SLAA870 February 2019 AFE7422 , AFE7444
-
Evaluating the frequency hopping capability of the AFE74xx
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Phase Coherency vs Phase Continuity
- 3 AFE74xx Architecture
- 4 Frequency Hopping Methods
- 5 NCO Frequency Resolution Versus Hop Time
- 6 Fast Frequency Hopping With the Load and Switch
- 7 Register Addresses
- 8 References
4.1.1.1 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Understanding the SPI instruction cycle is critical to approximating the time required for the AFE74xx to hop frequencies after the command is received through SPI. Each SPI read/write operation is framed by signal SDEN (serial data enable bar) asserted low. The first two bytes are the instruction cycle that identifies the following data transfer cycle as read or write, as well as the 15-bit address to be accessed. The last byte labeled D7 through D0 in the SPI instruction cycle contains the data written to the designated AFE74xx register address.
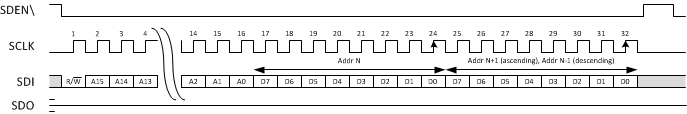 Figure 11. SPI Bus Write Cycle
Figure 11. SPI Bus Write Cycle The reprogramming the NCO frequency in the AFE74xx DAC, the first four SPI writes program the 32-bit NCO accumulator word. The last two SPI writes toggle the NCO reset bit to reflect the change in frequency on the designated DAC output.