SNOA961A February 2017 – February 2023 LDC2112 , LDC2114 , LDC3114 , LDC3114-Q1
- Inductive Touch System Design Guide for HMI Button Applications
- 1Mechanical Design
- 2Sensor Design
- 3Summary
- 4Revision History
1.4.1.1 Material Stiffness
The material choice has a large impact on how much force is needed to achieve the required deflection for a given metal thickness. The key material parameter is the Young’s modulus, which is a measure of the elasticity of the metal and is measured in units of pascal (Pa). Materials with a lower Young’s modulus are typically more flexible. For example, aluminum (AL6061-T6) has a Young’s modulus of 68.9 GPa, while stainless steel (for example, SS304) has a Young’s modulus of about 200 GPa, which makes stainless steel about three times stiffer than aluminum. #T4726003-13 shows the difference in deflection versus force for a given circular sensor between the two materials.
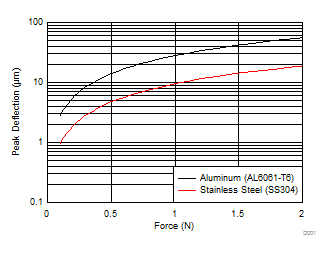 Figure 1-4 Deflection vs Force for Al and Steel Targets, Circular Button, Diameter = 20 mm, Thickness = 0.25 mm
Figure 1-4 Deflection vs Force for Al and Steel Targets, Circular Button, Diameter = 20 mm, Thickness = 0.25 mm