SPRS999 August 2017 AM5718-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Device Comparison
-
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Terminal Assignment
- 4.2 Ball Characteristics
- 4.3 Multiplexing Characteristics
- 4.4
Signal Descriptions
- 4.4.1 Video Input Ports (VIP)
- 4.4.2 Display Subsystem - Video Output Ports
- 4.4.3 Display Subsystem - High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 4.4.4 Camera Serial Interface 2 CAL bridge (CSI2)
- 4.4.5 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 4.4.6 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 4.4.7 Timers
- 4.4.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 4.4.9 HDQ / 1-Wire Interface (HDQ1W)
- 4.4.10 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 4.4.11 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (McSPI)
- 4.4.12 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 4.4.13 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 4.4.14 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 4.4.15 SATA
- 4.4.16 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 4.4.17 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 4.4.18 Ethernet Interface (GMAC_SW)
- 4.4.19 Media Local Bus (MLB) Interface
- 4.4.20 eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 4.4.21 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 4.4.22 Keyboard controller (KBD)
- 4.4.23 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Interface
- 4.4.24 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem and Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 4.4.25 Test Interfaces
- 4.4.26 System and Miscellaneous
- 4.4.27 Power Supplies
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power On Hours (POH) Limits
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Operating Performance Points
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7
Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.1 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.2 HDMIPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.3 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.4 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.5 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.6 LVCMOS OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.7 LVCMOS CSI2 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.8 BMLB18 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.9 BC1833IHHV Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.10 USBPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.11 Dual Voltage SDIO1833 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.12 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.13 SATAPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.14 SERDES DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.9 Power Supply Sequences
- 6 Clock Specifications
-
7 Timing Requirements and Switching Characteristics
- 7.1 Timing Test Conditions
- 7.2 Interface Clock Specifications
- 7.3 Timing Parameters and Information
- 7.4 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.5 Virtual and Manual I/O Timing Modes
- 7.6 Video Input Ports (VIP)
- 7.7 Display Subsystem - Video Output Ports
- 7.8 Display Subsystem - High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 7.9 Camera Serial Interface 2 CAL bridge (CSI2)
- 7.10 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 7.11 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.12 Timers
- 7.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 7.14 HDQ / 1-Wire Interface (HDQ1W)
- 7.15 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 7.16 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (McSPI)
- 7.17 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 7.18 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 7.19 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 7.20 Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
- 7.21 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 7.22 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 7.23 Ethernet Interface (GMAC_SW)
- 7.24
eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 7.24.1
MMC1-SD Card Interface
- 7.24.1.1 Default speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.2 High speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.3 SDR12, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.4 SDR25, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.5 UHS-I SDR50, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.6 UHS-I SDR104, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.7 UHS-I DDR50, 4-bit data
- 7.24.2 MMC2 - eMMC
- 7.24.3 MMC3 and MMC4-SDIO/SD
- 7.24.1
MMC1-SD Card Interface
- 7.25 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 7.26 PRU-ICSS Interfaces
- 7.27 System and Miscellaneous interfaces
- 7.28 Test Interfaces
-
8 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Power Supply Mapping
- 8.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.1 DDR3 General Board Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.2.1 Board Designs
- 8.2.2.2 DDR3 EMIF
- 8.2.2.3 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 8.2.2.4 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 8.2.2.5 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 8.2.2.6 PCB Stackup
- 8.2.2.7 Placement
- 8.2.2.8 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 8.2.2.9 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 8.2.2.10 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 Net Classes
- 8.2.2.12 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 8.2.2.13 VREF_DDR Routing
- 8.2.2.14 VTT
- 8.2.2.15 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 8.2.2.16 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 8.2.2.17 Routing Specification
- 8.3 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 8.4 Power Distribution Network Implementation Guidance
- 8.5 Single-Ended Interfaces
- 8.6 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZBO|760
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Specifications
NOTE
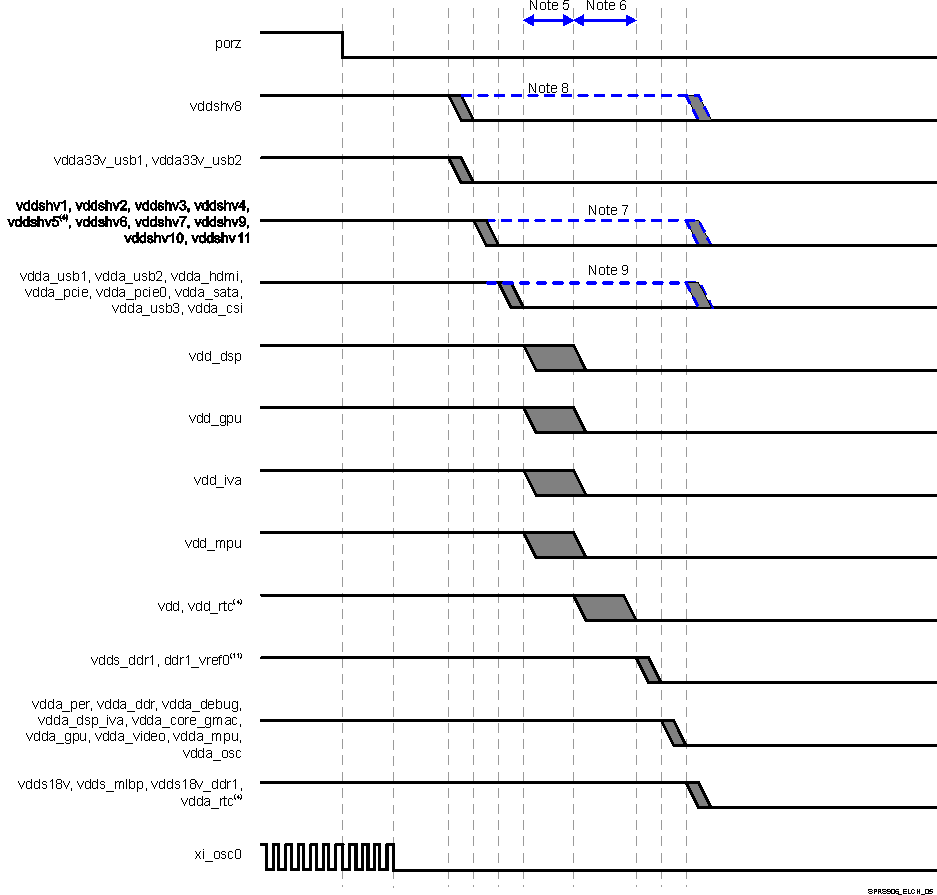
For more information, see Power, Reset, and Clock Management / PRCM Subsystem Environment / External Voltage Inputs or Initialization / Preinitialization / Power Requirements section of the Device TRM.
NOTE
The index numbers 1 which is part of the EMIF1 signal prefixes (ddr1_*) listed in Table 4-8, EMIF Signal Descriptions, column "SIGNAL NAME" not to be confused with DDR1 type of SDRAM memories.
NOTE
Audio Back End (ABE) module is not supported for this family of devices, but “ABE” name is still present in some clock or DPLL names.
CAUTION
All IO Cells are NOT Fail-safe compliant and should not be externally driven in absence of their IO supply.
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses beyond those listed as Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those listed under Section 5.4, Recommended Operating Conditions, is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Table 5-1 Absolute Maximum Rating Over Junction Temperature Range
| PARAMETER(1) | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSUPPLY (steady-state) | Supply voltage ranges (steady-state) | Core (vdd, vdd_mpu, vdd_gpu, vdd_dsp, vdd_iva, vdd_rtc) | –0.3 | 1.5 | V |
| Analog (vdda_usb1, vdda_usb2, vdda_per, vdda_ddr, vdda_debug, vdda_mpu_abe, vdda_usb3, vdda_csi, vdda_core_gmac, vdda_pll_spare, vdda_dsp_iva, vdda_gpu, dda_hdmi, vdda_pcie, vdda_pcie0, vdda_sata, vdda_video, vdda_osc, vdda_rtc) | –0.3 | 2.0 | V | ||
| Analog 3.3-V (vdda33v_usb1, vdda33v_usb2) | –0.3 | 3.8 | V | ||
| vdds18v, vdds18v_ddr1, vdds_mlbp, vdds_ddr1 | –0.3 | 2.1 | V | ||
| vddshv1-11 (1.8-V mode) | –0.3 | 2.1 | V | ||
| vddshv1-7 (3.3-V mode), vddshv9-11 (3.3-V mode) | –0.3 | 3.8 | V | ||
| vddshv8 (3.3-V mode) | –0.3 | 3.6 | V | ||
| VIO (steady-state) | Input and output voltage ranges (steady-state) | Core I/Os | –0.3 | 1.5 | V |
| Analog I/Os (except HDMI) | –0.3 | 2.0 | V | ||
| HDMI I/Os | –0.3 | 3.5 | V | ||
| I/O 1.35 V | –0.3 | 1.65 | V | ||
| I/O 1.5 V | –0.3 | 1.8 | V | ||
| 1.8-V I/Os | –0.3 | 2.1 | V | ||
| 3.3-V I/Os (except those powered by vddshv8) | –0.3 | 3.8 | V | ||
| 3.3-V I/Os (powered by vddshv8) | –0.3 | 3.6 | V | ||
| SR | Maximum slew rate, all supplies | 105 | V/s | ||
| VIO (transient overshoot and undershoot) | Input and output voltage ranges (transient overshoot/undershoot) Note: valid for up to 20% of the signal period |
0.2 * VDD (2) | V | ||
| TSTG | Storage temperature range after soldered onto PC board | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Latch-up I-test | I-test(3), All I/Os (if different levels then one line per level) | –100 | 100 | mA | |
| Latch-up OV-test | Over-voltage test(4), All supplies (if different levels then one line per level) | N/A | 1.5 * Vsupply max | V | |
- See I/Os supplied by this power pin in Table 4-2 Ball Characteristics.
