SBAA492A September 2021 – April 2022 PCM3120-Q1 , PCM5120-Q1 , PCM6120-Q1 , TLV320ADC3120 , TLV320ADC5120 , TLV320ADC6120
3.1 Normal AGC Mode
AGC curves (output level vs. input level and THDN vs. input level) for different sampling rates, 48 KHz in Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2, 16 KHz in Figure 3-3 and Figure 3-4 and 96 KHz in Figure 3-5 and Figure 3-6 for normal AGC mode.
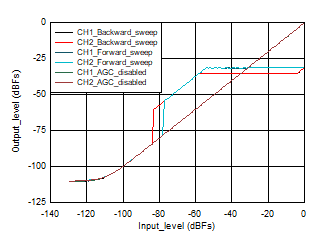 Figure 3-1 Output Level vs. Input Level 48 KHz
Figure 3-1 Output Level vs. Input Level 48 KHz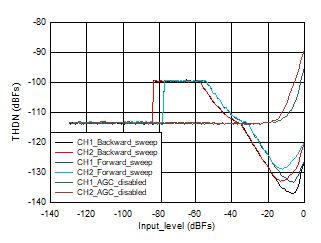 Figure 3-2 THDN vs. Input_Level 48 KHz
Figure 3-2 THDN vs. Input_Level 48 KHzForward sweep: When the input level is swept in the forward direction starting from -130 db, as the input level is less than the noise threshold AGC does not amplify the signal and output level tracks input level as the AGC disabled case, it waits for the input level to cross the noise threshold, also we have noise hysteresis of 4 dB , hence AGC should start applying gain when input level crosses -81 dB, but output level estimation of AGC can have an error in the range of ~1.5 dB to 2 dB, this could vary from device to device, hence AGC starts applying gain when input is at -79 dB. When input is at -79 dB, AGC applies its maximum gain possible trying to achieve the target level. Maximum gain of 24dB is applied by AGC from input level -79 dB to -55 dB (actual should have been -58 dB , but because of output level estimation error of 2 dB and attack hysteresis of 1 dB , AGC applies maximum gain till -55 dB), now as the input increases further AGC starts attacking by decreasing the PGA gain and maintaining the output at -31 dB level (Output maintained = Target programmed (-34 dB) + attack hysteresis (1 dB) + output level estimation error (2 dB) ). For further increase in the input level from -54 dB to -1 dB, AGC decreases the PGA gain accordingly and maintains the output at -31 dB level. For full scale input (0dB ) AGC output level drops by 2 dB and output is held at -33 dB. To get rid of this full scale input issue , user should use Enhanced AGC mode.
Backward sweep: When the input level is swept in the backward direction starting from 0db , as the input level is suddenly full scale (for example, 2 VRms) , AGC cannot maintaining the output level constant to the target level instantaneously. Now as the input level goes down AGC starts responding and output level is maintained at -35 dB when input reaches around -4 dB (Output maintained = Target programmed (-34 dB) - release hysteresis (3 dB) + output level estimation error (2 dB)). As the input signal level decreases further, output level is maintained constant at -35 dB by increasing the PGA gain till input level of -58 dB. As the input level goes down further AGC applies its maximum gain possible (24 dB) and the output level = input level + maximum gain , this continues till the input signal level reaches noise threshold of -85 dB. For further reduction in input, AGC stops working and output level tracks input level as in AGC disabled case.
AGC disabled: When AGC is disabled , output level tracks input level (channel gain programmed to 0 dB), when input is swept from High input (0 dB for example, 2 VRms ) to low input (-130 dB for example, 0.64 uVRms ) or Low input (-130 dB for example, 0.64 uVRms) to High input (0 dB for example, 2 VRms), till noise floor is reached.
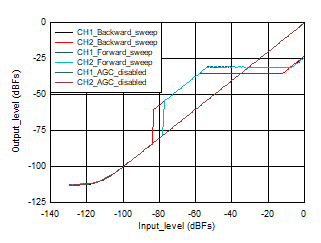 Figure 3-3 Output Level vs. Input Level 16 KHz
Figure 3-3 Output Level vs. Input Level 16 KHz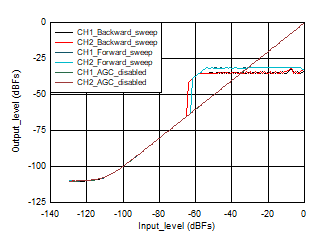 Figure 3-5 Output Level vs. Input Level 96 KHz
Figure 3-5 Output Level vs. Input Level 96 KHz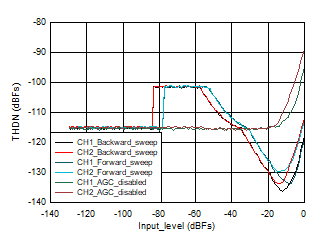 Figure 3-4 THDN vs. Input_Level 16 KHz
Figure 3-4 THDN vs. Input_Level 16 KHz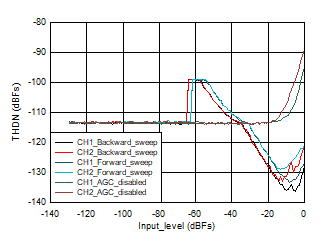 Figure 3-6 THDN vs. Input_Level 96 KHz
Figure 3-6 THDN vs. Input_Level 96 KHz