DLPA027B January 2024 – April 2024 DLP500YX , DLP5500 , DLP6500FLQ , DLP6500FYE , DLP650LNIR , DLP670S , DLP7000 , DLP7000UV , DLP9000 , DLP9000X , DLP9000XUV , DLP9500 , DLP9500UV
3 Sample Calculations
Below are detailed sample calculations that show how mirror surface temperature is calculated using the three temperature rises:
- Mirror Surface to Bulk Mirror Delta
- Bulk Mirror to Silicon Delta
- Silicon to Ceramic Delta
In the first example calculation, toff is greater than , therefore the bulk mirror fully cools after each pulse and only one pulse needs to be analyzed.
Example 1
A pulsed laser illuminates a DLP650LNIR DMD with 1064 nm wavelength light and fills the active array with no overfill.
Pulse duration (tpulse) = 1
toff = 999 (pulsed repetition rate of the optical source is 1 kHz)
Peak incident power during the pulse is 25 kW/cm2
Calculation of the temperature rise of the mirror surface above the DMD ceramic temperature:
- Mirror Surface to Bulk Mirror
Delta: ΔTMIRROR_SURFACE-TO-BULK_MIRROR
= temperature at time = t
= initial mirror temperature
q = absorbed heat flux on mirror surface [W/m2]
α = Mirror thermal diffusivity = 6.4667 x 10-5 m2/s
k = Mirror thermal conductivity = 160 W/m-ºC
q = 25 kW/cm2 × (1 – 0.94) = 1.50 kW/cm2
tpulse = 1
T(1 ) = 2 × 1.50 kW/cm2 × {[(6.4667e-5 m2/s × 1.0e-6 s)/π] /160 W/m-ºC} + 0 = 0.85 ºC
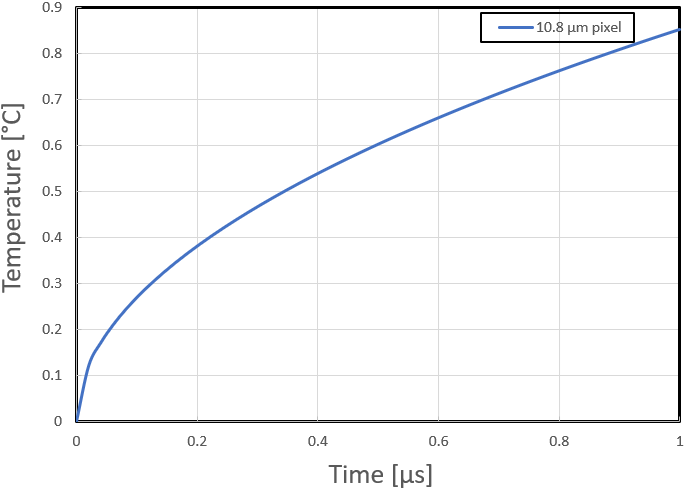 Figure 3-1 DMD Mirror Surface
Temperature Rise at 25 kW/cm2
Figure 3-1 DMD Mirror Surface
Temperature Rise at 25 kW/cm2 - Bulk Mirror to Silicon Delta:
ΔTBULK_MIRROR-TO-SILICON
= 25 kW/cm2 × (10.8 μm)2 = 0.02916 W
= 0.931 (on-state)
at 1064 nm = 0.94
= 0.02916 W × [0.931 × (1 – 0.94)] = 1.629 mW
= 3.39 x 105 ºC/W
= 0 + 1.629 mW × (3.39 x 105 ºC/W) = 552.23 ºC
= 32.27
toff = 999
tpulse = 1
= 5 × 32.27 = 161.35
Since toff = 999 (> ) the bulk mirror fully cools to the initial temperature Ti and analyzing a single pulse cycle is sufficient.
