SNVSB54A May 2018 – November 2018 LM5122ZA
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.2 High-Voltage VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Oscillator
- 7.3.4 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 PWM Comparator
- 7.3.7 Soft Start
- 7.3.8 HO and LO Drivers
- 7.3.9 Bypass Operation (VOUT = VIN)
- 7.3.10 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 7.3.11 Clock Synchronization
- 7.3.12 Maximum Duty Cycle
- 7.3.13 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Feedback Compensation
- 8.1.2 Sub-Harmonic Oscillation
- 8.1.3 Interleaved Boost Configuration
- 8.1.4 DCR Sensing
- 8.1.5 Output Overvoltage Protection
- 8.1.6 SEPIC Converter Simplified Schematic
- 8.1.7 Non-Isolated Synchronous Flyback Converter Simplified Schematic
- 8.1.8 Negative to Positive Conversion
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Timing Resistor RT
- 8.2.2.2 UVLO Divider RUV2, RUV1
- 8.2.2.3 Input Inductor LIN
- 8.2.2.4 Current Sense Resistor RS
- 8.2.2.5 Current Sense Filter RCSFP, RCSFN, CCS
- 8.2.2.6 Slope Compensation Resistor RSLOPE
- 8.2.2.7 Output Capacitor COUT
- 8.2.2.8 Input Capacitor CIN
- 8.2.2.9 VIN Filter RVIN, CVIN
- 8.2.2.10 Bootstrap Capacitor CBST and Boost Diode DBST
- 8.2.2.11 VCC Capacitor CVCC
- 8.2.2.12 Output Voltage Divider RFB1, RFB2
- 8.2.2.13 Soft-Start Capacitor CSS
- 8.2.2.14 Restart Capacitor CRES
- 8.2.2.15 Low-Side Power Switch QL
- 8.2.2.16 High-Side Power Switch QH and Additional Parallel Schottky Diode
- 8.2.2.17 Snubber Components
- 8.2.2.18 Loop Compensation Components CCOMP, RCOMP, CHF
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.12 Maximum Duty Cycle
When operating with a high PWM duty cycle, the low-side N-channel MOSFET device is forced off each cycle. This forced LO off-time limits the maximum duty cycle of the controller. When designing a boost regulator with high switching frequency and high duty-cycle requirements, check the required maximum duty cycle. The minimum input supply voltage that can achieve the target output voltage is estimated from Equation 14 or Equation 15.
Use Equation 14 if VVCC is greater than 5.5 V or VVIN is greater than 6 V. For low voltage applications that do not satisfy either of these conditions use Equation 15.
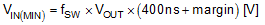
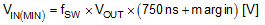
In normal operation, about 100 ns of margin is recommended.