DLPS048C March 2015 – June 2019 DLPC150
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 High-Speed Sub-LVDS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 Low-Speed SDR Electrical Characteristics
- 6.9 System Oscillators Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Power-Up and Reset Timing Requirements
- 6.11 Parallel Interface Frame Timing Requirements
- 6.12 Parallel Interface General Timing Requirements
- 6.13 Flash Interface Timing Requirements
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
-
11Layout
- 11.1
Layout Guidelines
- 11.1.1 PCB Layout Guidelines For Internal Controller PLL Power
- 11.1.2 DLPC150 Reference Clock
- 11.1.3 General PCB Recommendations
- 11.1.4 General Handling Guidelines for Unused CMOS-Type Pins
- 11.1.5 Maximum Pin-to-Pin, PCB Interconnects Etch Lengths
- 11.1.6 Number of Layer Changes
- 11.1.7 Stubs
- 11.1.8 Terminations
- 11.1.9 Routing Vias
- 11.2 Layout Example
- 11.3 Thermal Considerations
- 11.1
Layout Guidelines
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZEZ|201
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
6.9 System Oscillators Timing Requirements(3)
| NUMBER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | ƒclock | Clock frequency, MOSC(1) | Option 1: 24-MHz oscillator | 23.998 | 24.002 | MHz |
| 1a | tc | Cycle time, MOSC(1) | Option 1: 24-MHz oscillator | 41.67 | 41.663 | ns |
| 1b | ƒclock | Clock frequency, MOSC(1) | Option 2: 16-MHz oscillator | 15.998 | 16.002 | MHz |
| 1b | tc | Cycle time, MOSC(1) | Option 2: 16-MHz oscillator | 62.508 | 62.492 | ns |
| 2 | tw(H) | Pulse duration(2), MOSC, high | 50% to 50% reference points (signal) | 40 tc% | ||
| 3 | tw(L) | Pulse duration(2), MOSC, low | 50% to 50% reference points (signal) | 40 tc% | ||
| 4 | tt | Transition time(2), MOSC, tt = tf / tr | 20% to 80% reference points (signal) | 10 | ns | |
| 5 | tjp | Long-term, peak-to-peak, period jitter(2), MOSC
(that is the deviation in period from ideal period due solely to high frequency jitter) |
2% | |||
(1) The frequency accuracy for MOSC is ±200 PPM. (This includes impact to accuracy due to aging, temperature, and trim sensitivity.) The MOSC input cannot support spread spectrum clock spreading.
(2) Applies only when driven through an external digital oscillator.
(3) The I/O pin TSTPT_6 enables the DLPC150 controller to use two different oscillator frequencies through a pullup control at initial DLPC150 controller power-up. If a pullup is applied to this pin then a 16.0-MHz oscillator option must be used instead of the 24-MHz option shown.
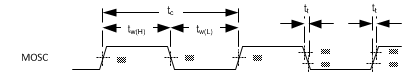 Figure 3. System Oscillators
Figure 3. System Oscillators