SNOA475F October 2016 – September 2020 LMV791
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2What Parameters Should Be Tested?
- 2.1 Open-Loop Gain (AOL) and Phase Margin
- 2.2 Slew Rate
- 2.3 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) and Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
- 2.4 Open-Loop Output Impedance (Zo)
- 2.5 Voltage Noise (en)
- 2.6 Current Noise (in)
- 2.7 Input Offset Voltage (VOS), Input Bias Current (Ib), and Quiescent Current (IQ)
- 2.8 Output Voltage Versus Output Current (Claw Curve)
- 2.9 Overload Recovery Time (tOR)
- 2.10 Common-mode Input Capacitance (CCM) and Common-mode Differential Capacitance (CDIFF)
- 2.11 Overshoot and Transient Response
- 2.12 Common-Mode Voltage Range (CMVR)
- 3Conclusion
- Revision History
2.12 Common-Mode Voltage Range (CMVR)
The common-mode voltage range (CMVR) parameter is important as it allows the user to see the head room or how far away the input common-mode needs to be from the supply. Figure 2-46 shows the CMVR Test Circuit and Figure 2-47 shows the corresponding simulation output. To learn more about CMVR, please refer to the Texas Instruments Precision Labs video series on input and output limitations. This circuit may be simulated by downloading the AN1516 Test Circuits in either TINA-TI™ or PSpice® for TI.
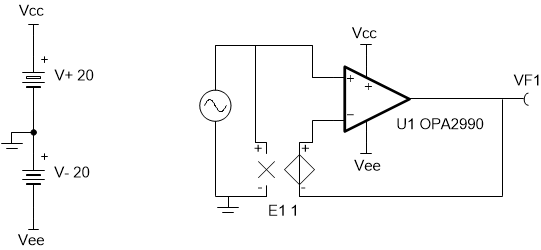 Figure 2-46 CMVR Test Circuit
Figure 2-46 CMVR Test Circuit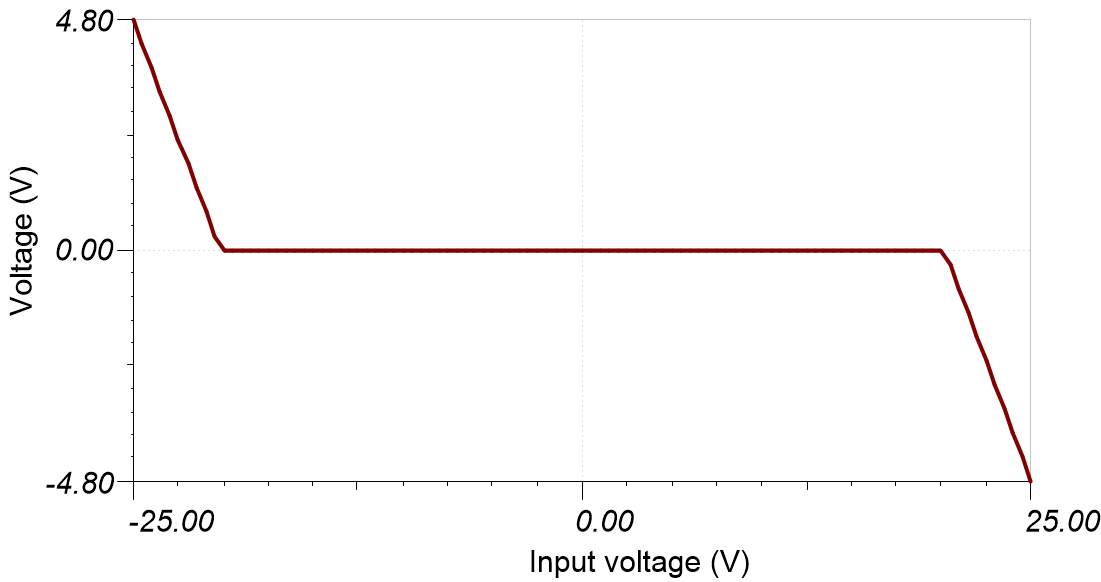 Figure 2-47 Simulated CMVR for
OPA2375
Figure 2-47 Simulated CMVR for
OPA2375 Figure 2-48 Data Sheet Specification of CMVR for
OPA2375
Figure 2-48 Data Sheet Specification of CMVR for
OPA2375