SNLA443 December 2023 DP83869HM
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1DP83869 Application Overview
- 2Troubleshooting the Application
- 3Operational Mode Clarification
- 4Tools and References
- 5Summary
- 6References
4.1 DP83869HM Register Access
If register access is not readily available in the application, USB-2-MDIO GUI is available from TI and can be used with an MSP430™ Launchpad, purchasable through the TI eStore. The GUI supports reading and writing registers, running script files, and can be used with the DP83869HM and the other devices in TI's Ethernet portfolio. USB-2-MDIO User's Guide and GUI are available for download.
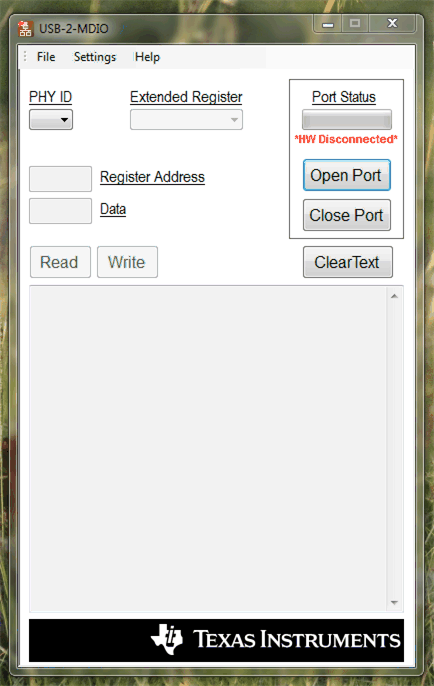 Figure 4-1 USB-2-MDIO GUI
Figure 4-1 USB-2-MDIO GUI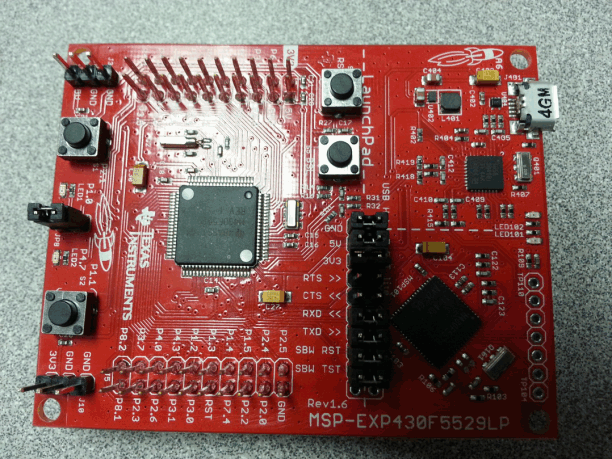 Figure 4-2 MSP430 LaunchPad
Figure 4-2 MSP430 LaunchPadBelow is an example script that can also be found in the USB-2-MDIO GUI in the Help menu:
// This is how you make a comment. All scripts must start with 'begin'
begin
// To read a register, all you need to do is put down the 4 digit
// HEX value of the registers (from 0000 to FFFF)
// Example to read registers 0001, 000A, and 0017
0001
000A
0017
// To write a register, all you need to do is put down the 4 digit
// HEX value of the register (from 0000 to FFFF) followed by the
// HEX you desire to configure the register to (from 0000 to FFFF)
// Example to write 2100 to register 0000 and
// Example to write 0110 to register 0016
0000 2100
0016 0110
// You must end the script by adding 'end' once you are finished
end
The Serial Management Interface defined by IEEE 802.3 is a single master bus. The MDC clock is generated by the bus master, typically an Ethernet MAC. To use the USB-2-MDIO GUI, connections must be made directly between the MSP430 Launchpad and the DP83867 MDIO and MDC pins. Specifically, pins 4.1 to MDC, 4.2 to MDIO, and any GND to the ground of the PHY allows the MSP to read and write the PHY's registers by USB-2-MDIO.