- VDD is the voltage on the corresponding power-supply pin(s) for the IO.
- Per JEDEC JESD78 at 125°C with specified I/O pin injection current and clamp voltage of 1.5 times maximum recommended I/O voltage and negative 0.5 times maximum recommended I/O voltage.
- Per JEDEC JESD78 at 125°C.
5.2 ESD Ratings
Table 5-2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±1000 | V | |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101 (2) | ±250 | ||||
- JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
- JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
5.3 Power On Hours (POH) Limits
The information in the section below is provided solely for your convenience and does not extend or modify the warranty provided under TI’s standard terms and conditions for TI semiconductor products.
NOTE
POH is a function of voltage, temperature and time. Usage at higher voltages and temperatures will result in a reduction in POH.
Table 5-3 Power On Hour (POH) Limits(1)
| OPERATING CONDITION | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPP | HDMI | JUNCTION TEMP (Tj) | LIFETIME (POH) | JUNCTION TEMP (Tj) | LIFETIME (POH) | JUNCTION TEMP (Tj) | LIFETIME (POH) | ||
| OPP_NOM or OPP_OD | Not used | 90°C | 100k | 100°C | 100k | 105°C | 100k (3) | ||
| Used(2) | 90°C | 100k | 100°C | 63k | 105°C | 45k | |||
| OPP_HIGH | Not used | 90°C | 65k | 100°C | 55k | 105°C | 50k | ||
| Used(2) | 90°C | 65k | 100°C | 55k | 105°C | 45k | |||
- Unless specified in Table 5-3, all voltage domains and operating conditions are supported in the device at the noted temperatures.
- Power-on hours (POH) assume HDMI is used at the maximum supported bit rate continuously and/or operating the device continuously at the VD_MPU operating point (OPP) noted.
- 90k POH only if SuperSpeed USB 3.0 Dual-Role-Device (at 5 Gbps) or PCIe in Gen-II mode (at 5 Gbps) are used.
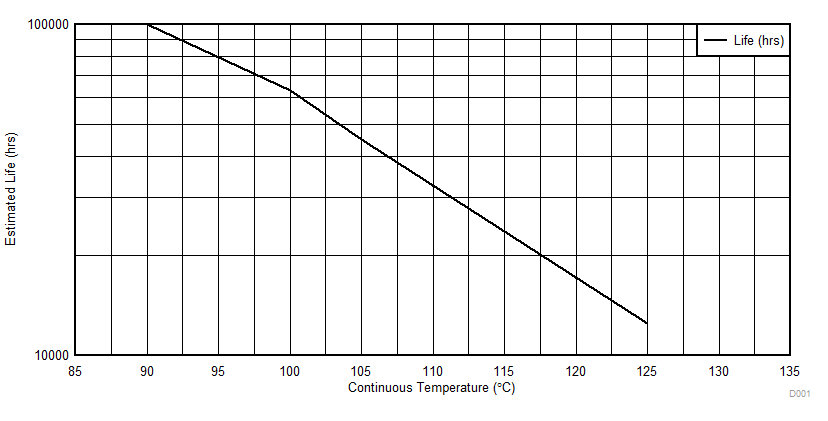 Figure 5-1 Operating Life Derating Chart
Figure 5-1 Operating Life Derating Chart
- See data sheet for absolute maximum and minimum recommended operating conditions.
- The predicted operating lifetime vs junction temperature is based on reliability modeling using electromigration as the dominant failure mechanism affecting device wear-out for the specific device process and design characteristics.
- Above derating lifetime is based on nominal OPP.
5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
The device is used under the recommended operating conditions described in Table 5-4.
NOTE
Logic functions and parameter values are not assured out of the range specified in the recommended operating conditions.
Table 5-4 Recommended Operating Conditions
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MIN (2) | NOM | MAX DC (3) | MAX (2) | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE RANGE | |||||||
| vdd | Core voltage domain supply | See Section 5.5 | V | ||||
| vdd_mpu | Supply voltage range for MPU domain | See Section 5.5 | V | ||||
| vdd_gpu | GPU voltage domain supply | See Section 5.5 | V | ||||
| vdd_dsp | DSP voltage domain supply | See Section 5.5 | V | ||||
| vdd_iva | IVA voltage domain supply | See Section 5.5 | V | ||||
| vdd_rtc | RTC voltage domain supply | See Section 5.5 | V | ||||
| vdda_usb1 | DPLL_USB and HS USB1 1.8-V analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_usb2 | HS USB2 1.8-V analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda33v_usb1 | HS USB1 3.3-V analog power supply.If USB1 is not used, this pin can alternatively be connected to VSS if the following requirements are met: - The usb1_dm/usb1_dp pins are left unconnected - The USB1 PHY is kept powered down |
3.135 | 3.3 | 3.366 | 3.465 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda33v_usb2 | HS USB2 3.3-V analog power supply. If USB2 is not used, this pin can alternatively be connected to VSS if the following requirements are met: - The usb2_dm/usb2_dp pins are left unconnected - The USB2 PHY is kept powered down |
3.135 | 3.3 | 3.366 | 3.465 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_per | PER PLL and PER HSDIVIDER analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_ddr | DPLL_DDR and DDR HSDIVIDER analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_debug | DPLL_DEBUG analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_dsp_iva | DPLL_DSP and DPLL_IVA analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_core_gmac | DPLL_CORE and CORE HSDIVIDER analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_pll_spare | DPLL_SPARE analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_gpu | DPLL_GPU analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_hdmi | PLL_HDMI and HDMI analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_pcie | DPLL_PCIe_REF and PCIe analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_pcie0 | PCIe ch0 RX/TX analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.89 | V | ||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_sata | DPLL_SATA and SATA RX/TX analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_usb3 | DPLL_USB_OTG_SS and USB3.0 RX/TX analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_video | DPLL_VIDEO1 analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdds_mlbp | MLBP IO power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.89 | V | ||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_mpu_abe | DPLL_MPU analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_osc | HFOSC analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.89 | V | ||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_rtc | RTC bias and RTC LFOSC analog power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.89 | V | ||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdda_csi | CSI Interface 1.8-V supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdds18v | 1.8-V power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdds18v_ddr1 | EMIF1 bias power supply | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V | |
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 50 | mVPPmax | |||||
| vdds_ddr1 | EMIF1 power supply (1.5 V for DDR3 mode / 1.35 V for DDR3L mode) | 1.35-V Mode | 1.28 | 1.35 | 1.377 | 1.42 | V |
| 1.5-V Mode | 1.43 | 1.50 | 1.53 | 1.57 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.35-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 1.5-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv5 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the RTC Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv1 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the VIN2 Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv10 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the GPMC Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv11 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the MMC2 Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv2 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the VOUT Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv3 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the GENERAL Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv4 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the MMC4 Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv6 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the VIN1 Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv7 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the WIFI Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv8 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the MMC1 Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vddshv9 | Dual Voltage (1.8 V or 3.3 V) power supply for the RGMII Power Group pins | 1.8-V Mode | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.836 | 1.89 | V |
| 3.3-V Mode | 3.135 | 3.30 | 3.366 | 3.465 | |||
| Maximum noise (peak-peak) | 1.8-V Mode | 50 | mVPPmax | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| vss | Ground supply | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_hdmi | DPLL_HDMI and HDMI PHY analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_pcie | PCIe analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_usb | HS USB1 and HS USB2 analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_usb3 | DPLL_USB and USB3.0 RX/TX analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_csi | CSI Interface 0v Supply | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_sata | SATA TX ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_video | DPLL_VIDEO1 analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_osc0 | OSC0 analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| vssa_osc1 | OSC1 analog ground | 0 | V | ||||
| TJ(1) | Operating junction temperature range | Extended | –55 | 125 | °C | ||
| ddr1_vref0 | Reference Power Supply EMIF1 | 0.5 * vdds_ddr1 | V | ||||
- Refer to Power On Hours table for limitations.
- The voltage at the device ball should never be below the MIN voltage or above the MAX voltage for any amount of time. This requirement includes dynamic voltage events such as AC ripple, voltage transients, voltage dips, etc.
- The DC voltage at the device ball should never be above the MAX DC voltage to avoid impact on device reliability and lifetime POH (Power-On-Hours). The MAX DC voltage is defined as the highest allowed DC regulated voltage, without transients, seen at the ball.
5.5 Operating Performance Points
This section describes the operating conditions of the device. This section also contains the description of each OPP (operating performance point) for processor clocks and device core clocks.
CAUTION
The OPP voltage and frequency values may change following the silicon characterization result.
Table 5-5 describes the maximum supported frequency per speed grade for AM5718 devices.
Table 5-5 Speed Grade Maximum Frequency
| DEVICE SPEED |
MAXIMUM FREQUENCY (MHz) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPU | DSP | IVA | GPU | IPU | L3 | DDR3/DDR3L | |
| AM5718xxX | 1500 | 750 | 532 | 532 | 212.8 | 266 | 667 (DDR3-1333) |
- N/A in this table stands for Not Applicable.
- Device will boot up initially at 588 MHz. An intermediate boot program must immediately reprogram the PLL to a frequency not over 500 MHz.
5.5.1 AVS and ABB Requirements
Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS) and Adaptive Body Biasing (ABB) are required on most of the vdd_* supplies as defined in Table 5-6.
Table 5-6 AVS and ABB Requirements per vdd_* Supply
| SUPPLY | AVS REQUIRED? | ABB REQUIRED? |
|---|---|---|
| vdd_core | Yes, for all OPPs | No |
| vdd_mpu | Yes, for all OPPs | Yes, for all OPPs |
| vdd_iva | Yes, for all OPPs | Yes, for all OPPs |
| vdd_dsp | Yes, for all OPPs | Yes, for all OPPs |
| vdd_gpu | Yes, for all OPPs | Yes, for all OPPs |
| vdd_rtc | No | No |
5.5.2 Voltage And Core Clock Specifications
Table 5-7 shows the recommended OPP per voltage domain.
