SWRU437B September 2015 – June 2020 WL1801MOD , WL1805MOD , WL1807MOD , WL1831MOD , WL1835MOD , WL1837MOD
10 WiFi_Zigbee Coex
- For Zigbee/WiFi Coexistence, the following should be connected:
- For signals level shifting between WL18XXMOD and CC2530, TI recommends the TXS0102 Bidirectional Voltage-Level Translator.
- For the TX disable, one of the options is to use resistor divider or use single bit Level Shifter.
 Figure 11. WLAN ZigBee Coexistence
Figure 11. WLAN ZigBee Coexistence Table 11. WLAN ZigBee Coex Lines
| Signal Name | WL18xxMOD IO (1.8 Bv) | CC2530 Zigbee IO (3.3 V) | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tx Active | GPIO12 (Pin 5) | P1_7 (Pin 37) | From WLAN |
| Rx Active | GPIO10 (Pin 4) | P0_0 (Pin 19) | From WLAN |
| PA SHUTDOWN/REQUEST | GPIO9 (Pin 3) | P1_6 (Pin 38) | To WLAN |
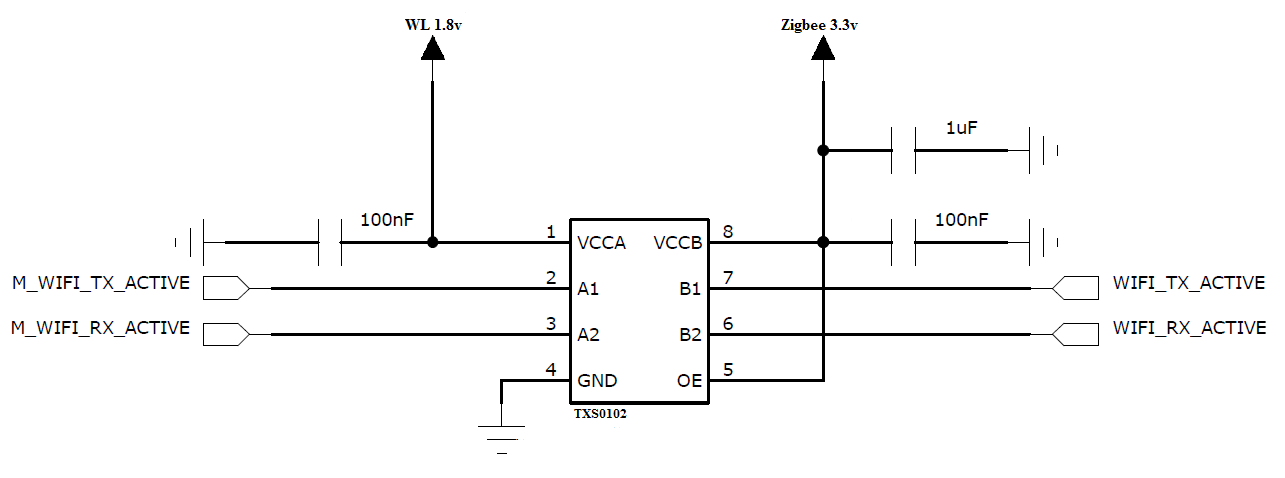 Figure 12. Zigbee_LS
Figure 12. Zigbee_LS 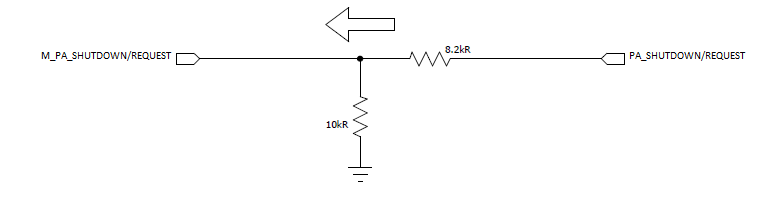 Figure 13. Zigbee_RNR
Figure 13. Zigbee_RNR