SPRAD41 May 2022 AM623 , AM625
1 Introduction
The increasing popularity of embedded systems in a wide range of applications pushes for a higher level of integration onto a single SoC. This high level of integration leads to higher power dissipation, increased thermal system cost, degraded performance, and reduced battery life. To overcome these challenges, SoCs should be defined, architected, and designed in the context of their usage in the targeted embedded systems. Since every application is different, picking the correct operating settings for the SoC will achieve optimal performance and power. This paper presents novel features and techniques developed on the AM62x processors - a next-generation Sitara MPU device from Texas Instruments.
AM62x processors feature a high-performance Quad-core Cortex A53 with 64-bit architecture, a powerful 3D Graphics Engine, an integrated M4F MCU Channel for general purpose usage or safety with full freedom-from interface (FFI) from the application domain, a Dual-core M4F for Foundational and Automotive/Industrial Security, a dedicated R5F core for device resources and low power management. The modular architecture of this device delivers performance with support for several low power modes without sacrificing critical system resources, such as connectivity, power, security, safety, and cost. Figure 1 shows a high-level AM62x processor block diagram.
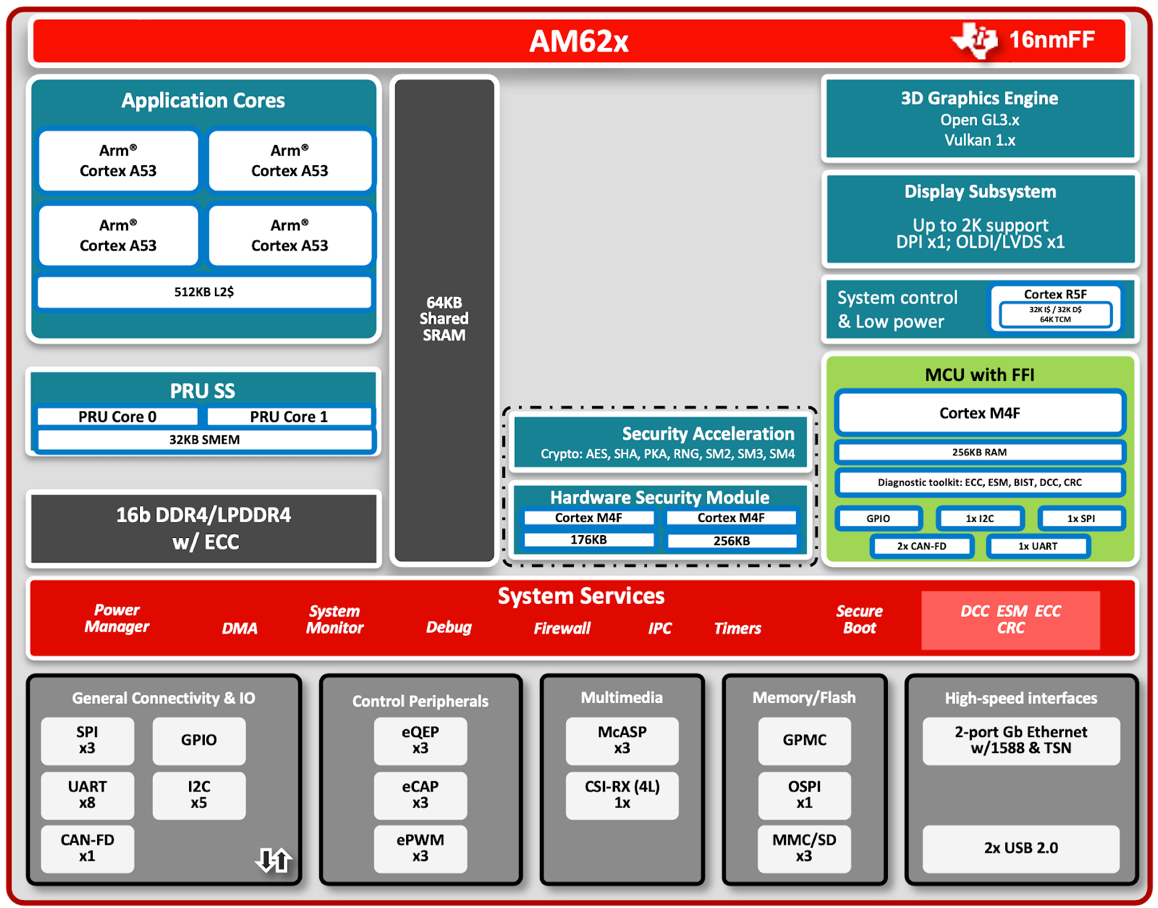 Figure 1-1 Block Diagram of the SitaraTM AM62x Processors
Figure 1-1 Block Diagram of the SitaraTM AM62x Processors