Table 5-7 Voltage Domains Operating Performance Points(1)
| DOMAIN | CONDITION | OPP_NOM | OPP_OD | OPP_HIGH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN (3) | NOM (2) | MAX (3) | MIN (3) | NOM (2) | MAX (3) | MIN (3) | NOM (2) | MAX DC (4) | MAX (3) | ||
| VD_CORE (V) | BOOT (Before AVS is enabled) (5) | 1.11 | 1.15 | 1.2 | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | |||||
| After AVS is enabled (5) | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | 1.16 | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | ||||||
| VD_MPU (V) | BOOT (Before AVS is enabled) (5) | 1.11 | 1.15 | 1.2 | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | |||||
| After AVS is enabled (5) | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | 1.16 | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | AVS Voltage (6) + 5% | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | AVS Voltage (6) +2% | AVS Voltage (6) + 5% | |
| VD_RTC (7) (V) | - | 0.84 | 0.88 to 1.06 | 1.16 | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | |||||
| Others (V) | BOOT (Before AVS is enabled) (5) | 1.02 | 1.06 | 1.16 | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | |||||
| After AVS is enabled (5) | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | 1.16 | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | AVS Voltage (6) + 5% | AVS Voltage (6) – 3.5% | AVS Voltage (6) | AVS Voltage (6) +2% | AVS Voltage (6) + 5% | |
- The voltage ranges in this table are preliminary, and final voltage ranges may be different than shown. Systems should be designed with the ability to modify the voltage to comply with future recommendations.
- In a typical implementation, the power supply should target the NOM voltage.
- The voltage at the device ball should never be below the MIN voltage or above the MAX voltage for any amount of time. This requirement includes dynamic voltage events such as AC ripple, voltage transients, voltage dips, etc.
- The DC voltage at the device ball should never be above the MAX DC voltage to avoid impact on device reliability and lifetime POH (Power-On-Hours). The MAX DC voltage is defined as the highest allowed DC regulated voltage, without transients, seen at the ball.
- For all OPPs, AVS must be enabled to avoid impact on device reliability, lifetime POH (Power-On-Hours), and device power.
- The AVS voltages are device-dependent, voltage domain-dependent, and OPP-dependent. They must be read from the STD_FUSE_OPP Registers. For information about STD_FUSE_OPP Registers address, please refer to Control Module Section of the TRM. The power supply should be adjustable over the following ranges for each required OPP:
- OPP_NOM for MPU: 0.85 V – 1.15 V
- OPP_NOM for CORE and Others: 0.85 V – 1.15 V
- OPP_OD: 0.94 V – 1.15 V
- OPP_HIGH: 1.05 V – 1.25 V
- VD_RTC can optionally be tied to VD_CORE and operate at the VD_CORE AVS voltages.
- The power supply must be programmed with the AVS voltages for the MPU and the CORE voltage domain, either just after the ROM boot or at the earliest possible time in the secondary boot loader before there is significant activity seen on these domains.
Table 5-8 describes the standard processor clocks speed characteristics vs OPP of the device.
Table 5-8 Supported OPP vs Max Frequency(2)
| DESCRIPTION | OPP_NOM | OPP_OD | OPP_HIGH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Freq. (MHz) | Max Freq. (MHz) | Max Freq. (MHz) | |
| VD_MPU | |||
| MPU_CLK | 1000 | 1176 | 1500 |
| VD_DSP | |||
| DSP_CLK | 600 | 700 | 750 |
| VD_IVA | |||
| IVA_GCLK | 388.3 | 430 | 532 |
| VD_GPU | |||
| GPU_CLK | 425.6 | 500 | 532 |
| VD_CORE | |||
| CORE_IPUx_CLK | 212.8 | N/A | N/A |
| L3_CLK | 266 | N/A | N/A |
| DDR3 / DDR3L | 667 (DDR3-1333) | N/A | N/A |
| VD_RTC | |||
| RTC_FCLK | 0.034 | N/A | N/A |
- N/A in this table stands for Not Applicable.
- Maximum supported frequency is limited according to the Device Speed Grade (see Table 5-5).
5.5.3 Maximum Supported Frequency
Device modules either receive their clock directly from an external clock input, directly from a PLL, or from a PRCM. Table 5-9 lists the clock source options for each module on this device, along with the maximum frequency that module can accept. To ensure proper module functionality, the device PLLs and dividers must be programmed not to exceed the maximum frequencies listed in this table.
Table 5-9 Maximum Supported Frequency
| MODULE | CLOCK SOURCES | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance Name | Input Clock Name | Clock Type | Max. Clock Allowed (MHz) | PRCM Clock Name | PLL / OSC / Source Clock Name | PLL / OSC / Source Name |
| AES1 | AES1_L3_CLK | Int | 266 | L4SEC_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| AES2 | AES2_L3_CLK | Int | 266 | L4SEC_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| BB2D | BB2D_FCLK | Func | 354.6 | BB2D_GFCLK | BB2D_GFCLK | DPLL_CORE |
| BB2D_ICLK | Int | 266 | DSS_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| COUNTER_32K | COUNTER_32K_FCLK | Func | 0.032 | FUNC_32K_CLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 |
| COUNTER_32K_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| CTRL_MODULE_BANDGAP | L3INSTR_TS_GCLK | Int | 4.8 | L3INSTR_TS_GCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| CTRL_MODULE_CORE | L4CFG_L4_GICLK | Int | 133 | L4CFG_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| CTRL_MODULE_WKUP | WKUPAON_GICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| DCAN1 | DCAN1_FCLK | Func | 38.4 | DCAN1_SYS_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| DCAN1_ICLK | Int | 266 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| DCAN2 | DCAN2_FCLK | Func | 38.4 | DCAN2_SYS_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DCAN2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| DES3DES | DES_CLK_L3 | Int | 266 | L4SEC_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| DLL | EMIF_DLL_FCLK | Func | EMIF_DLL_FCLK | EMIF_DLL_GCLK | EMIF_DLL_GCLK | DPLL_DDR |
| DLL_AGING | FCLK | Int | 38.4 | L3INSTR_DLL_AGING_GCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| DMM | DMM_CLK | Int | 266 | EMIF_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| DPLL_DEBUG | SYSCLK | Int | 38.4 | EMU_SYS_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DSP1 | DSP1_FICLK | Int & Func | DSP_CLK | DSP1_GFCLK | DSP_GFCLK | DPLL_DSP |
| DSS | DSS_HDMI_CEC_CLK | Func | 0.032 | HDMI_CEC_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 |
| DSS_HDMI_PHY_CLK | Func | 48 | HDMI_PHY_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| DSS_CLK | Func | 192 | DSS_GFCLK | DSS_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| HDMI_CLKINP | Func | 38.4 | HDMI_DPLL_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| DSS_L3_ICLK | Int | 266 | DSS_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| VIDEO1_CLKINP | Func | 38.4 | VIDEO1_DPLL_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| VIDEO2_CLKINP | Func | 38.4 | VIDEO2_DPLL_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| DPLL_DSI1_A_CLK1 | Func | 209.3 | N/A | HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |
| VIDEO1_CLKOUT1 | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| DPLL_DSI1_B_CLK1 | Func | 209.3 | N/A | VIDEO1_CLKOUT3 | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| DPLL_DSI1_C_CLK1 | Func | 209.3 | N/A | HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |
| VIDEO1_CLKOUT3 | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| DPLL_HDMI_CLK1 | Func | 185.6 | N/A | HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |
| DSS DISPC | LCD1_CLK | Func | 209.3 | N/A | DPLL_DSI1_A_CLK1 | See DSS data in the rows above |
| DSS_CLK | ||||||
| LCD2_CLK | Func | 209.3 | N/A | DPLL_DSI1_B_CLK1 | ||
| DSS_CLK | ||||||
| LCD3_CLK | Func | 209.3 | N/A | DPLL_DSI1_C_CLK1 | ||
| DSS_CLK | ||||||
| F_CLK | Func | 209.3 | N/A | DPLL_DSI1_A_CLK1 | ||
| DPLL_DSI1_B_CLK1 | ||||||
| DPLL_DSI1_C_CLK1 | ||||||
| DSS_CLK | ||||||
| DPLL_HDMI_CLK1 | ||||||
| EFUSE_CTRL_CUST | ocp_clk | Int | 133 | CUSTEFUSE_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| sys_clk | Func | 38.4 | CUSTEFUSE_SYS_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| ELM | ELM_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| EMIF_OCP_FW | L3_CLK | Int | 266 | EMIF_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| EMIF_PHY1 | EMIF_PHY1_FCLK | Func | DDR | EMIF_PHY_GCLK | EMIF_PHY_GCLK | DPLL_DDR |
| EMIF1 | EMIF1_ICLK | Int | 266 | EMIF_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GMAC_SW | CPTS_RFT_CLK | Func | 266 | GMAC_RFT_CLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |||||
| MAIN_CLK | Int | 125 | GMAC_MAIN_CLK | GMAC_250M_CLK | DPLL_GMAC | |
| MHZ_250_CLK | Func | 250 | GMII_250MHZ_CLK | GMII_250MHZ_CLK | DPLL_GMAC | |
| MHZ_5_CLK | Func | 5 | RGMII_5MHZ_CLK | GMAC_RMII_HS_CLK | DPLL_GMAC | |
| MHZ_50_CLK | Func | 50 | RMII_50MHZ_CLK | GMAC_RMII_HS_CLK | DPLL_GMAC | |
| RMII1_MHZ_50_CLK | Func | 50 | RMII_50MHZ_CLK | GMAC_RMII_HS_CLK | DPLL_GMAC | |
| RMII2_MHZ_50_CLK | Func | 50 | RMII_50MHZ_CLK | GMAC_RMII_HS_CLK | DPLL_GMAC | |
| GPIO1 | GPIO1_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| GPIO1_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | WKUPAON_SYS_GFCLK | WKUPAON_32K_GFCLK | OSC1 | |
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| GPIO2 | GPIO2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO2_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| GPIO3 | GPIO3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO3_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| GPIO4 | GPIO4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO4_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| PIDBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | ||
| GPIO5 | GPIO5_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO5_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| PIDBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | ||
| GPIO6 | GPIO6_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO6_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| PIDBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | ||
| GPIO7 | GPIO7_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO7_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| PIDBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | ||
| GPIO8 | GPIO8_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPIO8_DBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| PIDBCLK | Func | 0.032 | GPIO_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | ||
| GPMC | GPMC_FCLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| GPU | GPU_FCLK1 | Func | GPU_CLK | GPU_CORE_GCLK | CORE_GPU_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| PER_GPU_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| GPU_GCLK | DPLL_GPU | |||||
| GPU_FCLK2 | Func | GPU_CLK | GPU_HYD_GCLK | CORE_GPU_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| PER_GPU_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| GPU_GCLK | DPLL_GPU | |||||
