SLVS351Q September 2002 – June 2025 TPS796
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
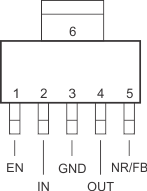 Figure 4-1 DCQ Package, 6-Pin SOT-223
Figure 4-1 DCQ Package, 6-Pin SOT-223
(Top View, Legacy Chip)
 Figure 4-3 KTT Package, 5-Pin TO-263
Figure 4-3 KTT Package, 5-Pin TO-263
(Top View, Legacy Chip)
Figure 4-2 DCQ Package, 6-Pin SOT-223
(Top View, New Chip)
(Top View, New Chip)
 Figure 4-4 DRB Package, 8-Pin VSON
Figure 4-4 DRB Package, 8-Pin VSON
(Top View, Legacy Chip)
Figure 4-5 DRB Package, 8-Pin VSON
(Top View, New Chip)
(Top View, New Chip)
Table 4-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | SOT-223 TO-263 |
VSON | ||
| EN | 1 | 8 | I | Enable pin. Driving the enable pin (EN) high turns on the regulator. Driving this pin low puts the regulator into shutdown mode. EN can be connected to IN if not used. |
| FB | 5 | 5 | I | Feedback pin. This terminal is the feedback input voltage for the adjustable device. |
| GND | 3, Tab | 6, PowerPAD | — | Regulator ground |
| IN | 2 | 1, 2 | I | Input to the device. |
| N/C | 5 | 7 | — | Not internally connected. This pin must either be left open, or tied to GND. |
| NR | 5 | 5 | — | Noise-reduction pin (legacy chip). Connecting an external capacitor to this pin bypasses noise generated by the internal band gap. This bypass improves power-supply rejection and reduces output noise. For a lower noise performance device, consider the TPS7A91. |
| OUT | 4 | 3, 4 | O | Output of the regulator. |