SLVSC87C October 2013 – December 2018 TPS24750 , TPS24751
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Descriptions
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1
Power-Limited Start-Up
- 10.2.2.1.1 STEP 1. Choose RSENSE, RSET, and RIMON
- 10.2.2.1.2 STEP 2. Choose Power-Limit Value, PLIM, and RPROG
- 10.2.2.1.3 STEP 3. Choose Output Voltage Rising Time, tON, and Timing Capacitor CT
- 10.2.2.1.4 STEP 4. Calculate the Retry-Mode Duty Ratio
- 10.2.2.1.5 STEP 5. Select R1, R2, and R3 for UV and OV
- 10.2.2.1.6 STEP 6. Choose R4, R5, and C1
- 10.2.2.2 Alternative Design Example: Gate Capacitor (dv/dt) Control in Inrush Mode
- 10.2.2.3 Additional Design Considerations
- 10.2.2.1
Power-Limited Start-Up
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 System Examples
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUV|36
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUV|36
Orderable Information
9.3.12 TIMER
A capacitor CT connected from the TIMER pin to GND determines the overload fault timing. TIMER sources 10 µA when an overload is present, and discharges CT at 10 µA otherwise. Internal FET is turned off when VTIMER reaches 1.35 V. In an application implementing auto-retry after a fault, this capacitor also determines the period before the internal FET is re-enabled. A minimum timing capacitance of 1 nF is recommended to ensure proper operation of the fault timer. The value of CT can be calculated from the desired fault time tFLT, using Equation 4.
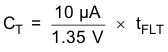
Either latch mode (TPS24750) or retry mode (TPS24751) occurs if the load current exceeds the current limit threshold or the fast trip shutdown threshold. While in latch mode, the TIMER pin continues to periodically charge and discharge the attached capacitor. In retry mode, the internal MOSFET is disabled for sixteen cycles of TIMER charging and discharging. The TIMER pin is pulled to GND by a 2 mA current source at the end of the 16th cycle of charging and discharging. The internal MOSFET is then re-enabled. The TIMER pin capacitor, CT, can also be discharged to GND during latch mode or retry mode in the following way:
- A 2-mA current sinks TIMER whenever any of the following occurs:
- VEN is below its falling threshold.
- VVCC drops below the UVLO threshold.
- VOV is above its rising threshold.
TIMER is not affected when the die temperature exceeds the OTSD threshold.