| GPU_ICLK | Int | 266 | GPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| HDMI PHY | DSS_HDMI_PHY_CLK | Func | 38.4 | HDMI_PHY_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| HDQ1W | HDQ1W_ICLK | Int & Func | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| HDQ1W_FCLK | Func | 12 | PER_12M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| I2C1 | I2C1_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| I2C1_FCLK | Func | 96 | PER_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| I2C2 | I2C2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| I2C2_FCLK | Func | 96 | PER_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| I2C3 | I2C3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| I2C3_FCLK | Func | 96 | PER_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| I2C4 | I2C4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| I2C4_FCLK | Func | 96 | PER_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| I2C5 | I2C5_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| I2C5_FCLK | Func | 96 | IPU_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| IEEE1500_2_OCP | PI_L3CLK | Int & Func | 266 | L3INIT_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| IPU1 | IPU1_GFCLK | Int & Func | 425.6 | IPU1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| CORE_IPU_ISS_BOOST_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |||||
| IPU2 | IPU2_GFCLK | Int & Func | 425.6 | IPU2_GFCLK | CORE_IPU_ISS_BOOST_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| IVA | IVA_GCLK | Int | IVA_GCLK | IVA_GCLK | IVA_GFCLK | DPLL_IVA |
| KBD | KBD_FCLK | Func | 0.032 | WKUPAON_SYS_GFCLK | WKUPAON_32K_GFCLK | OSC1 |
| PICLKKBD | Func | 0.032 | WKUPAON_SYS_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | ||
| KBD_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| PICLKOCP | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| L3_INSTR | L3_CLK | Int | L3_CLK | L3INSTR_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| L3_MAIN | L3_CLK1 | Int | L3_CLK | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| L3_CLK2 | Int | L3_CLK | L3INSTR_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| L4_CFG | L4_CFG_CLK | Int | 133 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| L4_PER1 | L4_PER1_CLK | Int | 133 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| L4_PER2 | L4_PER2_CLK | Int | 133 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| L4_PER3 | L4_PER3_CLK | Int | 133 | L4PER3_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| L4_WKUP | L4_WKUP_CLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| MAILBOX1 | MAILBOX1_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX2 | MAILBOX2_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX3 | MAILBOX3_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX4 | MAILBOX4_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX5 | MAILBOX5_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX6 | MAILBOX6_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX7 | MAILBOX7_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX8 | MAILBOX8_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX9 | MAILBOX9_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX10 | MAILBOX10_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX11 | MAILBOX11_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX12 | MAILBOX12_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MAILBOX13 | MAILBOX13_FLCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| McASP1 | MCASP1_AHCLKR | Func | 100 | MCASP1_AHCLKR | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP1_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP1_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP1_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP1_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP1_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP2 | MCASP2_AHCLKR | Func | 100 | MCASP2_AHCLKR | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP2_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP2_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP2_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP2_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP3 | MCASP3_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP3_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP3_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP3_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP4 | MCASP4_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP4_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP4_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP4_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP5 | MCASP5_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP5_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP5_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP5_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP5_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP6 | MCASP6_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP6_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP6_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP6_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP6_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP7 | MCASP7_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP7_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP7_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP7_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP7_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McASP8 | MCASP8_AHCLKX | Func | 100 | MCASP8_AHCLKX | DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE |
| SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |||||
| FUNC_96M_AON_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| MCASP8_FCLK | Func | 192 | MCASP8_AUX_GFCLK | PER_ABE_X1_GFCLK | DPLL_ABE | |
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| MCASP8_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| McSPI1 | SPI1_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SPI1_FCLK | Func | 48 | PER_48M_GFCLK | PER_48M_GFCLK | DPLL_PER | |
| McSPI2 | SPI2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SPI2_FCLK | Func | 48 | PER_48M_GFCLK | PER_48M_GFCLK | DPLL_PER | |
| McSPI3 | SPI3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SPI3_FCLK | Func | 48 | PER_48M_GFCLK | PER_48M_GFCLK | DPLL_PER | |
| McSPI4 | SPI4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SPI4_FCLK | Func | 48 | PER_48M_GFCLK | PER_48M_GFCLK | DPLL_PER | |
| CSI2_0 | CTRLCLK | Int & Func | 96 | LVDSRX_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| CAL_FCLK | Int & Func | 266 | CAL_GICLK | CORE_ISS_MAIN_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| L3_ICLK | CM_CORE_AON | |||||
| CSI2_1 | CTRLCLK | Int & Func | 96 | LVDSRX_96M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| CAL_FCLK | Int & Func | 266 | CAL_GICLK | CORE_ISS_MAIN_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| L3_ICLK | CM_CORE_AON | |||||
| MMC1 | MMC1_CLK_32K | Func | 0.032 | L3INIT_32K_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 |
| MMC1_FCLK | Func | 192 | MMC1_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| 128 | FUNC_256M_CLK | DPLL_PER | ||||
| MMC1_ICLK1 | Int | 266 | L3INIT_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| MMC1_ICLK2 | Int | 133 | L3INIT_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| MMC2 | MMC2_CLK_32K | Func | 0.032 | L3INIT_32K_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 |
| MMC2_FCLK | Func | 192 | MMC2_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| 128 | FUNC_256M_CLK | DPLL_PER | ||||
| MMC2_ICLK1 | Int | 266 | L3INIT_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| MMC2_ICLK2 | Int | 133 | L3INIT_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| MMC3 | MMC3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MMC3_CLK_32K | Func | 0.032 | L4PER_32K_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| MMC3_FCLK | Func | 48 | MMC3_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| 192 | ||||||
| MMC4 | MMC4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MMC4_CLK_32K | Func | 0.032 | L4PER_32K_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |
| MMC4_FCLK | Func | 48 | MMC4_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| 192 | ||||||
| MMU_EDMA | MMU1_CLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MMU_PCIESS | MMU2_CLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| MPU | MPU_CLK | Int & Func | MPU_CLK | MPU_GCLK | MPU_GCLK | DPLL_MPU |
| MPU_EMU_DBG | FCLK | Int | 38.4 | EMU_SYS_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| MPU_GCLK | DPLL_MPU | |||||
| OCMC_RAM1 | OCMC1_L3_CLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| OCMC_ROM | OCMC_L3_CLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| OCP_WP_NOC | PICLKOCPL3 | Int | 266 | L3INSTR_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| OCP2SCP1 | L4CFG1_ADAPTER_CLKIN | Int | 133 | L3INIT_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| OCP2SCP2 | L4CFG2_ADAPTER_CLKIN | Int | 133 | L4CFG_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| OCP2SCP3 | L4CFG3_ADAPTER_CLKIN | Int | 133 | L3INIT_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| PCIe_SS1 | PCIE1_PHY_WKUP_CLK | Func | 0.032 | PCIE_32K_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | RTC Oscillator |
| PCIe_SS1_FICLK | Int | 266 | PCIE_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| PCIEPHY_CLK | Func | 2500 | PCIE_PHY_GCLK | PCIE_PHY_GCLK | APLL_PCIE | |
| PCIEPHY_CLK_DIV | Func | 1250 | PCIE_PHY_DIV_GCLK | PCIE_PHY_DIV_GCLK | APLL_PCIE | |
| PCIE1_REF_CLKIN | Func | 34.3 | PCIE_REF_GFCLK | CORE_USB_OTG_SS_LFPS_TX_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| PCIE1_PWR_CLK | Func | 38.4 | PCIE_SYS_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| PCIe_SS2 | PCIE2_PHY_WKUP_CLK | Func | 0.032 | PCIE_32K_GFCLK | FUNC_32K_CLK | RTC Oscillator |
| PCIe_SS2_FICLK | Func | 266 | PCIE_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| PCIEPHY_CLK | Func | 2500 | PCIE_PHY_GCLK | PCIE_PHY_GCLK | APLL_PCIE | |
| PCIEPHY_CLK_DIV | Func | 1250 | PCIE_PHY_DIV_GCLK | PCIE_PHY_DIV_GCLK | APLL_PCIE | |
| PCIE2_REF_CLKIN | Func | 34.3 | PCIE_REF_GFCLK | CORE_USB_OTG_SS_LFPS_TX_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| PCIE2_PWR_CLK | Func | 38.4 | PCIE_SYS_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| PRCM_MPU | 32K_CLK | Func | 0.032 | FUNC_32K_CLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 |
| SYS_CLK | Func | 38.4 | WKUPAON_ICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| PWMSS1 | PWMSS1_GICLK | Int & Func | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| PWMSS2 | PWMSS2_GICLK | Int & Func | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| PWMSS3 | PWMSS3_GICLK | Int & Func | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| QSPI | QSPI_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| QSPI_FCLK | Func | 128 | QSPI_GFCLK | FUNC_256M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| PER_QSPI_CLK | DPLL_PER | |||||
