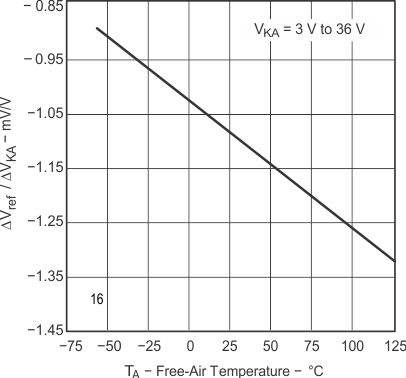 Figure 7-6 Ratio of Delta Reference Voltage to Delta Cathode Voltage vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 7-6 Ratio of Delta Reference Voltage to Delta Cathode Voltage vs Free-Air Temperature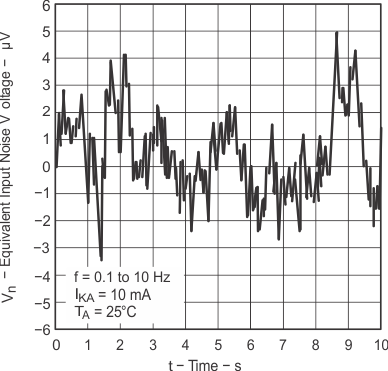 Figure 7-8 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage Over
a 10-S Period
Figure 7-8 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage Over
a 10-S Period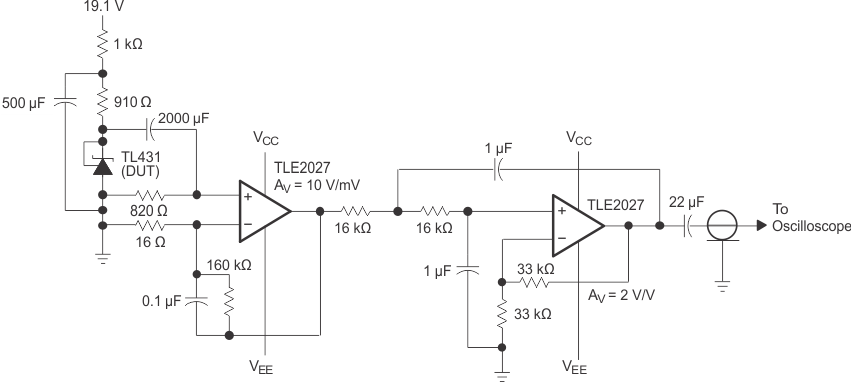 Figure 7-9 Test Circuit for Equivalent Input Noise Voltage Over a 10-S Period
Figure 7-9 Test Circuit for Equivalent Input Noise Voltage Over a 10-S Period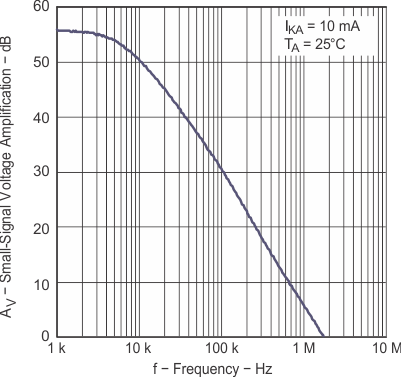 Figure 7-10 Small-Signal Voltage Amplification
vs Frequency
Figure 7-10 Small-Signal Voltage Amplification
vs Frequency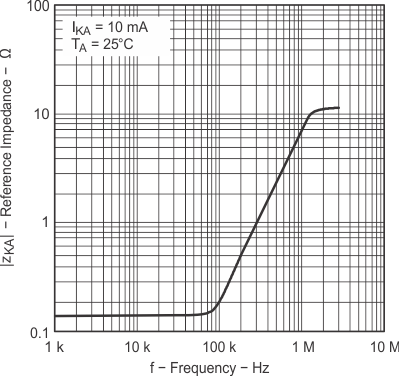 Figure 7-12 Reference
Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 7-12 Reference
Impedance vs Frequency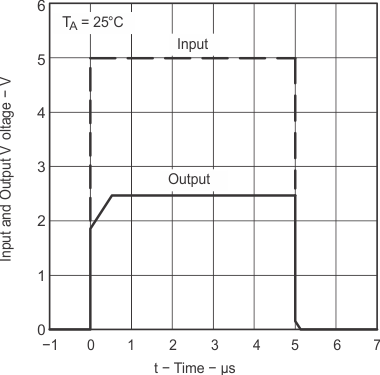 Figure 7-14 Pulse
Response
Figure 7-14 Pulse
Response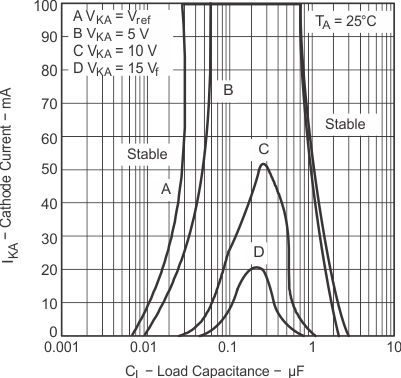
|
