SLVSDR2B November 2018 – March 2021 ADC12DJ3200QML-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Dual-Channel Mode)
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Single-Channel Mode)
- 6.9 Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Timing Diagrams
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Analog Inputs
- 7.3.2 ADC Core
- 7.3.3 Timestamp
- 7.3.4 Clocking
- 7.3.5 Digital Down Converters (Dual-Channel Mode Only)
- 7.3.6 JESD204B Interface
- 7.3.7 Alarm Monitoring
- 7.3.8 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 7.3.9 Analog Reference Voltage
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Dual-Channel Mode
- 7.4.2 Single-Channel Mode (DES Mode)
- 7.4.3 JESD204B Modes
- 7.4.4 Power-Down Modes
- 7.4.5 Test Modes
- 7.4.6 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 7.4.7 Offset Calibration
- 7.4.8 Trimming
- 7.4.9 Offset Filtering
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
7.3.6.6 Multi-Device Synchronization and Deterministic Latency
JESD204B subclass 1 outlines a method to achieve deterministic latency across the serial link. If two devices achieve the same deterministic latency then they can be considered synchronized. This latency must be achieved from system startup to startup to be deterministic. There are two key requirements to achieve deterministic latency. The first is proper capture of SYSREF for which the ADC12DJ3200QML-SP provides a number of features to simplify this requirement at giga-sample clock rates (see the SYSREF Capture for Multi-Device Synchronization and Deterministic Latency section for more information).
The second requirement is to choose a proper elastic buffer release point in the receiver. Because the ADC12DJ3200QML-SP is an ADC, the ADC12DJ3200QML-SP is the transmitter (TX) in the JESD204B link and the logic device is the receiver (RX). The elastic buffer is the key block for achieving deterministic latency, and does so by absorbing variations in the propagation delays of the serialized data as the data travels from the transmitter to the receiver. A proper release point is one that provides sufficient margin against delay variations. An incorrect release point results in a latency variation of one LMFC period. Choosing a proper release point requires knowing the average arrival time of data at the elastic buffer, referenced to an LMFC edge, and the total expected delay variation for all devices. With this information the region of invalid release points within the LMFC period can be defined, which stretches from the minimum to maximum delay for all lanes. Essentially, the designer must make certain that the data for all lanes arrives at all devices before the release point occurs.
Figure 7-20 illustrates a timing diagram that demonstrates this requirement. In this figure, the data for two ADCs is shown. The second ADC has a longer routing distance (tPCB) and results in a longer link delay. First, the invalid region of the LMFC period is marked off as determined by the data arrival times for all devices. Then, the release point is set by using the release buffer delay (RBD) parameter to shift the release point an appropriate number of frame clocks from the LMFC edge so that the release point occurs within the valid region of the LMFC cycle. In the case of Figure 7-20, the LMFC edge (RBD = 0) is a good choice for the release point because there is sufficient margin on each side of the valid region.
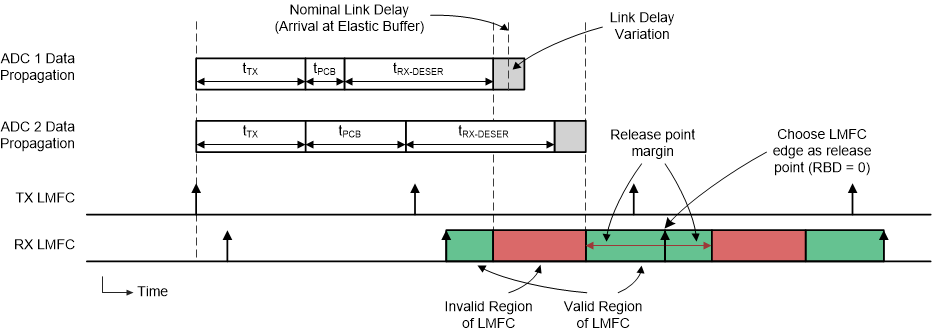 Figure 7-20 LMFC Valid Region Definition for Elastic Buffer Release Point Selection
Figure 7-20 LMFC Valid Region Definition for Elastic Buffer Release Point SelectionThe TX and RX LMFCs do not necessarily need to be phase aligned, but knowledge of their phase is important for proper elastic buffer release point selection. Also, the elastic buffer release point occurs within every LMFC cycle, but the buffers only release when all lanes have arrived. Therefore, the total link delay can exceed a single LMFC period; see the JESD204B multi-device synchronization: Breaking down the requirements techincal brief for more information.