JAJSMX0 September 2020 INA848
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.3 Input Protection
The inputs of the INA848 device are individually protected for voltages up to ±20 V which is stated in Section 7.1. If these rating cannot be met, additional protection circuitry must be considered at the input pins to minimize the current flowing in case of fault.
During an input overvoltage condition, current flows through the input protection diodes into the power supplies; see Figure 8-3 . If the power supplies are unable to sink current, then Zener diode clamps (ZD1 and ZD2) must be placed on the power supplies to provide a current pathway to ground.
For an overvoltage condition, use an external resistor (RIN1, RIN2) to limit the current. The following equation gives the calculation for the protection resistors:
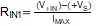
where:
- V+IN is the maximum input voltage
- +VS is the positive supply rail
- IMAX is the maximum current allowed = 10 mA
Calclate RIN2 using the same method, substituting with V–IN, –VS, and –IMAX.
Any additional resistance to the input pins adds more noise to the system. For more details, see Section 9.2.2.2.