SPRS982H December 2016 – December 2019 AM5746 , AM5748 , AM5749
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Pin Diagram
- 4.2 Pin Attributes
- 4.3
Signal Descriptions
- 4.3.1 VIP
- 4.3.2 DSS
- 4.3.3 HDMI
- 4.3.4 EMIF
- 4.3.5 GPMC
- 4.3.6 Timer
- 4.3.7 I2C
- 4.3.8 HDQ1W
- 4.3.9 UART
- 4.3.10 McSPI
- 4.3.11 QSPI
- 4.3.12 McASP
- 4.3.13 USB
- 4.3.14 SATA
- 4.3.15 PCIe
- 4.3.16 DCAN and MCAN
- 4.3.17 GMAC_SW
- 4.3.18 MLB
- 4.3.19 eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 4.3.20 GPIO
- 4.3.21 KBD
- 4.3.22 PWM
- 4.3.23 PRU-ICSS
- 4.3.24 Test Interfaces
- 4.3.25 System and Miscellaneous
- 4.4 Pin Multiplexing
- 4.5 Connections for Unused Pins
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours (POH) Limits
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Operating Performance Points
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7
Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-7 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-8 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-9 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-10 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-11 LVCMOS OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-12 BC1833IHHV Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-13 Dual Voltage SDIO1833 DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-14 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.1 HDMIPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.2 USBPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.3 SATAPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.4 PCIEPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 5.9 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.10
Timing Requirements and Switching Characteristics
- 5.10.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 5.10.2 Interface Clock Specifications
- 5.10.3 Power Supply Sequences
- 5.10.4 Clock Specifications
- 5.10.5 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.10.6
Peripherals
- 5.10.6.1 Timing Test Conditions
- 5.10.6.2 Virtual and Manual I/O Timing Modes
- 5.10.6.3 VIP
- 5.10.6.4 DSS
- 5.10.6.5 HDMI
- 5.10.6.6 EMIF
- 5.10.6.7 GPMC
- 5.10.6.8 I2C
- 5.10.6.9 HDQ1W
- 5.10.6.10 UART
- 5.10.6.11 McSPI
- 5.10.6.12 QSPI
- 5.10.6.13
McASP
- Table 5-80 Timing Requirements for McASP1
- Table 5-81 Timing Requirements for McASP2
- Table 5-82 Timing Requirements for McASP3/4/5/6/7/8
- Table 5-83 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP1
- Table 5-84 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP2
- Table 5-85 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP3/4/5/6/7/8
- 5.10.6.14 USB
- 5.10.6.15 SATA
- 5.10.6.16 PCIe
- 5.10.6.17 CAN
- 5.10.6.18
GMAC_SW
- 5.10.6.18.1
GMAC MII Timings
- Table 5-99 Timing Requirements for miin_rxclk - MII Operation
- Table 5-100 Timing Requirements for miin_txclk - MII Operation
- Table 5-101 Timing Requirements for GMAC MIIn Receive 10/100 Mbit/s
- Table 5-102 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GMAC MIIn Transmit 10/100 Mbits/s
- 5.10.6.18.2 GMAC MDIO Interface Timings
- 5.10.6.18.3
GMAC RMII Timings
- Table 5-107 Timing Requirements for GMAC REF_CLK - RMII Operation
- Table 5-108 Timing Requirements for GMAC RMIIn Receive
- Table 5-109 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GMAC REF_CLK - RMII Operation
- Table 5-110 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GMAC RMIIn Transmit 10/100 Mbits/s
- 5.10.6.18.4
GMAC RGMII Timings
- Table 5-114 Timing Requirements for rgmiin_rxc - RGMIIn Operation
- Table 5-115 Timing Requirements for GMAC RGMIIn Input Receive for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- Table 5-116 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for rgmiin_txctl - RGMIIn Operation for 10/100/1000 Mbit/s
- Table 5-117 Switching Characteristics for GMAC RGMIIn Output Transmit for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- 5.10.6.18.1
GMAC MII Timings
- 5.10.6.19
eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 5.10.6.19.1
MMC1—SD Card Interface