T(1 ) = 552.23 ºC + (0 – 552.23 ºC)e-(1 μs/32.27 μs) = 16.85 ºC
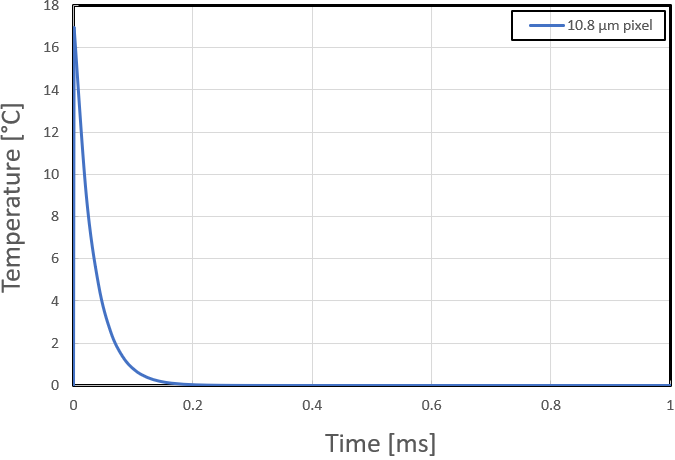 Figure 3-2 DMD Bulk Mirror
Temperature Rise 25 kW/cm2
Figure 3-2 DMD Bulk Mirror
Temperature Rise 25 kW/cm2 - Silicon to Ceramic Delta: ΔTSILICON-TO-CERAMIC
From the DLP650LNIR data sheet:
= 0.5 ºC/W
= 1.8 W
= 0.726 (off-state)
at 1064 nm = 0.94
at 1064 nm = 0.007 (per pass)
= 0
= (1 - 0) × {[0.726 × (1-0.94)] + [1-0.726]} + (2 × 0.007) + 0
= 0.33 (off-state)
= total incident average optical power to DMD
Active array area = (1280 × 10.8 μm) × (800 × 10.8 μm) = 1.1944 cm2
tpulse = 1 , toff = 999
Therefore pulse duty cycle = 1 / ( 1 + 999 ) x 100% = 0.1%
Average optical power density = (25 kW/cm2) × 0.1% = 25 W/cm2
Average optical power = 25 W/cm2 × 1.1944 cm2 = 29.86 W
Average absorbed optical power = 29.86 W × 0.33 = 9.85 W
= (1.8 W + 9.85 W) × 0.5 ºC/W = 5.8 ºC
Mirror Surface to Ceramic Delta: (ΔTMIRROR_SURFACE-TO-CERAMIC)
TMIRROR SURFACE - TCERAMIC = ΔTSILICON-TO-CERAMIC + ΔTBULK_MIRROR-TO-SILICON + ΔTMIRROR_SURFACE-TO-BULK_MIRRORTMIRROR_SURFACE - TCERAMIC = 5.8 ºC + 16.85 ºC + 0.85 ºC = 23.5 ºC
In the second example calculation, since tpulse and toff are both < , analysis is required over several pulses until the temperature rise stabilizes.
Example 2
A pulsed laser illuminates a DLP650LNIR DMD with 1064 nm wavelength light and fills the active array with no overfill.
Pulse duration (tpulse) = 10 ps
toff = 99.99999 (pulsed repetition rate of the optical source is 10 kHz)
Peak incident power during the pulse is 250 MW/cm2
Calculation of the temperature rise of the mirror surface above the DMD ceramic temperature:
- Mirror Surface to Bulk Mirror
Delta: ΔTMIRROR_SURFACE-TO-BULK_MIRROR
= temperature at time = t
= initial mirror temperature
q = absorbed heat flux on mirror surface [W/m2]
α = Mirror thermal diffusivity = 6.4667 x 10-5 m2/s
k = Mirror thermal conductivity = 160 W/m-ºC
q = 250 MW/cm2 × (1 – 0.94) = 15 MW/cm2
tpulse = 10 ps
T(10 ps) = 2 × 15 MW/cm2 × {[(6.4667e-5 m2/s × 1.0e-11 s)/π] /160 W/m-ºC} + 0 = 26.9 ºC
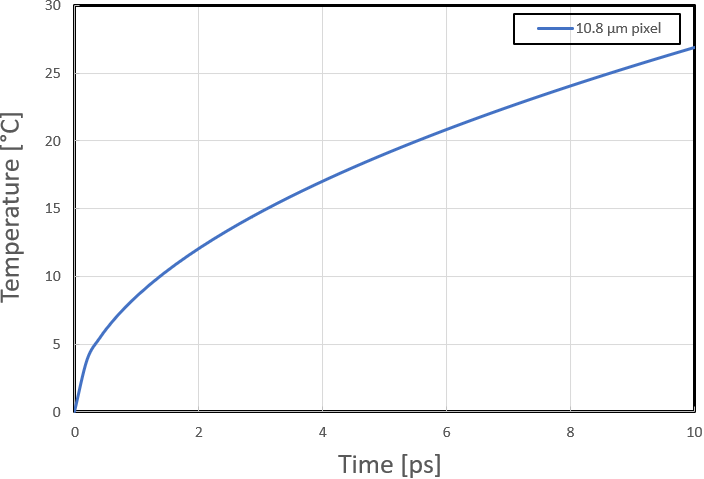 Figure 3-3 DMD Mirror Surface
Temperature Rise at 250 MW/cm2
Figure 3-3 DMD Mirror Surface
Temperature Rise at 250 MW/cm2 - Bulk
Mirror to Silicon Delta: ΔTBULK_MIRROR-TO-SILICON
= 250 MW/cm2 × (10.8 m)2 = 291.6 W= 0.931 (on-state)
at 1064 nm = 0.94
= 291.6 W × [0.931 × (1 – 0.94)] = 16.289 W
= 3.39 x 105 ºC/W
= 0 + 16.289 W × (3.39 x 105 ºC/W) = 5.522 x 106 ºC
= 32.27
toff = 99.99999
tpulse = 10 ps
= 5 × 32.27 = 161.35
Bulk mirror only partially heats and partially cools between pulses and we need to iterate and analyze a series of pulses until the mirror temperature no longer changes.