| RNG | RNG_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4SEC_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| RTC_SS | RTC_ICLK | Int | 133 | RTC_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| RTC_FCLK | Func | RTC_FCLK | RTC_AUX_CLK | SYS_32K | RTC Oscillator | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 | ||||
| SAR_ROM | PRCM_ROM_CLOCK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SATA | SATA_FICLK | Int | 266 | L3INIT_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SATA_PMALIVE_FCLK | Func | 48 | L3INIT_48M_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER | |
| REF_CLK | Func | 38 | SATA_REF_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| SDMA | SDMA_FCLK | Int & Func | 266 | DMA_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SHA2MD51 | SHAM_1_CLK | Int | 266 | L4SEC_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SHA2MD52 | SHAM_2_CLK | Int | 266 | L4SEC_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SL2 | IVA_GCLK | Int | IVA_GCLK | IVA_GCLK | IVA_GFCLK | DPLL_IVA |
| SMARTREFLEX_CORE | MCLK | Int | 133 | COREAON_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SYSCLK | Func | 38.4 | WKUPAON_ICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| SMARTREFLEX_DSP | MCLK | Int | 133 | COREAON_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SYSCLK | Func | 38.4 | WKUPAON_ICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| SMARTREFLEX_GPU | MCLK | Int | 133 | COREAON_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SYSCLK | Func | 38.4 | WKUPAON_ICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| SMARTREFLEX_IVAHD | MCLK | Int | 133 | COREAON_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SYSCLK | Func | 38.4 | WKUPAON_ICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| SMARTREFLEX_MPU | MCLK | Int | 133 | COREAON_L4_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| SYSCLK | Func | 38.4 | WKUPAON_ICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| SPINLOCK | SPINLOCK_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4CFG_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER1 | TIMER1_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| TIMER1_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER1_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER2 | TIMER2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER2_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER2_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER3 | TIMER3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER3_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER3_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER4 | TIMER4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER4_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER4_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER5 | TIMER5_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER5_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER5_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| CLKOUTMUX[0] | CLKOUTMUX[0] | |||||
| TIMER6 | TIMER6_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER6_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER6_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| CLKOUTMUX[0] | CLKOUTMUX[0] | |||||
| TIMER7 | TIMER7_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER7_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER7_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| CLKOUTMUX[0] | CLKOUTMUX[0] | |||||
| TIMER8 | TIMER8_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER8_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER8_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| CLKOUTMUX[0] | CLKOUTMUX[0] | |||||
| TIMER9 | TIMER9_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER9_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER9_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER10 | TIMER10_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER10_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER10_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER11 | TIMER11_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER11_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER11_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER12 | TIMER12_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| TIMER12_FCLK | Func | 0.032 | OSC_32K_CLK | RC_CLK | RC oscillator | |
| TIMER13 | TIMER13_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER3_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER13_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER13_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER14 | TIMER14_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER3_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER14_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER14_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER15 | TIMER15_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER3_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER15_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER15_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TIMER16 | TIMER16_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER3_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TIMER16_FCLK | Func | 100 | TIMER16_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| FUNC_32K_CLK | OSC1 | |||||
| RTC Oscillator | ||||||
| SYS_CLK2 | OSC2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK0 | XREF_CLK0 | |||||
| XREF_CLK1 | XREF_CLK1 | |||||
| XREF_CLK2 | XREF_CLK2 | |||||
| XREF_CLK3 | XREF_CLK3 | |||||
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| VIDEO1_CLK | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| HDMI_CLK | DPLL_HDMI | |||||
| TPCC | TPCC_GCLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TPTC1 | TPTC0_GCLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| TPTC2 | TPTC1_GCLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| UART1 | UART1_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART1_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART1_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART2 | UART2_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART2_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART2_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART3 | UART3_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART3_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART3_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART4 | UART4_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART4_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART4_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART5 | UART5_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART5_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART5_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART6 | UART6_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART6_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART6_ICLK | Int | 266 | IPU_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART7 | UART7_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART7_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART7_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART8 | UART8_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART8_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART8_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART9 | UART9_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART9_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART9_ICLK | Int | 266 | L4PER2_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| UART10 | UART10_FCLK | Func | 48 | UART10_GFCLK | FUNC_192M_CLK | DPLL_PER |
| UART10_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| USB1 | USB1_MICLK | Int | 266 | L3INIT_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| USB3PHY_REF_CLK | Func | 34.3 | USB_LFPS_TX_GFCLK | CORE_USB_OTG_SS_LFPS_TX_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |
| USB2PHY1_TREF_CLK | Func | 38.4 | USB_OTG_SS_REF_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| USB2PHY1_REF_CLK | Func | 960 | L3INIT_960M_GFCLK | L3INIT_960_GFCLK | DPLL_USB | |
| USB2 | USB2_MICLK | Int | 266 | L3INIT_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| USB2PHY2_TREF_CLK | Func | 38.4 | USB_OTG_SS_REF_CLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 | |
| USB2PHY2_REF_CLK | Func | 960 | L3INIT_960M_GFCLK | L3INIT_960_GFCLK | DPLL_USB | |
| USB_PHY1_CORE | USB2PHY1_WKUP_CLK | Func | 0.032 | COREAON_32K_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 |
| USB_PHY2_CORE | USB2PHY2_WKUP_CLK | Func | 0.032 | COREAON_32K_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 |
| USB_PHY3_CORE | USB3PHY_WKUP_CLK | Func | 0.032 | COREAON_32K_GFCLK | SYS_CLK1/610 | OSC1 |
| VCP1 | VCP1_CLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| VCP2 | VCP2_CLK | Int | 266 | L3MAIN1_L3_GICLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| VIP1 | L3_CLK_PROC_CLK | Int & Func | 266 | VIP1_GCLK | CORE_X2_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| CORE_ISS_MAIN_CLK | DPLL_CORE | |||||
| VPE | L3_CLK_PROC_CLK | Int & Func | 300 | VPE_GCLK | CORE_ISS_MAIN_CLK | DPLL_CORE |
| VIDEO1_CLKOUT4 | DPLL_VIDEO1 | |||||
| WD_TIMER1 | PIOCPCLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| PITIMERCLK | Func | 0.032 | OSC_32K_CLK | RC_CLK | RC oscillator | |
| WD_TIMER2 | WD_TIMER2_ICLK | Int | 38.4 | WKUPAON_GICLK | SYS_CLK1 | OSC1 |
| DPLL_ABE_X2_CLK | DPLL_ABE | |||||
| WD_TIMER2_FCLK | Func | 0.032 | WKUPAON_SYS_GFCLK | WKUPAON_32K_GFCLK | RTC Oscillator | |
5.6 Power Consumption Summary
NOTE
Maximum power consumption for this SoC depends on the specific use conditions for the end system. Contact your TI representative for assistance in estimating maximum power consumption for the end system use case.
5.7 Electrical Characteristics
NOTE
The data specified in Section 5.7.1 through Section 5.7.14 are subject to change.
NOTE
The interfaces or signals described in Section 5.7.1 through Section 5.7.14 correspond to the interfaces or signals available in multiplexing mode 0 (Function 1).
All interfaces or signals multiplexed on the balls described in these tables have the same DC electrical characteristics, unless multiplexing involves a PHY/GPIO combination in which case different DC electrical characteristics are specified for the different multiplexing modes (Functions).
5.7.1 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-10 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for LVCMOS DDR Buffers.
NOTE
For more information on the I/O cell configurations (i[2:0], sr[1:0]), see the Chapter Control Module of the Device TRM.