The areas under the curves represent conditions that may cause the device to oscillate. For curves B, C, and D, R2 and V+ are adjusted to establish the initial VKA and IKA conditions, with CL = 0. VBATT and CL then are adjusted to determine the ranges of stability. |
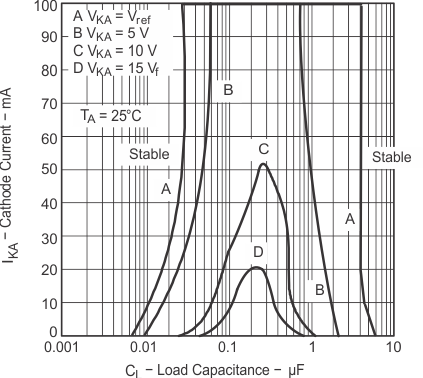
|
The areas under the curves represent conditions that may cause the device to oscillate. For curves B, C, and D, R2 and V+ are adjusted to establish the initial VKA and IKA conditions, with CL = 0. VBATT and CL then are adjusted to determine the ranges of stability. |
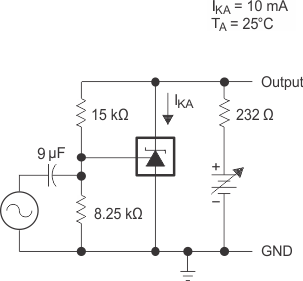 Figure 7-11 Test Circuit
for Voltage Amplification
Figure 7-11 Test Circuit
for Voltage Amplification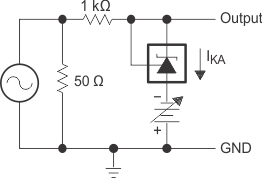 Figure 7-13 Test Circuit
for Reference Impedance
Figure 7-13 Test Circuit
for Reference Impedance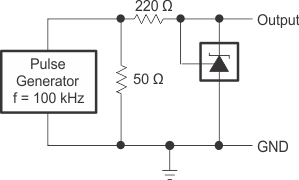 Figure 7-15 Test Circuit
for Pulse Response
Figure 7-15 Test Circuit
for Pulse Response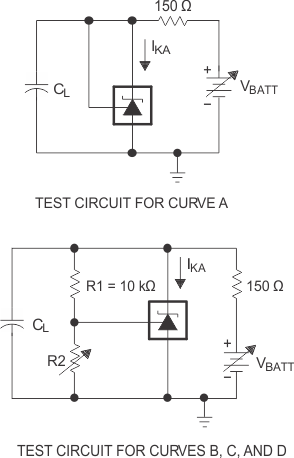 Figure 7-17 Test Circuits
for Stability Boundary Conditions
Figure 7-17 Test Circuits
for Stability Boundary Conditions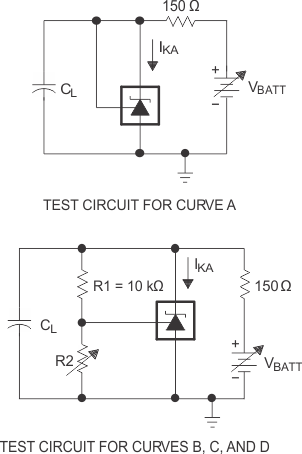 Figure 7-19 Test
Circuit for Stability Boundary Conditions
Figure 7-19 Test
Circuit for Stability Boundary Conditions