- 5.10.6.19.1.1 Default speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 5.10.6.19.1.2 High speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 5.10.6.19.1.3 SDR12, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 5.10.6.19.1.4 SDR25, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 5.10.6.19.1.5 UHS-I SDR50, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 5.10.6.19.1.6 UHS-I SDR104, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 5.10.6.19.1.7 UHS-I DDR50, 4-bit data
- 5.10.6.19.2 MMC2 — eMMC
- 5.10.6.19.3 MMC3 and MMC4—SDIO/SD
- 5.10.6.19.1
MMC1—SD Card Interface
- 5.10.6.20
PRU-ICSS
- 5.10.6.20.1 Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU-ICSS PRU)
- 5.10.6.20.2
PRU-ICSS EtherCAT (PRU-ICSS ECAT)
- 5.10.6.20.2.1
PRU-ICSS ECAT Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-174 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements – Input Validated With LATCH_IN
- Table 5-175 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements – Input Validated With SYNCx
- Table 5-176 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements – Input Validated With Start of Frame (SOF)
- Table 5-177 PRU-ICSS ECAT Timing Requirements - LATCHx_IN
- Table 5-178 PRU-ICSS ECAT Switching Requirements - Digital IOs
- 5.10.6.20.2.1
PRU-ICSS ECAT Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.10.6.20.3 PRU-ICSS MII_RT and Switch
- 5.10.6.20.4 PRU-ICSS Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (PRU-ICSS UART)
- 5.10.6.20.5 PRU-ICSS IOSETs
- 5.10.6.20.6 PRU-ICSS Manual Functional Mapping
- 5.10.6.21 System and Miscellaneous interfaces
- 5.10.7
Emulation and Debug Subsystem
- 5.10.7.1
JTAG
- 5.10.7.1.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- Table 5-210 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 5-211 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 5-212 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- Table 5-213 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- 5.10.7.1.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- 5.10.7.2 TPIU
- 5.10.7.1
JTAG
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Processor Subsystems
- 6.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 6.4
Other Subsystems
- 6.4.1 Memory Subsystem
- 6.4.2 EDMA
- 6.4.3 Peripherals
- 6.4.4 On-Chip Debug
- 6.5 Identification
- 6.6 Boot Modes
-
7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7.1 Power Supply Mapping
- 7.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.2.1 DDR3 General Board Layout Guidelines
- 7.2.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.2.2.1 Board Designs
- 7.2.2.2 DDR3 EMIFs
- 7.2.2.3 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 7.2.2.4 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 7.2.2.5 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 7.2.2.6 PCB Stackup
- 7.2.2.7 Placement
- 7.2.2.8 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 7.2.2.9 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.2.2.10 High Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.2.2.11 Net Classes
- 7.2.2.12 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 7.2.2.13 VREF_DDR Routing
- 7.2.2.14 VTT
- 7.2.2.15 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.2.2.16 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.2.2.17 Routing Specification
- 7.3 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 7.4 Power Distribution Network Implementation Guidance
- 7.5 Thermal Solution Guidance
- 7.6 Single-Ended Interfaces
- 7.7 LJCB_REFN/P Connections
- 7.8 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ABZ|760
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.10.6.7.3 GPMC/NAND Flash Interface Asynchronous Timing
CAUTION
The IO Timings provided in this section are only valid for some GPMC usage modes when the corresponding Virtual IO Timings or Manual IO Timings are configured as described in the tables found in this section.
Table 5-62 and Table 5-63 assume testing over the recommended operating conditions and electrical characteristic conditions below (see Figure 5-36, Figure 5-37, Figure 5-38, and Figure 5-39).
