JAJSEA6B December 2017 – February 2019 LMH5401-SP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8.1 Output Reference Nodes and Gain Nomenclature
- 8.2 ATE Testing and DC Measurements
- 8.3 Frequency Response
- 8.4 S-Parameters
- 8.5 Frequency Response with Capacitive Load
- 8.6 Distortion
- 8.7 Noise Figure
- 8.8 Pulse Response, Slew Rate, and Overdrive Recovery
- 8.9 Power Down
- 8.10 VCM Frequency Response
- 8.11 Test Schematics
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
10.2.2.6 Common-Mode Voltage Correction
The LMH5401-SP can set the output common-mode voltage to within a typical value of ±30 mV. If greater accuracy is desired, a simple circuit can improve this accuracy by an order of magnitude. A precision, low-power operational amplifier is used to sense the error in the output common-mode of the LMH5401-SP and corrects the error by adjusting the voltage at the CM pin. In Figure 71, the precision of the op amp replaces the less accurate precision of the LMH5401-SP common-mode control circuit while still using the LMH5401-SP common-mode control circuit speed. The op amp in this circuit must have better than a 1-mV input-referred offset voltage and low noise. Otherwise the specifications are not very critical because the LMH5401-SP is responsible for the entire differential signal path.
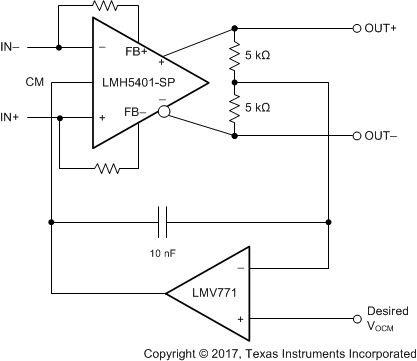 Figure 71. Common-Mode Correction Circuit
Figure 71. Common-Mode Correction Circuit