SWRA654A December 2019 – April 2020 CC2652R , CC2652R7 , CC2652RSIP
2 WLAN Access Point Using SimpleLink Platform
It does not have to be complicated to add additional functionalities in an existing WLAN Access Point. Adding extra hardware from the SimpleLink family provides the opportunity to add Zigbee, Thread, or Bluetooth Low Energy to an existing WLAN Access Point. Zigbee and Thread add mesh network abilities to expand the network and reach distant nodes within the network. Bluetooth Low Energy will add multiple features, for example, the ability to interact with Smartphones or track beacons. The addition of Bluetooth allows using Angle of Arrival (AoA) to triangulate and find the direction of the incoming Bluetooth packets.
To be able to use the technologies concurrently, the Dynamic Multi-protocol Manager (DMM) and the TI Coexistence feature are used. The DMM handles the scheduling within the chip, making it possible to use multiple protocols in the same CPU. The TI Coexistence feature allows different technologies operating at the same frequency to coexist and not use the antenna simultaneously to decrease the risk of losing packets.
There are two proposed solutions to extend the functionalities of the WLAN Access Point using one or two CC26x2 devices. The CC2652 device, see CC2652R Product Page, has support for Zigbee, Thread, and Bluetooth Low Energy and is used in the one-chip solution. The two-chip solution uses the CC2652 device for Zigbee and Thread while either a CC2652 device or a CC2642 device, see CC2642R Product Page, is used for Bluetooth.
There is a large variety when it comes to developing applications for either of the solutions. For example, some applications might only require the use of Bluetooth to enable device tracking, using either connection based or connectionless communication. Other applications might require only using a Zigbee or Thread network to fetch data from remote sensors. Examples can be detecting smoke or classifying sound to detect if glass breaks, gunshots, and so forth. The different technologies can also be combined to create a more extensive solution.
The two-chip solution, illustrated in Figure 1, uses dedicated MCUs for each protocol. Both CC2652R and CC2642R can be used as the Bluetooth device, but only CC2652 can be used for Zigbee or Thread. This solution is recommended for applications that require controlling roles for two protocols, such as Bluetooth Low Energy Central and Zigbee Controller. Both the Central and Controller must listen to incoming packets at all times; they cannot share the use of one antenna. Instead, they must use dedicated devices and antennas in order to function properly.
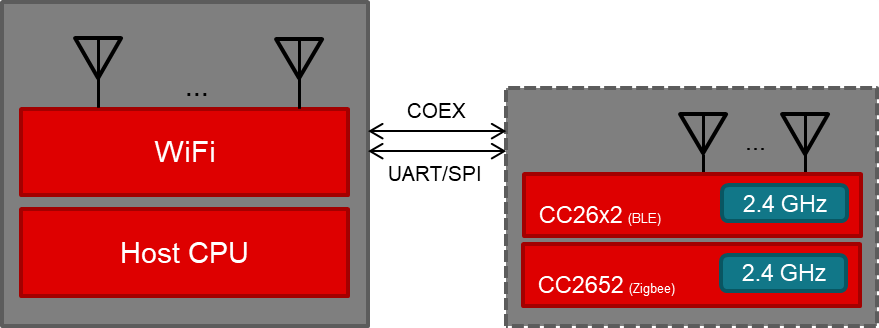 Figure 1. WLAN Solution Using a Two-Chip CC26x2 Solution
Figure 1. WLAN Solution Using a Two-Chip CC26x2 Solution The one-chip solution, illustrated in Figure 2, uses a single CC2652R device that supports Zigbee, Thread, and Bluetooth Low Energy. This solution is recommended for applications that only use one protocol, or use roles for two protocols that can share the antenna resource. The DMM handles the prioritization if two protocols are used.
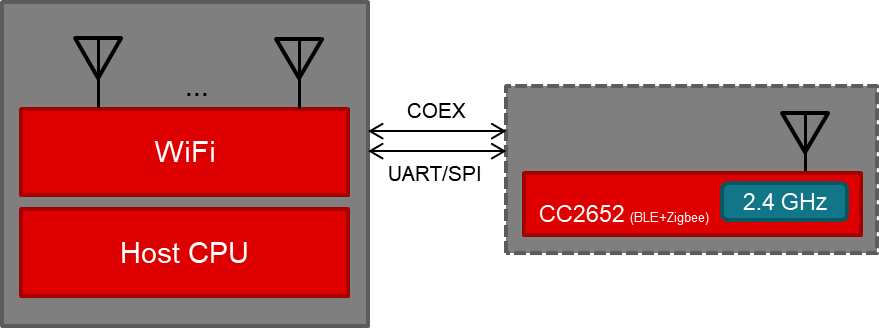 Figure 2. WLAN Solution Using a One-Chip CC2652 Solution
Figure 2. WLAN Solution Using a One-Chip CC2652 Solution Both solutions have the advantage of using the same Software Development Kit (SDK) for Zigbee, Thread, Bluetooth Low Energy and the DMM. They also use the same tools such as Code Composer Studio™ (CCS). The firmware images of the devices can be updated by using a serial bootloader or over the air, Over the Air Download (OAD) (Bluetooth low energy, Zigbee, Thread) or Over The Air update (OTA) (Wi-Fi).