SNVAA73 may 2023 LM53602 , LM53602-Q1 , LM53603-Q1 , LM63625-Q1 , LM63635-Q1 , LMR14020-Q1 , LMR14030-Q1
5.1 BT-SW UVLO
When the HS MOSFET is turned on, the current that flows from the bootstrap capacitor through RBOOT causes a drop in the voltage from the BOOT to SW pins. If this voltage drop is large, the voltage on the HS MOSFET gate-source is reduced, leading to potential slow device turn-on and or triggering the BOOT UVLO circuit.
LM53602 is a 36-V, 2-A synchronous buck converter. The BT-SW voltage UVLO threshold is 2.5 V (typical) with 50 ns (typical) delay time. Figure 5-1 shows the BT-SW voltage measured on the LM53602 application circuit for 12 V to 3.3 V conversion at 2 MHz and FWPM mode. With an RBOOT value of 20 Ω, the BT-SW voltage drops below 2.5 V for 44 ns, which risks hitting the UVLO threshold.
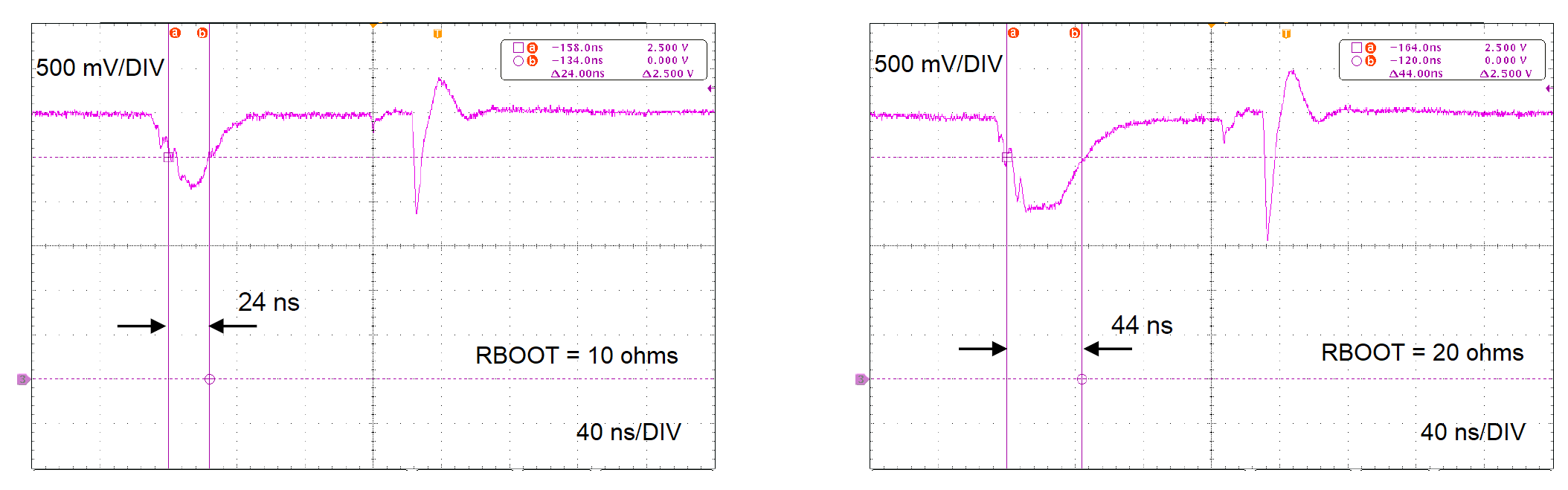 Figure 5-1 BT-SW Voltage Drop
Figure 5-1 BT-SW Voltage DropTypically, the HS FET is turned-off immediately until the next cycle when BOOT UVLO is triggered, but there can be unexpected switching behavior if combined with other abnormal conditions, so the BT-SW voltage must be carefully checked in various operating condition to avoid hitting the UVLO threshold.