Table 5-10 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0 (Single-Ended Signals): ddr1_d[31:0], ddr1_a[15:0], ddr1_dqm[3:0], ddr1_ba[2:0], ddr1_csn[1:0], ddr1_cke, ddr1_odt[1:0], ddr1_casn, ddr1_rasn, ddr1_wen, ddr1_rst, ddr1_ecc_d[7:0], ddr1_dqm_ecc; | ||||||
| Balls: AH23 / AB16 / AG22 / AE20 / AC17 / AC18 / AF20 /AH21 / AG21 / AF17 / AE18 / AB18 / AD20 / AC19 / AC20 / AB19 / AF21 / AH22 / AG23 / AE21 / AF22 / AE22 / AD21 / AD22 / AC21 / AF18 / AE17 / AD18 / AF25 / AF26 / AG26 / AH26 / AF24 / AE24 / AF23 / AE23 / AC23 / AF27 / AG27 / AF28 / AE26 / AC25 / AC24 / AD25 / V20 / W20 / AB28 / AC28 / AC27 / Y19 / AB27 / Y20 / AA23 / Y22 / Y23 / AA24 / Y24 / AA26 / AA25 / AA28 / W22 / V23 / W19 / W23 / Y25 / V24 / V25 / Y26 / AD23 / AB23 / AC26 / AA27 / V26; | ||||||
| Driver Mode | ||||||
| VOH | High-level output threshold (IOH = 0.1 mA) | 0.9*VDDS | V | |||
| VOL | Low-level output threshold (IOL = 0.1 mA) | 0.1*VDDS | V | |||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 3 | pF | |||
| ZO | Output impedance (drive strength) | l[2:0] = 000 (Imp80) | 80 | Ω | ||
| l[2:0] = 001 (Imp60) | 60 | |||||
| l[2:0] = 010 (Imp48) | 48 | |||||
| l[2:0] = 011 (Imp40) | 40 | |||||
| l[2:0] = 100 (Imp34) | 34 | |||||
| Single-Ended Receiver Mode | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input threshold | DDR3/DDR3L | VREF + 0.1 | VDDS + 0.2 | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input threshold | DDR3/DDR3L | –0.2 | VREF – 0.1 | V | |
| VCM | Input common-mode voltage | VREF – 10%vdds | VREF + 10%vdds | V | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 3 | pF | |||
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0 (Differential Signals): ddr1_dqs[3:0], ddr1_dqsn[3:0], ddr1_ck, ddr1_nck, ddr1_dqs_ecc, ddr1_dqsn_ecc | ||||||
| Bottom Balls: AH25 / AG25 / AE27 / AE28 / AD27 / AD28 / Y28 / Y27 / V27 / V28 / AG24 / AH24 | ||||||
| Driver Mode | ||||||
| VOH | High-level output threshold (IOH = 0.1 mA) | 0.9 × VDDS | V | |||
| VOL | Low-level output threshold (IOL = 0.1 mA) | 0.1 × VDDS | V | |||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 3 | pF | |||
| ZO | Output impedance (drive strength) | l[2:0] = 000 (Imp80) | 80 | Ω | ||
| l[2:0] = 001 (Imp60) | 60 | |||||
| l[2:0] = 010 (Imp48) | 48 | |||||
| l[2:0] = 011 (Imp40) | 40 | |||||
| l[2:0] = 100 (Imp34) | 34 | |||||
| Single-Ended Receiver Mode | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input threshold | DDR3/DDR3L | VREF + 0.1 | VDDS + 0.2 | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input threshold | DDR3/DDR3L | –0.2 | VREF – 0.1 | V | |
| VCM | Input common-mode voltage | VREF – 10%vdds | VREF + 10%vdds | V | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 3 | pF | |||
| Differential Receiver Mode | ||||||
| VSWING | Input voltage swing | DDR3/DDR3L | 0.2 | vdds + 0.4 | V | |
| VCM | Input common-mode voltage | VREF – 10%vdds | VREF + 10%vdds | V | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 3 | pF | |||
- VDDS in this table stands for corresponding power supply (i.e. vdds_ddr1). For more information on the power supply name and the corresponding ball, see Table 4-2, POWER [10] column.
- VREF in this table stands for corresponding Reference Power Supply (i.e. ddr1_vref0). For more information on the power supply name and the corresponding ball, see Table 4-2, POWER [10] column.
5.7.2 HDMIPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
The HDMIPHY DC Electrical Characteristics are compliant with the HDMI 1.4a specification and are not reproduced here.
5.7.3 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-11 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C Buffers.
NOTE
For more information on the I/O cell configurations, see the Control Module section of the Device TRM.
Table 5-11 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0: i2c2_scl; i2c1_scl; i2c1_sda; i2c2_sda; | ||||||
| Balls: F17 / C20 / C21 / C25 | ||||||
| I2C Standard Mode – 1.8 V | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.7*VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.3*VDDS | V | |||
| Vhys | Hysteresis | 0.1*VDDS | V | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin with an input voltage between 0.1*VDDS to 0.9*VDDS | 12 | µA | |||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 12 | µA | |||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 10 | pF | |||
| VOL3 | Output low-level threshold open-drain at 3-mA sink current | 0.2*VDDS | V | |||
| IOLmin | Low-level output current @VOL=0.2*VDDS | 3 | mA | |||
| tOF | Output fall time from VIHmin to VILmax with a bus capacitance CB from 5 pF to 400 pF | 250 | ns | |||
| I2C Fast Mode – 1.8 V | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.7*VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.3*VDDS | V | |||
| Vhys | Hysteresis | 0.1*VDDS | V | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin with an input voltage between 0.1*VDDS to 0.9*VDDS | 12 | µA | |||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 12 | µA | |||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 10 | pF | |||
| VOL3 | Output low-level threshold open-drain at 3-mA sink current | 0.2*VDDS | V | |||
| IOLmin | Low-level output current @VOL=0.2*VDDS | 3 | mA | |||
| tOF | Output fall time from VIHmin to VILmax with a bus capacitance CB from 10 pF to 400 pF | 20+0.1*Cb | 250 | ns | ||
| I2C Standard Mode – 3.3 V | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.7*VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.3*VDDS | V | |||
| Vhys | Hysteresis | 0.05*VDDS | V | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin with an input voltage between 0.1*VDDS to 0.9*VDDS | 31 | 80 | µA | ||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 31 | 80 | µA | ||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 10 | pF | |||
| VOL3 | Output low-level threshold open-drain at 3-mA sink current | 0.4 | V | |||
| IOLmin | Low-level output current @VOL=0.4V | 3 | mA | |||
| IOLmin | Low-level output current @VOL=0.6V for full drive load (400pF/400KHz) | 6 | mA | |||
| tOF | Output fall time from VIHmin to VILmax with a bus capacitance CB from 5 pF to 400 pF | 250 | ns | |||
| I2C Fast Mode – 3.3 V | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.7*VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.3*VDDS | V | |||
| Vhys | Hysteresis | 0.05*VDDS | V | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin with an input voltage between 0.1*VDDS to 0.9*VDDSS | 31 | 80 | µA | ||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 31 | 80 | µA | ||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 10 | pF | |||
| VOL3 | Output low-level threshold open-drain at 3-mA sink current | 0.4 | V | |||
| IOLmin | Low-level output current @VOL=0.4V | 3 | mA | |||
| IOLmin | Low-level output current @VOL=0.6V for full drive load (400pF/400KHz) | 6 | mA | |||
| tOF | Output fall time from VIHmin to VILmax with a bus capacitance CB from 10 pF to 200 pF (Proper External Resistor Value should be used as per I2C spec) | 20+0.1*Cb | 250 | ns | ||
| Output fall time from VIHmin to VILmax with a bus capacitance CB from 300 pF to 400 pF (Proper External Resistor Value should be used as per I2C spec) | 40 | 290 | ||||
5.7.4 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-12 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for IQ1833 Buffers.
Table 5-12 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0: tclk; | ||||||
| Balls: E20; | ||||||
| 1.8-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold (Does not meet JEDEC VIH) | 0.75 * VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold (Does not meet JEDEC VIL) | 0.25 * VDDS | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 100 | mV | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 2 | 11 | µA | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 1 | pF | |||
| 3.3-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold (Does not meet JEDEC VIH) | 2.0 | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold (Does not meet JEDEC VIL) | 0.6 | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 400 | mV | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 5 | 11 | µA | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 1 | pF | |||
5.7.5 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-13 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for IHHV1833 Buffers.
Table 5-13 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0: porz / rtc_iso / rtc_porz / wakeup [3:0]; | ||||||
| Balls: F22 / AF14 / AB17 / AD17 / AC17 / AB16 / AC16; | ||||||
| 1.8-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 1.2(1) | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.4 | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 40 | mV | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 0.02 | 1 | µA | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 1 | pF | |||
| 3.3-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 1.2(1) | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.4 | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 40 | mV | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 5 | 8 | µA | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 1 | pF | |||
- The IHHV1833 buffer exists in the dual-voltage IO logic that can be powered by either 1.8V or 3.3V provided by vddshv3. However, the vddshv3 supply is only used for input protection circuitry, not for logic functionality. The logic in this buffer operates entirely on the vdds18v supply. Therefore, IHHV control is asserted whenever the input is low and vdds18v is valid.
5.7.6 LVCMOS OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-14 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for LVCMOS OSC Buffers.
Table 5-14 LVCMOS OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0: rtc_osc_xi_clkin32 / rtc_osc_xo; | ||||||
| Balls: AE14 / AD14; | ||||||
| 1.8-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.65 * VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.35 * VDDS | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 150 | mV | |||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 3 | pF | |||
5.7.7 LVCMOS CSI2 DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-15 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for LVSMOS CSI2 Buffers.
Table 5-15 LVCMOS CSI2 DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signals MUXMODE0 : csi2_0_dx[4:0]; csi2_0_dy[4:0]; csi2_1_dx[2:0]; csi2_1_dy[2:0]; | |||||
| Bottom Balls: AE1 / AD2 / AF1 / AE2 / AF2 / AF3 / AH4 / AG4 / AH3 / AG3 / AG5 / AH5 / AG6 / AH6 / AH7 / AG7 | |||||
| MIPI D-PHY Mode Low-Power Receiver (LP-RX) | |||||
| VIH | Input high-level voltage | 880 | 1350 | mV | |
| VIL | Input low-level voltage | 550 | mV | ||
| VITH | Input high-level threshold | 880 | mV | ||
| VITL | Input low-level threshold | 550 | mV | ||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis | 25 | mV | ||
| MIPI D-PHY Mode Ultralow Power Receiver (ULP-RX) | |||||
| VIH | Input high-level voltage | 880 | mV | ||
| VIL | Input low-level voltage | 300 | mV | ||
| VITH | Input high-level threshold | 880 | mV | ||
| VITL | Input low-level threshold | 300 | mV | ||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis | 25 | mV | ||
| MIPI D-PHY Mode High-Speed Receiver (HS-RX) | |||||
| VIDTH | Differential input high-level threshold | 70 | mV | ||
| VIDTL | Differential input low-level threshold | –70 | mV | ||
| VIDMAX | Maximum differential input voltage | 270 | mV | ||
| VIHHS | Single-ended input high voltage | 460 | mV | ||
| VILHS | Single-ended input low voltage | –40 | mV | ||
| VCMRXDC | Differential input common-mode voltage | 70 | 330 | mV | |
| ZID | Differential input impedance | 80 | 100 | 125 | Ω |
- VITH is the voltage at which the receiver is required to detect a high state in the input signal.
- VITL is the voltage at which the receiver is required to detect a low state in the input signal. VITL is larger than the maximum single-ended line high voltage during HS transmission. Therefore, both low-power (LP) receivers will detect low during HS signaling.
