TIDUF09 December 2022
3.3.9 Thermal Limit Protection
The thermal protection performance of the parallel LDOs exhibits a staircase effect on VLOAD during turn off and turn on as each LDO enters and exits thermal shutdown. Thermal protection is repeatedly engaged until the power dissipation from the parallel LDOs is removed. Figure 3-25 demonstrates the desired effect of the thermal protection circuitry in the presence of heavy power dissipation across the LDOs. The parallel LDOs require 12.5 W dissipation in this reference design to enter thermal shutdown when operated from room temperature.
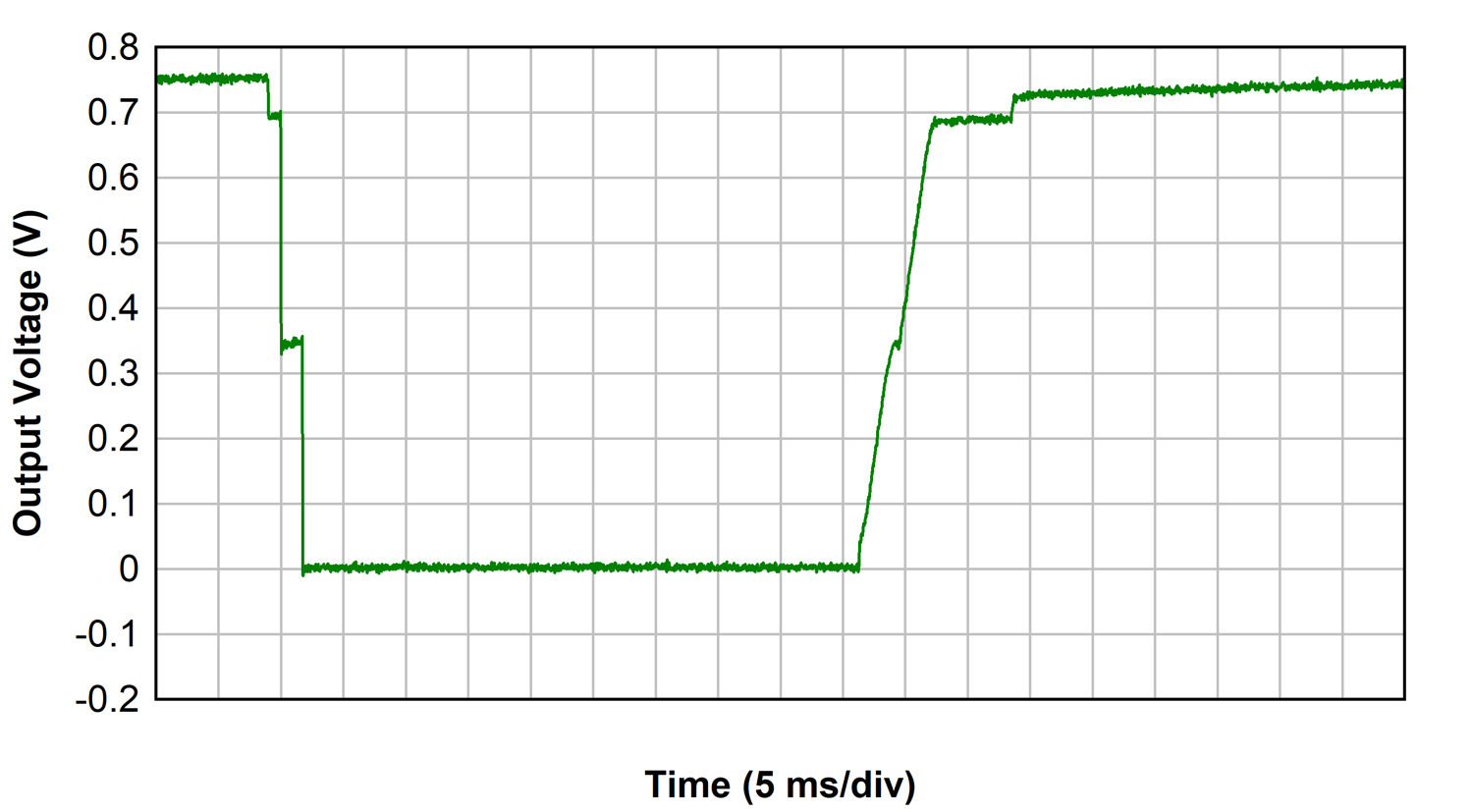
| VIN= 1.9 V, ILOAD = 13.5 A |
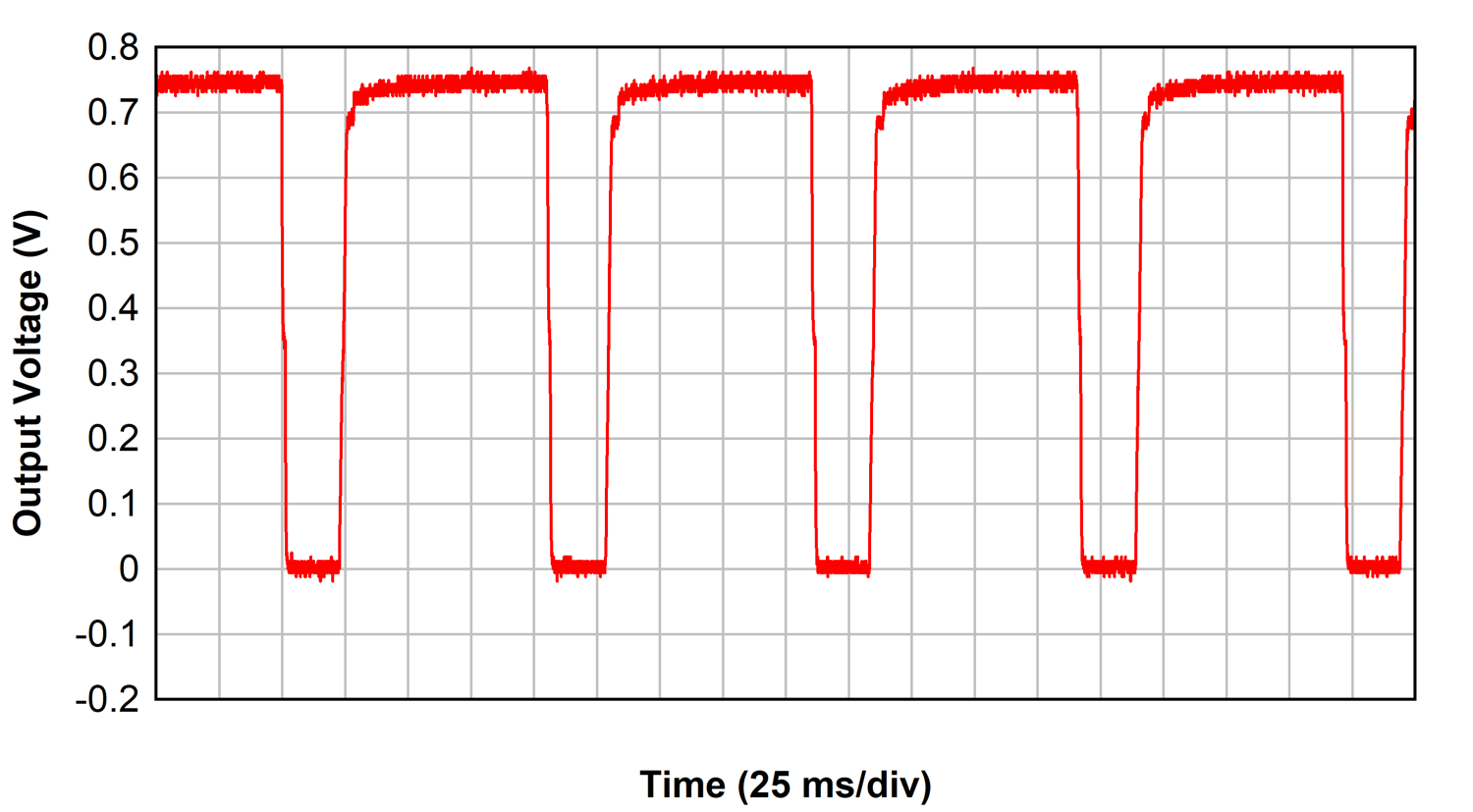
| VIN= 2 V, ILOAD = 13.5 A |