JAJSJM0B june 2021 – april 2023 JFE150
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
9.1.3 Common-Source Amplifier
The common-source amplifier is a commonly used open-loop gain stage for JFET amplifiers. Figure 9-2 shows the basic circuit.
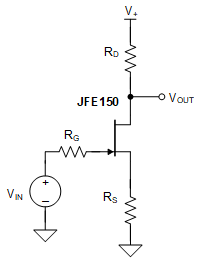 Figure 9-2 Common-Source
Amplifier
Figure 9-2 Common-Source
AmplifierEquation 1 shows the equation for gain of the circuit in Figure 9-2.
Generally, higher gain results in improved noise performance. Gain increases as the bias current is increased as a result of increasing gm (see Figure 6-4). As a result, the input-referred noise decreases as bias current is increased (see Figure 6-9). Any JFET design must make a tradeoff between current consumption and noise performance. The JFE150, however, delivers significantly lower noise performance than most operational amplifiers at the same current consumption. The bias current (IDS) is set by the value of the source resistor, RS, and the threshold voltage, VT, of the JFE150. Figure 9-3 is a graph showing nominal IDS vs RS.
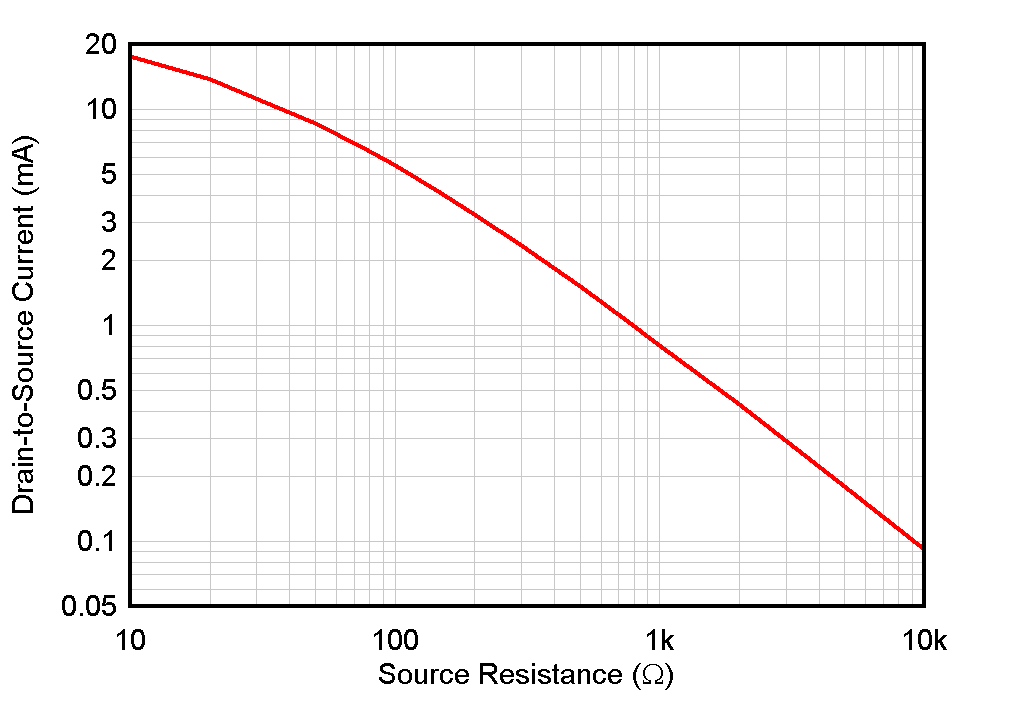 Figure 9-3 Drain-to-Source Current vs
RS, VDS = 5 V
Figure 9-3 Drain-to-Source Current vs
RS, VDS = 5 VThe bias current varies according to the resistor and threshold voltage tolerances. Additionally, thermal noise associated with RS couples directly into the gain of the circuit, degrading the overall noise performance. To improve the circuit in Figure 9-4, use a current-source biasing scheme. Current-source biasing removes the JFET threshold variation from the biasing scheme, and allows for lower-value filtering capacitance (CS) for equivalent filtering due to the high output impedance of current sources.
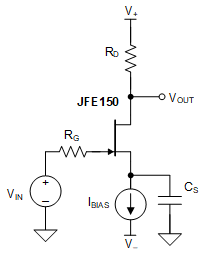 Figure 9-4 Common-Source Amplifier With
Current-Source Biasing
Figure 9-4 Common-Source Amplifier With
Current-Source Biasing