SNAS513F August 2011 – November 2015 LM48560
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Minimize trace impedance of the power, ground and all output traces for optimum performance. Voltage loss due to trace resistance between the LM48560 device and the load results in decreased output power and efficiency. Trace resistance between the power supply and ground has the same effect as a poorly regulated supply, increased ripple and reduced peak output power. Use wide traces for power supply inputs and amplifier outputs to minimize losses due to trace resistance, as well as route heat away from the device. Proper grounding improves audio performance, minimizes crosstalk between channels and prevents switching noise from interfering with the audio signal. Use of power and ground planes is recommended.
Place all digital components and route digital signal traces as far as possible from analog components and traces. Do not run digital and analog traces in parallel on the same PCB layer. If digital and analog signal lines must cross either over or under each other, ensure that they cross in a perpendicular fashion.
11.2 Layout Example
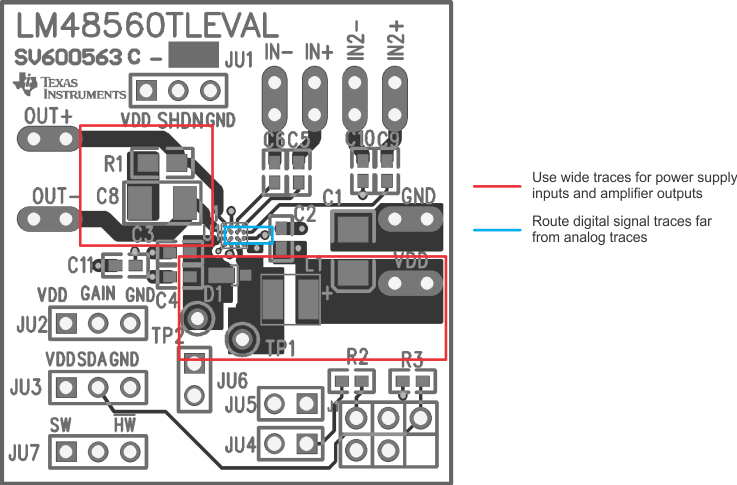 Figure 30. PCB Layout Example
Figure 30. PCB Layout Example