1st tpulse heating:
T(10 ps) = 5.522 x 106 ºC + (0 – 5.522 x 106 ºC)e-(10 ps/32.27 μs) = 1.710 ºC
1st toff cooling:
T(99.99999 μs) = 0 ºC + (1.720 – 0 ºC)e-(99.99999 μs/32.27 μs) = 0.077 ºC
2nd tpulse heating:
T(10 ps) = 5.522 x 106 ºC + (0.077 ºC – 5.522 x 106 ºC)e-(10 ps/32.27 μs) = 1.787 ºC
2nd toff cooling:
T(99.99999 μs) = 0 ºC + (1.787 – 0 ºC)e-(99.99999 μs/32.27 μs) = 0.081 ºC
3rd tpulse heating:
T(10 ps) = 5.522 x 106 ºC + (0.081 ºC – 5.522 x 106 ºC)e-(10 ps/32.27 μs) = 1.791 ºC
3rd toff cooling:
T(99.99999 μs) = 0 ºC + (1.791 – 0 ºC)e-(99.99999 μs/32.27 μs) = 0.081 ºC
4th tpulse heating:
T(10 ps) = 5.522 x 106 ºC + (0.081 ºC – 5.522 x 106 ºC)e-(10 ps/32.27 μs) = 1.791 ºC
4th toff cooling:
T(99.99999 μs) = 0 ºC + (1.791 – 0 ºC)e-(99.99999 μs/32.27 μs) = 0.081 ºC
Notice the temperature did not change from the 3rd pulse to the 4th pulse. When the temperature after each pulse iteration stops changing, it has reached steady-state. The bulk mirror temperature rise above the silicon is 1.8 ºC.
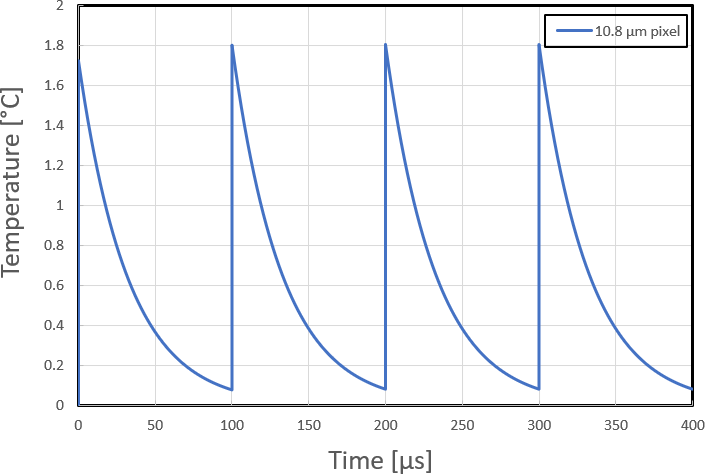 Figure 3-4 DMD Bulk Mirror
Temperature Rise at 250 MW/cm2
Figure 3-4 DMD Bulk Mirror
Temperature Rise at 250 MW/cm2 - DMD silicon temperature rise
above ceramic: ΔTSILICON-TO-CERAMIC
From the DLP650LNIR data sheet:
= 0.5 ºC/W
= 1.8 W
= 0.726 (off-state)
at 1064 nm = 0.94
at 1064 nm = 0.007 (per pass)
= 0
= (1 - 0) × {[0.726 × (1-0.94)] + [1-0.726]} + (2 × 0.007) + 0
= 0.33 (off-state)
= total incident average optical power to DMD
Active array area = (1280 × 10.8 μm) × (800 × 10.8 μm) = 1.1944 cm2
tpulse = 10 ps, toff = 99.99999
Therefore pulse duty cycle = 10 ps / ( 10 ps + 99.99999 ) x 100% = 0.00001%
Average optical power density = (250 MW/cm2) × 0.00001% = 25 W/cm2
Average optical power = 25 W/cm2 × 1.1944 cm2 = 29.86 W
Average absorbed optical power = 29.86 W × 0.33 = 9.85 W
= (1.8 W + 9.85 W) × 0.5 ºC/W = 5.8 ºC
Mirror Surface to Ceramic Delta: (ΔTMIRROR_SURFACE-TO-CERAMIC)
TMIRROR SURFACE - TCERAMIC = ΔTSILICON-TO-CERAMIC + ΔTBULK_MIRROR-TO-SILICON + ΔTMIRROR_SURFACE-TO-BULK_MIRRORTMIRROR_SURFACE - TCERAMIC = 5.8 ºC + 1.8 ºC + 26.9 ºC = 34.5 ºCIn the second example, the mirror surface temperature rise above the bulk mirror is much larger than the bulk mirror temperature rise above the silicon. This is common with very short pulses of high intensity. Notice the average power is the same between examples 1 and 2 (29.86 W) and therefore the temperature rise of the silicon above the ceramic is equal in the two examples.