Table 5-62 GPMC/NAND Flash Interface Timing Requirements
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNF12 | tacc(DAT) | Data maximum access time (GPMC_FCLK Cycles) | J (1) | cycles | |
| - | tsu(DV-OEH) | Setup time, read gpmc_ad[15:0] valid before gpmc_oen_ren high | 1.9 | ns | |
| - | th(OEH-DV) | Hold time, read gpmc_ad[15:0] valid after gpmc_oen_ren high | 1 | ns |
- J = AccessTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1)
Table 5-63 GPMC/NAND Flash Interface Switching Characteristics
| NO. | PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNF0 | tw(nWEV) | Pulse duration, gpmc_wen valid time | A (1) | ns | |
| GNF1 | td(nCSV-nWEV) | Delay time, gpmc_cs[7:0] valid to gpmc_wen valid | B - 2 (2) | B + 4 (2) | ns |
| GNF2 | td(CLEH-nWEV) | Delay time, gpmc_ben[1:0] high to gpmc_wen valid | C - 2 (3) | C + 4 (3) | ns |
| GNF3 | td(nWEV-DV) | Delay time, gpmc_ad[15:0] valid to gpmc_wen valid | D - 2 (4) | D + 4 (4) | ns |
| GNF4 | td(nWEIV-DIV) | Delay time, gpmc_wen invalid to gpmc_ad[15:0] invalid | E - 2 (5) | E + 4 (5) | ns |
| GNF5 | td(nWEIV-CLEIV) | Delay time, gpmc_wen invalid to gpmc_ben[1:0] invalid | F - 2 (6) | F + 4 (6) | ns |
| GNF6 | td(nWEIV-nCSIV) | Delay time, gpmc_wen invalid to gpmc_cs[7:0] invalid | G - 2 (7) | G + 4 (7) | ns |
| GNF7 | td(ALEH-nWEV) | Delay time, gpmc_advn_ale high to gpmc_wen valid | C - 2 (3) | C + 4 (3) | ns |
| GNF8 | td(nWEIV-ALEIV) | Delay time, gpmc_wen invalid to gpmc_advn_ale invalid | F - 2 (6) | F + 4 (6) | ns |
| GNF9 | tc(nWE) | Cycle time, write cycle time | H (8) | ns | |
| GNF10 | td(nCSV-nOEV) | Delay time, gpmc_cs[7:0] valid to gpmc_oen_ren valid | I - 2 (9) | I + 4 (9) | ns |
| GNF13 | tw(nOEV) | Pulse duration, gpmc_oen_ren valid time | K (10) | ns | |
| GNF14 | tc(nOE) | Cycle time, read cycle time | L (11) | ns | |
| GNF15 | td(nOEIV-nCSIV) | Delay time, gpmc_oen_ren invalid to gpmc_cs[7:0] invalid | M - 2 (12) | M + 4 (12) | ns |
- A = (WEOffTime – WEOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK
- B = ((WEOnTime – CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × (WEExtraDelay – CSExtraDelay)) × GPMC_FCLK
- C = ((WEOnTime – ADVOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × (WEExtraDelay – ADVExtraDelay)) × GPMC_FCLK
- D = (WEOnTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × WEExtraDelay) × GPMC_FCLK
- E = (WrCycleTime – WEOffTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) – 0.5 × WEExtraDelay) × GPMC_FCLK
- F = (ADVWrOffTime – WEOffTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × (ADVExtraDelay – WEExtraDelay) × GPMC_FCLK
- G = (CSWrOffTime – WEOffTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × (CSExtraDelay – WEExtraDelay) × GPMC_FCLK
- H = WrCycleTime × (1 + TimeParaGranularity) × GPMC_FCLK
- I = ((OEOffTime + (n – 1) × PageBurstAccessTime – CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × (OEExtraDelay – CSExtraDelay)) × GPMC_FCLK
- K = (OEOffTime – OEOnTime) × (1 + TimeParaGranularity) × GPMC_FCLK
- L = RdCycleTime × (1 + TimeParaGranularity) × GPMC_FCLK
- M = (CSRdOffTime – OEOffTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) + 0.5 × (CSExtraDelay – OEExtraDelay) × GPMC_FCLK
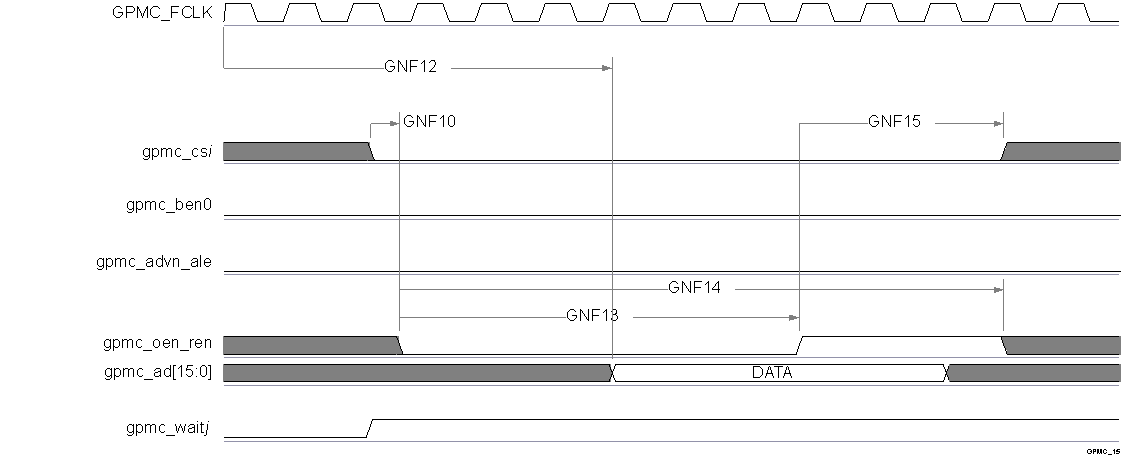
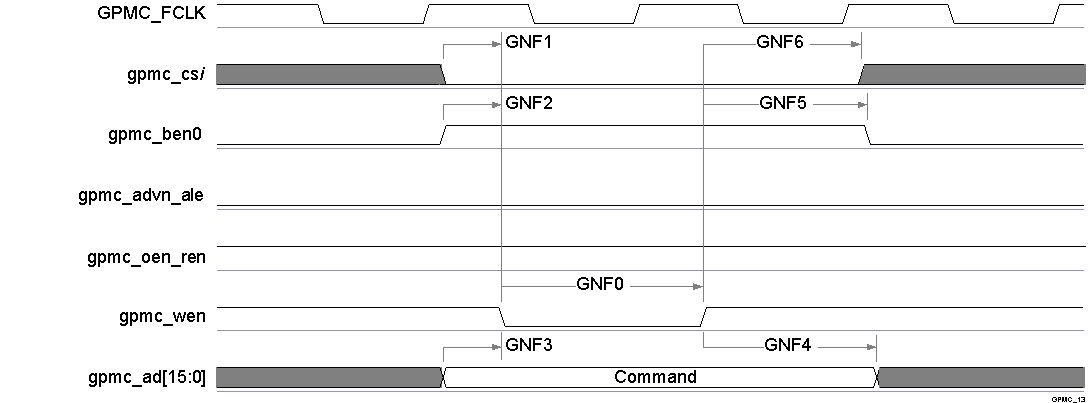 Figure 5-36 GPMC / NAND Flash - Command Latch Cycle Timing(1)
Figure 5-36 GPMC / NAND Flash - Command Latch Cycle Timing(1) - In gpmc_csi, i = 0 to 7.
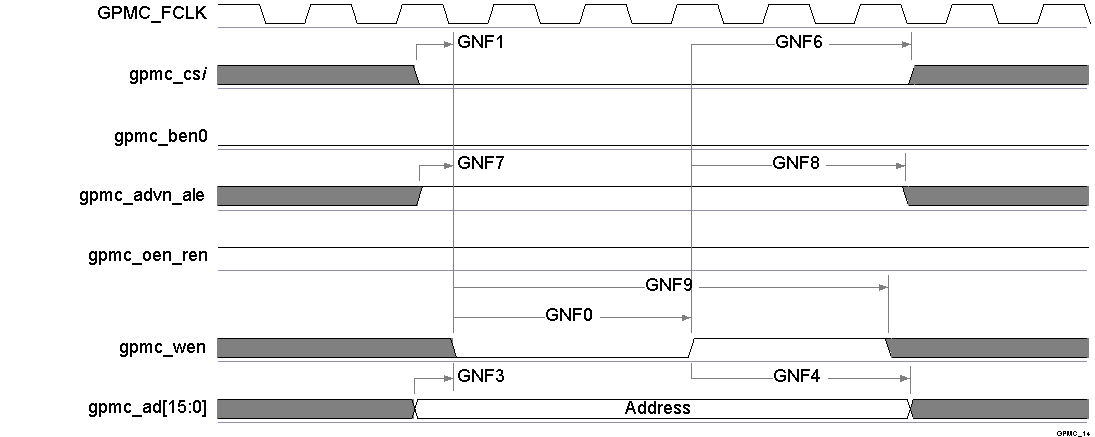 Figure 5-37 GPMC / NAND Flash - Address Latch Cycle Timing(1)
Figure 5-37 GPMC / NAND Flash - Address Latch Cycle Timing(1) - In gpmc_csi, i = 0 to 7.
- GNF12 parameter illustrates amount of time required to internally sample input Data. It is expressed in number of GPMC functional clock cycles. From start of read cycle and after GNF12 functional clock cycles, input data will be internally sampled by active functional clock edge. GNF12 value must be stored inside AccessTime register bits field.
- GPMC_FCLK is an internal clock (GPMC functional clock) not provided externally.
- In gpmc_csi, i = 0 to 7. In gpmc_waitj, j = 0 to 1.