- To reduce noise sensitivity on the received signal, the LP receiver is required to incorporate a hysteresis, VHYST. VHYST is the difference between the VITH threshold and the VITL threshold.
- VITL is the voltage at which the receiver is required to detect a low state in the input signal. Specification is relaxed for detecting 0 during ultralow power (ULP) state. The LP receiver is not required to detect HS single-ended voltage as 0 in this state.
- Excluding possible additional RF interference of 200 mVPP beyond 450 MHz.
- This value includes a ground difference of 50 mV between the transmitter and the receiver, the static common-mode level tolerance and variations below 450 MHz.
- This number corresponds to the VODMAX transmitter.
- Common mode is defined as the average voltage level of X and Y: VCMRX = (VX + VY) / 2.
- Common mode ripple may be due to tR or tF and transmission line impairments in the PCB.
- For more information regarding the pin name (or ball name) and corresponding signal name, see Table 4-7, CSI 2 Signal Descriptions.
5.7.8 BMLB18 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-16 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for BMLB18 Buffers.
Table 5-16 BMLB18 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0: mlbp_dat_n / mlbp_dat_p / mlbp_sig_n / mlbp_sig_p / mlbp_clk_n / mlbp_clk_p; | ||||||
| Balls: AB2 / AB1 / AA2 / AA1 / AC2 / AC1; | ||||||
| 1.8-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH/VIL | Input high-level threshold | VCM ± 50mV | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | NONE | mV | |||
| VOD | Differential output voltage (measured with 50ohm resistor between PAD and PADN) | 300 | 500 | mV | ||
| VCM | Common mode output voltage | 1 | 1.5 | V | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 4 | pF | |||
5.7.9 BC1833IHHV Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-17 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for BC1833IHHV Buffers.
Table 5-17 BC1833IHHV Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in MUXMODE 0: on_off; | ||||||
| Balls: Y11; | ||||||
| 1.8-V Mode | ||||||
| VOH | Output high-level threshold (IOH = 2 mA) | VDDS-0.45 | V | |||
| VOL | Output low-level threshold (IOL = 2 mA) | 0.45 | V | |||
| IDRIVE | Pin Drive strength at PAD Voltage = 0.45V or VDDS-0.45V | 6 | mA | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 6 | 12 | µA | ||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 6 | µA | |||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 4 | pF | |||
| 3.3-V Mode | ||||||
| VOH | Output high-level threshold (IOH =100µA) | VDDS-0.2 | V | |||
| VOL | Output low-level threshold (IOL = 100µA) | 0.2 | V | |||
| IDRIVE | Pin Drive strength at PAD Voltage = 0.45V or VDDS-0.45V | 6 | mA | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 60 | µA | |||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 60 | µA | |||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 4 | pF | |||
5.7.10 USBPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
NOTE
USB1 instance is compliant with the USB3.0 SuperSpeed Transmitter and Receiver Normative Electrical Parameters as defined in the USB3.0 Specification Rev 1.0 dated Jun 6, 2011.
NOTE
USB1 and USB2 Electrical Characteristics are compliant with USB2.0 Specification Rev 2.0 dated April 27, 2000 including ECNs and Errata as applicable.
5.7.11 Dual Voltage SDIO1833 DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-18 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for SDIO1833 Buffers.
Table 5-18 Dual Voltage SDIO1833 DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Names in Mode 0: mmc1_clk, mmc1_cmd, mmc1_data[3:0] | |||||||
| Bottom Balls: W6 / Y6 / AA6 / Y4 / AA5 / Y3 | |||||||
| 1.8-V Mode | |||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 1.27 | V | ||||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.58 | V | ||||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 50 (2) | mV | ||||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 30 | µA | ||||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 30 | µA | ||||
| IIN with pulldown enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pulldown enabled measured when PAD = VDDS | 50 | 120 | 210 | µA | ||
| IIN with pullup enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pullup enabled measured when PAD = 0 | 60 | 120 | 200 | µA | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 5 | pF | ||||
| VOH | Output high-level threshold (IOH = 2 mA) | 1.4 | V | ||||
| VOL | Output low-level threshold (IOL = 2 mA) | 0.45 | V | ||||
| 3.3-V Mode | |||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.625 × VDDS | V | ||||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.25 × VDDS | V | ||||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 40 (2) | mV | ||||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 110 | µA | ||||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 110 | µA | ||||
| IIN with pulldown enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pulldown enabled measured when PAD = VDDS | 40 | 100 | 290 | µA | ||
| IIN with pullup enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pullup enabled measured when PAD = 0 | 10 | 100 | 290 | µA | ||
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 5 | pF | ||||
| VOH | Output high-level threshold (IOH = 2 mA) | 0.75 × VDDS | V | ||||
| VOL | Output low-level threshold (IOL = 2 mA) | 0.125 × VDDS | V | ||||
5.7.12 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-19 summarizes the DC electrical characteristics for Dual Voltage LVCMOS Buffers.
Table 5-19 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.8-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 0.65*VDDS | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.35*VDDS | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 100 | mV | |||
| VOH | Output high-level threshold (IOH = 2 mA) | VDDS-0.45 | V | |||
| VOL | Output low-level threshold (IOL = 2 mA) | 0.45 | V | |||
| IDRIVE | Pin Drive strength at PAD Voltage = 0.45V or VDDS-0.45V | 6 | mA | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 16 | µA | |||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 16 | µA | |||
| IIN with pulldown enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pulldown enabled measured when PAD = VDDS | 50 | 120 | 210 | µA | |
| IIN with pullup enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pullup enabled measured when PAD = 0 | 60 | 120 | 200 | µA | |
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 4 | pF | |||
| ZO | Output impedance (drive strength) | 40 | Ω | |||
| 3.3-V Mode | ||||||
| VIH | Input high-level threshold | 2 | V | |||
| VIL | Input low-level threshold | 0.8 | V | |||
| VHYS | Input hysteresis voltage | 200 | mV | |||
| VOH | Output high-level threshold (IOH = 100 µA) | VDDS-0.2 | V | |||
| VOL | Output low-level threshold (IOL = 100 µA) | 0.2 | V | |||
| IDRIVE | Pin Drive strength at PAD Voltage = 0.45V or VDDS-0.45V | 6 | mA | |||
| IIN | Input current at each I/O pin | 65 | µA | |||
| IOZ | IOZ(IPAD Current) for BIDI cell. This current is contributed by the tristated driver leakage + input current of the Rx + weak pullup/pulldown leakage. PAD is swept from 0 to VDDS and the Max(I(PAD)) is measured and is reported as IOZ | 65 | µA | |||
| IIN with pulldown enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pulldown enabled measured when PAD = VDDS | 40 | 100 | 200 | µA | |
| IIN with pullup enabled | Input current at each I/O pin with weak pullup enabled measured when PAD = 0 | 10 | 100 | 290 | µA | |
| CPAD | Pad capacitance (including package capacitance) | 4 | pF | |||
| ZO | Output impedance (drive strength) | 40 | Ω | |||
5.7.13 SATAPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
NOTE
The SATA module is compliant with the electrical parameters specified in the SATA-IO SATA Specification, Revision 3.2, August 7, 2013.
5.7.14 SERDES DC Electrical Characteristics
NOTE
The PCIe interfaces are compliant with the electrical parameters specified in PCI Express® Base Specification Revision 3.0.
NOTE
USB1 instance is compliant with the USB3.0 SuperSpeed Transmitter and Receiver Normative Electrical Parameters as defined in the USB3.0 Specification Rev 1.0 dated Jun 6, 2011.
5.8 Thermal Characteristics
For reliability and operability concerns, the maximum junction temperature of the Device has to be at or below the TJ value identified in Table 5-4, Recommended Operating Conditions.
It is recommended to perform thermal simulations at the system level with the worst case device power consumption.
5.8.1 Package Thermal Characteristics
Table 5-20 provides the thermal resistance characteristics for the package used on this device.
NOTE
Power dissipation of 1.5 W and an ambient temperature of 85°C is assumed for ZBO package.
Table 5-20 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | °C/W(1) | AIR FLOW (m/s)(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | RΘJC | Junction-to-case | 0.41 | N/A |
| T2 | RΘJB | Junction-to-board | 4.74 | N/A |
| T3 | RΘJA | Junction-to-free air | 11.9 | 0 |
| T4 | Junction-to-moving air | 8.9 | 1 | |
| T5 | 8.0 | 2 | ||
| T6 | 7.4 | 3 | ||
| T7 | ΨJT | Junction-to-package top | 0.22 | 0 |
| T8 | 0.22 | 1 | ||
| T9 | 0.22 | 2 | ||
| T10 | 0.23 | 3 | ||
| T11 | ΨJB | Junction-to-board | 4.12 | 0 |
| T12 | 3.73 | 1 | ||
| T13 | 3.59 | 2 | ||
| T14 | 3.48 | 3 |
- These measurements were conducted in a JEDEC defined 2S2P system (with the exception of the Theta JC [RΘJC] measurement, which was conducted in a JEDEC defined 1S0P system) and will change based on environment as well as application. For more information, see these EIA/JEDEC standards:
- JESD51-2, Integrated Circuits Thermal Test Method Environment Conditions - Natural Convection (Still Air)
- JESD51-3, Low Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages
- JESD51-7, High Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages
- JESD51-9, Test Boards for Area Array Surface Mount Packages
- m/s = meters per second
5.9 Power Supply Sequences
This section describes the power-up and power-down sequence required to ensure proper device operation. The power supply names described in this section comprise a superset of a family of compatible devices. Some members of this family will not include a subset of these power supplies and their associated device modules. Refer to the Section 4.2, Ball Characteristics of the Section 4, Terminal Configuration and Functions to determine which power supplies are applicable.
NOTE
RTC only mode is not supported feature.
