SBOU180B november 2016 – july 2023 INA260
3.2 INA260EVM Jumper Settings
Figure 3-3 shows the default jumper configuration for the INA260EVM and Table 3-1 explain the purpose of each jumper. Ensure that the jumpers are installed in the correct positions, based on the required test conditions.
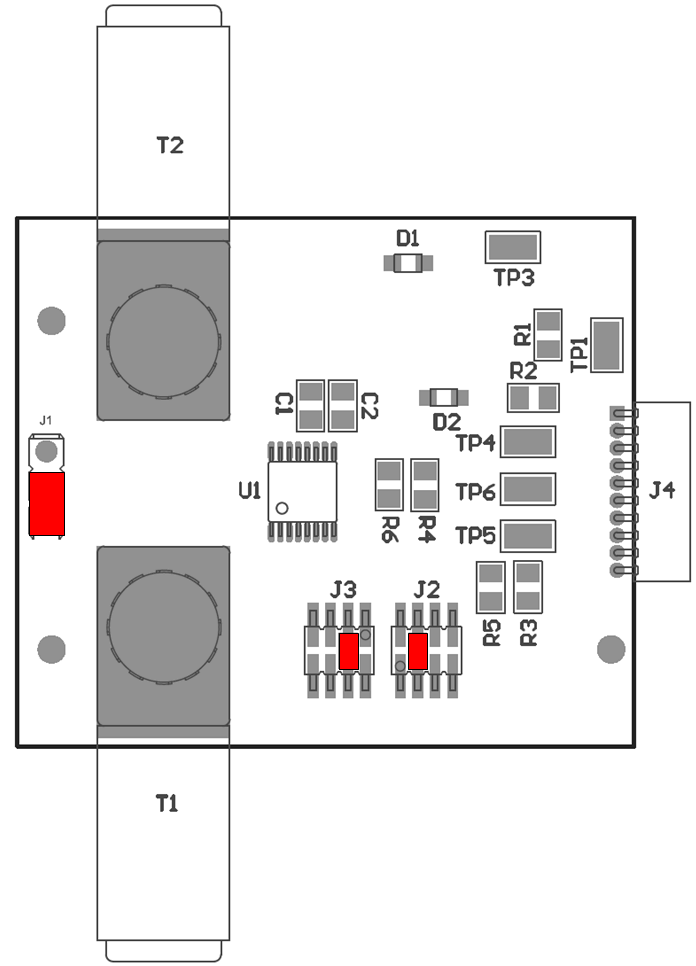 Figure 3-3 INA260EVM
Default Jumper Settings
Figure 3-3 INA260EVM
Default Jumper SettingsTable 3-1 INA260EVM Test Board Jumper
Functions
|
JUMPER |
DEFAULT |
PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|
| J1 | IN+ | This jumper selects whether the VBUS pin on the INA260 is connected to the IN+ or IN– pin; see Section 2.2.2 for details. |
| J2 | GND | This jumper sets the A0 character of the 2-character I2C device address; see Section 2.3 for details. |
| J3 | GND | This jumper sets the A1 character of the 2-character I2C device address; see Section 2.3 for details. |