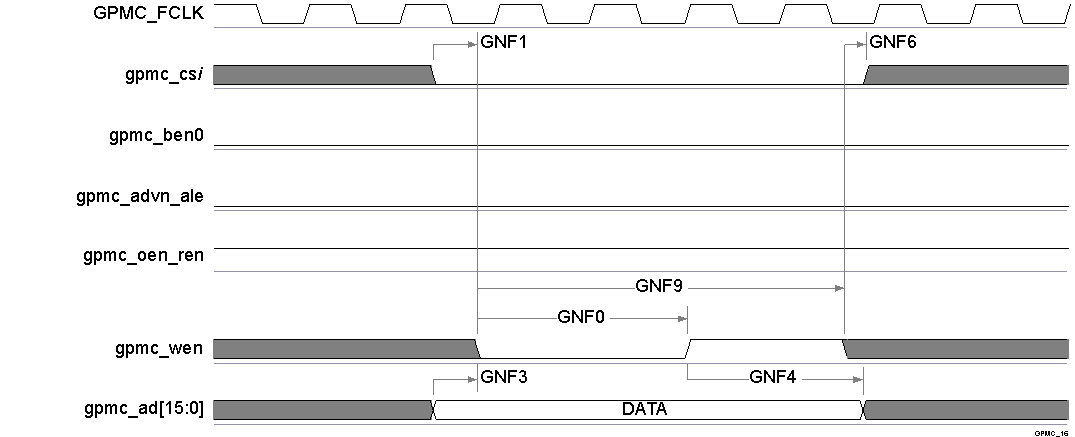 Figure 5-39 GPMC / NAND Flash - Data Write Cycle Timing(1)
Figure 5-39 GPMC / NAND Flash - Data Write Cycle Timing(1) - In gpmc_csi, i = 0 to 7.
NOTE
To configure the desired virtual mode the user must set MODESELECT bit and DELAYMODE bit field for each corresponding pad control register.
The pad control registers are presented in Table 4-33 and described in chapter Control Module in the device TRM.
Virtual IO Timings Modes must be used to ensure some IO timings for GPMC. See Table 5-33, Modes Summary for a list of IO timings requiring the use of Virtual IO Timings Modes. See Table 5-64, Virtual Functions Mapping for GPMC for a definition of the Virtual modes.
Table 5-64 presents the values for DELAYMODE bit field.
Table 5-64 Virtual Functions Mapping for GPMC
| BALL | BALL NAME | Delay Mode Value | MUXMODE[15:0] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPMC_VIRTUAL1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 14(1) | 14(1) | ||
| M6 | gpmc_ad0 | 11 | gpmc_ad0 | |||||||
| M2 | gpmc_ad1 | 11 | gpmc_ad1 | |||||||
| L5 | gpmc_ad2 | 11 | gpmc_ad2 | |||||||
| M1 | gpmc_ad3 | 11 | gpmc_ad3 | |||||||
| L6 | gpmc_ad4 | 11 | gpmc_ad4 | |||||||
| L4 | gpmc_ad5 | 11 | gpmc_ad5 | |||||||
| L3 | gpmc_ad6 | 11 | gpmc_ad6 | |||||||
| L2 | gpmc_ad7 | 11 | gpmc_ad7 | |||||||
| L1 | gpmc_ad8 | 11 | gpmc_ad8 | |||||||
| K2 | gpmc_ad9 | 11 | gpmc_ad9 | |||||||
| J1 | gpmc_ad10 | 11 | gpmc_ad10 | |||||||
| J2 | gpmc_ad11 | 11 | gpmc_ad11 | |||||||
| H1 | gpmc_ad12 | 11 | gpmc_ad12 | |||||||
| J3 | gpmc_ad13 | 11 | gpmc_ad13 | |||||||
| H2 | gpmc_ad14 | 11 | gpmc_ad14 | |||||||
| H3 | gpmc_ad15 | 11 | gpmc_ad15 | |||||||
| R6 | gpmc_a0 | 11 | gpmc_a0 | gpmc_a26 | gpmc_a16 | |||||
| T9 | gpmc_a1 | 11 | gpmc_a1 | |||||||
| T6 | gpmc_a2 | 11 | gpmc_a2 | |||||||
| T7 | gpmc_a3 | 10 | gpmc_a3 | |||||||
| P6 | gpmc_a4 | 10 | gpmc_a4 | |||||||
| R9 | gpmc_a5 | 11 | gpmc_a5 | |||||||
| R5 | gpmc_a6 | 11 | gpmc_a6 | |||||||
| P5 | gpmc_a7 | 11 | gpmc_a7 | |||||||
| N7 | gpmc_a8 | 12 | gpmc_a8 | |||||||
| R4 | gpmc_a9 | 12 | gpmc_a9 | |||||||
| N9 | gpmc_a10 | 12 | gpmc_a10 | |||||||
| P9 | gpmc_a11 | 11 | gpmc_a11 | |||||||
| P4 | gpmc_a12 | 13 | gpmc_a12 | gpmc_a0 | ||||||
| R3 | gpmc_a13 | 12 | gpmc_a13 | |||||||
