SLVA927A November 2017 – April 2019 LM25066A , LM25066I , LM5050-1 , LM5051 , LM5064 , LM5066 , LM5067 , LM5069 , LM66100 , LM74500-Q1 , LM74700-Q1 , TPL7407LA , TPS1H100-Q1 , TPS1HA08-Q1 , TPS2113A , TPS2115A , TPS22810 , TPS22915 , TPS22916 , TPS22918 , TPS22971 , TPS22990 , TPS23525 , TPS2412 , TPS24751 , TPS24770 , TPS25942A , TPS2595 , TPS2660 , TPS27S100 , TPS2H160-Q1 , TPS4H160-Q1 , ULN2003A
3 eFuses
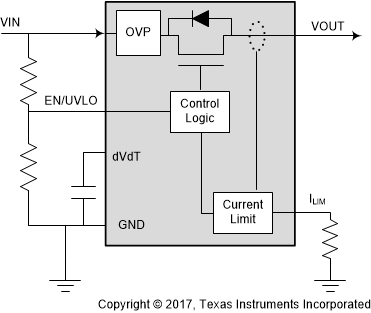 Figure 4. eFuse Block Diagram
Figure 4. eFuse Block Diagram eFuses are integrated power protection switches that provide voltage and current protection during fault events. These include short-circuit, overcurrent, overvoltage, undervoltage, and temperature events that might otherwise damage downstream loads. During a short-circuit transient event, the current through the eFuse increases very rapidly. The eFuse enables a fast-trip current threshold that terminates this rapid increase in less than 200 ns, protecting the supply. If an overvoltage event occurs on the input (VIN), the eFuse monitors the voltage across the internal FET and clamps the output voltage until the input falls below the overvoltage threshold. eFuses also come with built-in overtemperature protection that shuts down the FET if the junction temperature exceeds 150°C (typical). The eFuse either remains off (latch-off version) or attempts to restart (auto retry version) the device after the junction temperature decreases. eFuses offer many additional features similar to load switches including adjustable inrush current control and reverse current protection.
Managing current flow from an active power bus to a subsidiary system can be a challenging task. As a device is inserted or removed from a live supply, it is possible to see a very large spike in current during the initial capacitor charging. An eFuse or Section 4 controller ensures the safe insertion and operation of these systems. Unlike hot swap controllers, eFuses contain an integrated FET which minimizes total solution size. This allows eFuses to be used in applications such as power multiplexing. By using two eFuses, each eFuse can control a power rail while providing reverse current protection for its respective supply. eFuses are also UL 2367 certified, cutting down on system testing time.
Table 4. eFuse Examples(1)
| DESCRIPTION | DEVICE | RECOMMENDED VOLTAGE RANGE | MAX CURRENT | TYPICAL Ron | PACKAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overvoltage or undervoltage clamp, QOD using FLT pin, adjustable current limit | TPS2595 | 2.7 V to 18 V | 4 A | 34 mΩ | SON |
| Lowest Ron circuit-breaker device, accurate load monitoring, adjustable transient fault management | TPS25982 | 2.5 V to 24 V | 15 A | 3 mΩ | QFN |
| Back to back FETs, status monitoring, thermal shutdown, internal reverse current blocking | TPS25942A | 2.7 V to 18 V | 5 A | 42 mΩ | QFN |
| Reverse polarity protection, current sense output, adjustable current limit | TPS2660 | 4.2 V to 55 V | 2 A | 150 mΩ | SOP and QFN |
| Power limiting, overvoltage cut-off or voltage clamping functionality | TPS1663 | 4.5 V to 60 V | 6 A | 31 mΩ | SOP and QFN |
| Power limiting, reverse current blocking, reverse polarity protection | TPS2663 | 4.5 V to 60 V | 6 A | 31 mΩ | SOP and QFN |