Figure 5-2 and Figure 5-3 describe the device Power Sequencing when RTC-mode is NOT used.
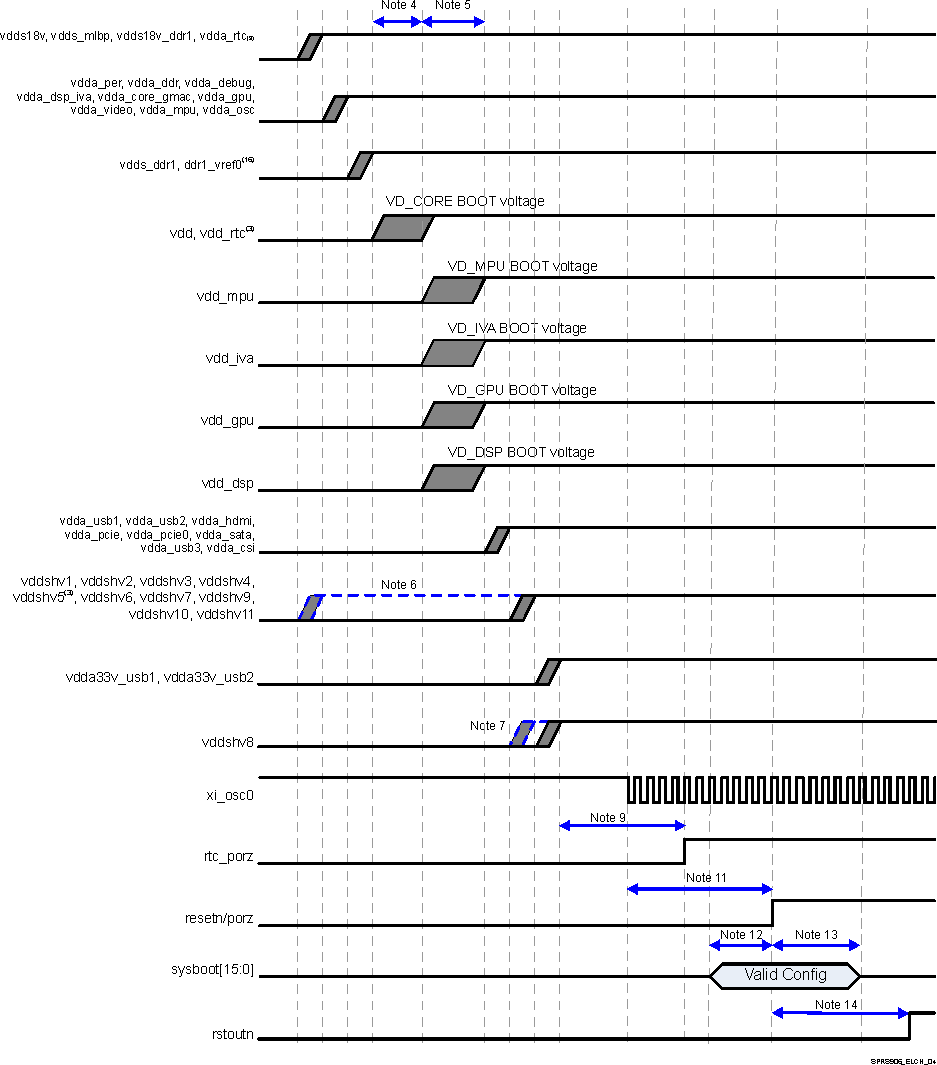 Figure 5-2 Power-Up Sequencing
Figure 5-2 Power-Up Sequencing
- Grey shaded areas are windows where it is valid to ramp the voltage rail.
- Blue dashed lines are not valid windows but show alternate ramp possibilities based on the associated note.
- RTC-only mode is not used and the following combinations are approved:
- vdda_rtc can be combined with vdds18v
- vdd_rtc can be combined with vdd
- vddshv5 can be combined with other 1.8-V or 3.3-V vddshvn rails.
If combinations listed above are not followed then sequencing for these 3 voltage rails should follow the RTC mode timing requirements. When using RTC mode timing:
- vdda_rtc rises coincident with, or before, the 1.8-V interface supplies (such as vdds18v).
- vdd_rtc rises coincident with vdd, or it may rise earlier. If rising earlier, it must rise after the 1.8-V interface supplies.
- vddshv5 rises coincident with the other vddshvn rails (of the same voltage) or it can rise about the same time as the 1.8-V PHY supplies (such as vdd_usb1).
- vdd must ramp before or at the same time as vdd_mpu, vdd_gpu, vdd_dsp and vdd_iva.
- vdd_mpu, vdd_gpu, vdd_dsp, vdd_iva can be ramped at the same time or can be staggered.
- If any of the vddshv[1-7,9-11] rails (not including vddshv8) are used as 1.8-V only, then these rails can be combined with vdds18v.
- vddshv8 is separated out to show support for dual voltage. If single voltage is used then vddshv8 can be combined with other vddshvn rails but vddshv8 must ramp after vdd.
- vdds and vdda rails must not be combined together, with the one exception of vdda_rtc when RTC-mode is not supported.
- Pulse duration: rtc_porz must remain low 1ms after vdda_rtc, vddshv5, and vdd_rtc are ramped and stable.
- The SYS_32K source must be stable and at a valid frequency 1ms prior to de-asserting rtc_porz high.
- Pulse duration: resetn/porz must remain low a minimum of 12P(15) after xi_osc0 is stable and at a valid frequency. resetn/porz must also remain low until all supply rails are valid and stable.
- Setup time: sysboot[15:0] pins must be valid 2P(15) before porz is de-asserted high.
- Hold time: sysboot[15:0] pins must be valid 15P(15) after porz is de-asserted high.
- resetn to rstoutn delay is 2 ms.
- P = 1/(SYS_CLK1/610) frequency in ns.
- ddr1_vref0 may rise coincident with vdds_ddr1 or at a later time. However, it must be valid before porz rising.
- Grey shaded areas are windows where it is valid to ramp the voltage rail.
- Blue dashed lines are not valid windows but show alternate ramp possibilities based on the associated note.
- xi_osc0 can be turned off anytime after porz assertion and must be turned off before vdda_osc voltage rail is shutdown.
- RTC-only mode is not used and the following combinations are approved:
- vdda_rtc can be combined with vdds18v
- vdd_rtc can be combined with vdd
- vddshv5 can be combined with other 1.8-V or 3.3-V vddshvn rails
If combinations listed above are not followed then sequencing for these 3 voltage rails should follow the RTC mode timing requirements. When using RTC mode timing:
- vdda_rtc falls coincident with, or later than, the 1.8-V interface supplies (such as vdds18v).
- vdd_rtc falls coincident with vdd, or it may fall later. If falling later, it must fall before, or coincident with, the 1.8-V interface supplies.
- vddshv5 falls coincident with the other vddshvn rails (of the same voltage) or it can fall about the same time as the 1.8-V PHY supplies (such as vdd_usb1).
- vdd_mpu, vdd_gpu, vdd_dsp, vdd_iva can be ramped at the same time or can be staggered.
- vdd must ramp after or at the same time as vdd_mpu, vdd_gpu, vdd_dsp and vdd_iva
- If any of the vddshv[1-7,9-11] rails (not including vddshv8) are used as 1.8 V only, then these rails can be combined with vdds18v.
- vddshv[1-7,9-11] is allowed to ramp down at either of the two points shown in the timing diagram in either 1.8-V mode or in 3.3-V mode.
- If vddshv[1-7,9-11] ramps down at the later time in the diagram then the board design must guarantee that the vddshv[1-7,9-11] rail is never higher than 2 V above the vdds18v rail. - vddshv8 is separated out to show support for dual voltage. If a dedicated LDO/supply source is used for vddshv8, then vddshv8 ramp down should occur at one of the two earliest points in the timing diagram. If vddshv8 is powered by the same supply source as the other vddshv[1-7,9-11] rails, then it is allowed to ramp down at either of the last two points in the timing diagram.
- The 1.8-V vdda_* supplies can either ramp down at the earlier time period shown or can be delayed to ramp down after the core supplies coincident with the vdds18v supply as long as porz is asserted (low) during the power down sequence.
- The power down sequence shown is the most general case and is always valid. An accelerated power down sequence is also available but is only valid when porz is asserted (low). This accelerated power down sequence has been implemented in the companion PMIC that is recommended for use with this SOC. The accelerated sequence has porz go low first, then all 3.3-V supplies simultaneously second, core supplies, DDR supplies and DDR references simultaneously third and all 1.8-V supplies simultaneously last.
- ddr1_vref0 may fall coincident with vdds_ddr1, or at a prior time but after porz is asserted low.
- Ramped Down is defined as reaching a voltage level of no more than 0.6 V.
Figure 5-4 describes vddshv[1-7,9-11] Supplies Falling Before vdds18v Supplies Delta.
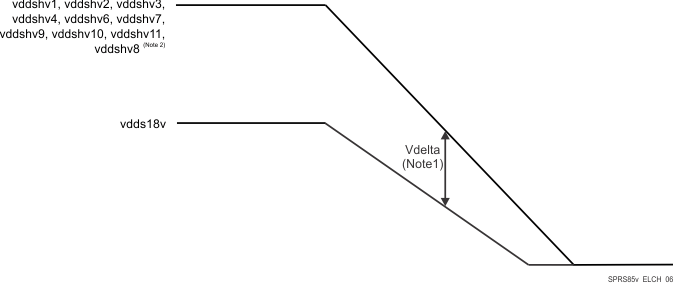 Figure 5-4 vddshv* Supplies Falling After vdds18v Supplies Delta
Figure 5-4 vddshv* Supplies Falling After vdds18v Supplies Delta
- Vdelta MAX = 2 V
- If vddshv8 is powered by the same supply source as the other vddshv[1-7,9-11] rails.