SBAS943A September 2018 – August 2019 ADS1284
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Synchronization (SYNC PIN and SYNC Command)
- 8.4.2 Reset (RESET Pin and Reset Command)
- 8.4.3 Master Clock Input (CLK)
- 8.4.4 Power-Down (PWDN Pin and STANDBY Command)
- 8.4.5 Power-On Sequence
- 8.4.6 DVDD Power Supply
- 8.4.7 Serial Interface
- 8.4.8 Data Format
- 8.4.9 Reading Data
- 8.4.10 One-Shot Operation
- 8.4.11 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration Registers
- 8.4.12 Calibration Commands (OFSCAL and GANCAL)
- 8.4.13 User Calibration
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.5.1.1 SDATAC Requirements
- 8.5.1.2 WAKEUP: Wake-Up From Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.3 STANDBY: Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.4 SYNC: Synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- 8.5.1.5 RESET: Reset the Device
- 8.5.1.6 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.7 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.8 RDATA: Read Data by Command
- 8.5.1.9 RREG: Read Register Data
- 8.5.1.10 WREG: Write to Register
- 8.5.1.11 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration
- 8.5.1.12 GANCAL: Gain Calibration
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID_CFG: ID_Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset =x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 HPF0 and HPF1 Registers
- 8.6.1.5 OFC0, OFC1, OFC2 Registers
- 8.6.1.6 FSC0, FSC1, FSC2 Registers
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHF|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2 Digital Interface
Figure 82 shows the digital connection to a controller (field programmable gate array or microcontroller). In this example, two ADCs are shown connected to one controller. The ADCs share the same serial interface (SCLK, DIN, and DOUT). The ADC is selected for communication by strobing each CS low. The DRDY output from both ADCs can be used; however, when the devices are synchronized, the DRDY output from only one device is sufficient.
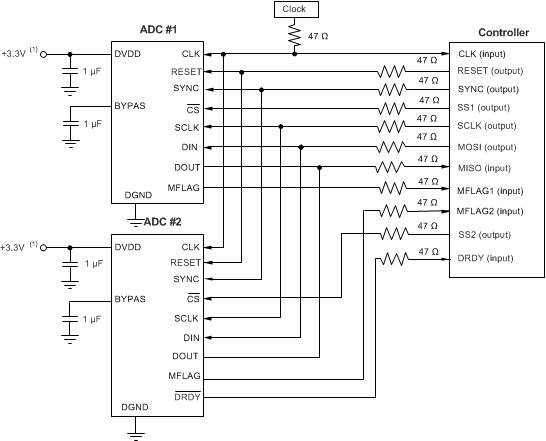
The modulator overrange flag (MFLAG) from each device ties to the controller input. For synchronization, connect all ADCs to the same SYNC signal. For reset, either connect all ADCs to the same RESET signal or connect the ADCs to individual RESET signals.
Avoid ringing on the digital inputs to the ADCs. Place 47-Ω resistors in series with the digital traces to help reduce ringing by controlling impedances. Place the resistors at the source (driver) end of the trace. Do not float unused digital inputs; tie them to DVDD or GND.