SLLSE11H March 2012 – March 2019 SN65HVD72 , SN65HVD75 , SN65HVD78
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Power Dissipation
- 7.7 Switching Characteristics: 250 kbps Device (SN65HVD72) Bit Time ≥ 4 µs
- 7.8 Switching Characteristics: 20 Mbps Device (SN65HVD75) Bit Time ≥50 ns
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: 50 Mbps Device (SN65HVD78) Bit Time ≥20 ns
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
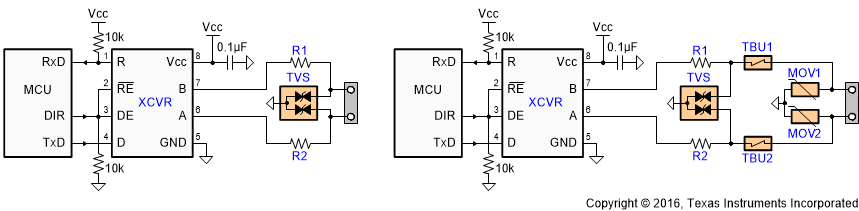
10.2.2.1 External Transient Protection
To protect bus nodes against high-energy transients, the implementation of external transient protection devices is necessary. Figure 26 suggests two circuits that provide protection against light and heavy surge transients, in addition to ESD and EFT transients. Table 4 presents the associated bill of materials.
Table 4. Bill of Materials
| DEVICE | FUNCTION | ORDER NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|
| XCVR | 3.3-V, 250-kbps RS-485 Transceiver | SN65HVD72D | TI |
| R1, R2 | 10-Ω, Pulse-Proof Thick-Film Resistor | CRCW060310RJNEAHP | Vishay |
| TVS | Bidirectional 400-W Transient Suppressor | CDSOT23-SM712 | Bourns |
| TBU1, TBU2 | Bidirectional Surge Suppressor | TBU-CA-065-200-WH | Bourns |
| MOV1, MOV2 | 200-mA Transient Blocking Unit, 200-V, Metal-Oxide Varistor | MOV-10D201K | Bourns |
The left-hand circuit provides surge protection of ≥500-V surge transients, while the right-hand circuit can withstand surge transients of up to 5 kV.