SLVA824A January 2017 – July 2025 TAS6422-Q1 , TAS6424-Q1 , TAS6424L-Q1 , TPA3111D1-Q1 , TPA3221 , TPA3244 , TPA3245 , TPA3250 , TPA3251 , TPA3255 , TPA3255-Q1
3.1 Partial Diagnostic Circuits
The diagnostic circuitry can be broken into two main parts. The open load, short to GND, and short to PVDD conditions all rely on the circuitry shown in Figure 3-3. Note that the outputs of the comparators need to go through level translation in the form of a resistor divider, depending on the logic levels of the MCU.
 Figure 3-3 Partial
Diagnostics Circuit Covering Short to GND, Battery, and Open Load
Figure 3-3 Partial
Diagnostics Circuit Covering Short to GND, Battery, and Open LoadBy contrast, the shorted load circuit detection is handled by measuring the voltage differential across the load. This functionality depends on a different diagnostic circuit, illustrated in Figure 3-4.
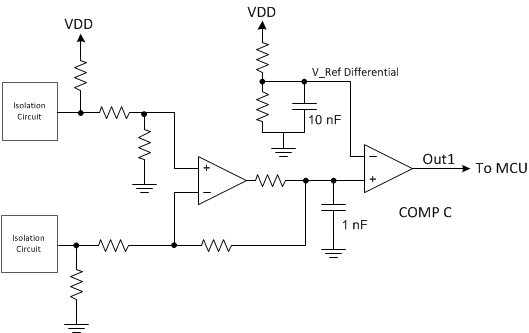 Figure 3-4 Partial
Diagnostics Circuit Covering Shorted Load
Figure 3-4 Partial
Diagnostics Circuit Covering Shorted LoadIn the event that the amplifier contains internal fault detection, this can implement a simpler circuit design by removing the redundant portions of the external diagnostics. For example, the TPA3111D1-Q1 has internal short-circuit detection. Therefore, the circuitry for detecting the shorted load condition can be omitted, leaving the circuitry for detecting the open circuit and the diagnostic capabilities for short to GND and short to PVDD conditions, and allowing the Fault pin to serve as the indicator for shorted load.