SBAU394A April 2022 – September 2022
- ADS1285 Evaluation Module
- Trademarks
- 1 EVM Overview
- 2 ADS1285EVM-PDK Quick-Start Guide
- 3 EVM Analog Interface
- 4 Digital Interface
- 5 Power Supplies
- 6 Digital-to-Analog Converter
- 7 ADS1285EVM-PDK Initial Setup
- 8 ADS1285EVM-PDK Software Reference
- 9 ADS1285EVM-PDK Bill of Materials, PCB Layout, and Schematics
- 10References
- 11Revision History
3.2 ADC Input Clock (CLK) Options
Using the onboard oscillator, clock dividers, and external connectors, the ADS1285EVM-PDK has device configuration flexibility. The ADC operates from CLK, which generates the modulator clock (fMOD), provided in one of two ways:
- A crystal oscillator and the accompanying clock dividers can provide a selectable frequency for the entire range of the ADC.
- The onboard crystal oscillator (Y1) provides the nominal 8.192-MHz clock frequency (default)
- The dividers (U6) step down the frequency to 4.096 MHz
- J8 allows the user to select between these frequencies and connect them directly to CLK by using a shunt
- An external main clock can be provided to a subminiature version A (SMA) connector (J5) or to pins 4 or 2 of J7 when a shunt does not select the frequency from the crystal oscillator.
- In this case, a shunt must not cover J7 so that CLK is connected to any of the crystal oscillator signals
- Be sure to review the valid CLKIN input frequency in the data sheet
Note: All clock sources are sourced back to the PHI
connector (J6) so that the GUI SCLK communication is synchronous with CLK.
Figure 3-2 shows a schematic for the clock source.
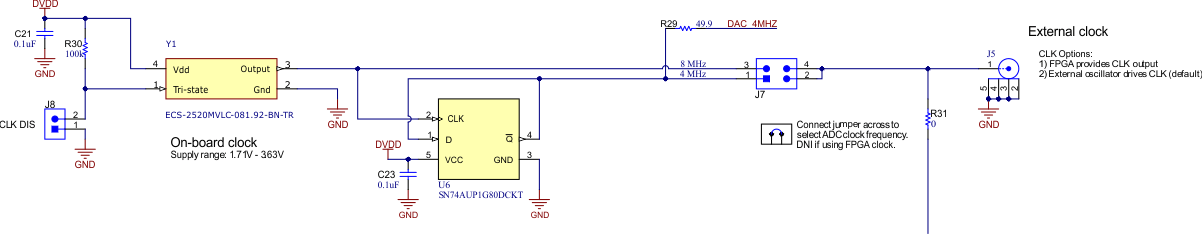 Figure 3-2 CLK Source (Schematic)
Figure 3-2 CLK Source (Schematic)