| T2 | gpmc_a14 | 12 | gpmc_a14 | |||||||
| U2 | gpmc_a15 | 12 | gpmc_a15 | |||||||
| U1 | gpmc_a16 | 12 | gpmc_a16 | |||||||
| P3 | gpmc_a17 | 12 | gpmc_a17 | |||||||
| R2 | gpmc_a18 | 12 | gpmc_a18 | |||||||
| K7 | gpmc_a19 | 11 | gpmc_a19 | gpmc_a13 | ||||||
| M7 | gpmc_a20 | 11 | gpmc_a20 | gpmc_a14 | ||||||
| J5 | gpmc_a21 | 11 | gpmc_a21 | gpmc_a15 | ||||||
| K6 | gpmc_a22 | 11 | gpmc_a22 | gpmc_a16 | ||||||
| J7 | gpmc_a23 | 11 | gpmc_a23 | gpmc_a17 | ||||||
| J4 | gpmc_a24 | 11 | gpmc_a24 | gpmc_a18 | ||||||
| J6 | gpmc_a25 | 11 | gpmc_a25 | gpmc_a19 | ||||||
| H4 | gpmc_a26 | 11 | gpmc_a26 | gpmc_a20 | ||||||
| H5 | gpmc_a27 | 11 | gpmc_a27 | gpmc_a21 | ||||||
| H6 | gpmc_cs1 | 11 | gpmc_cs1 | gpmc_a22 | ||||||
| T1 | gpmc_cs0 | 14 | gpmc_cs0 | |||||||
| P2 | gpmc_cs2 | 12 | gpmc_cs2 | gpmc_a23 | gpmc_a13 | |||||
| P1 | gpmc_cs3 | 10 | gpmc_cs3 | gpmc_a1 | gpmc_a24 | gpmc_a14 | ||||
| P7 | gpmc_clk | 12 | gpmc_clk | gpmc_cs7 | gpmc_wait1 | gpmc_a20 | ||||
| N1 | gpmc_advn_ale | 13 | gpmc_advn_ale | gpmc_cs6 | gpmc_wait1 | gpmc_a2 | gpmc_a23 | gpmc_a19 | ||
| M5 | gpmc_oen_ren | 14 | gpmc_oen_ren | |||||||
| M3 | gpmc_wen | 14 | gpmc_wen | |||||||
| N6 | gpmc_ben0 | 11 | gpmc_ben0 | gpmc_cs4 | gpmc_a21 | |||||
| M4 | gpmc_ben1 | 11 | gpmc_ben1 | gpmc_cs5 | gpmc_a3 | gpmc_a22 | ||||
| N2 | gpmc_wait0 | 14 | gpmc_wait0 | gpmc_a25 | gpmc_a15 | |||||
| E1 | vin2a_clk0 | 11 | gpmc_a27 | gpmc_a17 | ||||||
| H7 | vin2a_fld0 | 11 | gpmc_a27 | gpmc_a18 | ||||||
| G1 | vin2a_hsync0 | 9 | gpmc_a27 | |||||||
| F5 | vin2a_d8 | 9 | gpmc_a26 | |||||||
| E6 | vin2a_d9 | 9 | gpmc_a25 | |||||||
| D3 | vin2a_d10 | 9 | gpmc_a24 | |||||||
| F6 | vin2a_d11 | 9 | gpmc_a23 | |||||||
| F6 | vin2a_d11 | 9 | gpmc_a23 | |||||||
| AG5 | vin1a_d11 | 9 | gpmc_a23 | |||||||
| AF2 | vin1a_d12 | 9 | gpmc_a24 | |||||||
| AF6 | vin1a_d13 | 9 | gpmc_a25 | |||||||
| AF3 | vin1a_d14 | 9 | gpmc_a26 | |||||||
| AF4 | vin1a_d15 | 9 | gpmc_a27 | |||||||
- Some signals listed are virtual functions that present alternate multiplexing options. These virtual functions are controlled via CTRL_CORE_ALT_SELECT_MUX or CTRL_CORE_VIP_MUX_SELECT registers. For more information on how to use these options, refer to the device TRM, chapter Control Module, section Pad Configuration Registers.