SPRSP57E april 2020 – june 2023 DRA821U , DRA821U-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
-
6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 6.1 Pin Diagram
- 6.2 Pin Attributes
- 6.3
Signal Descriptions
- 6.3.1 ADC
- 6.3.2 DDRSS
- 6.3.3 GPIO
- 6.3.4 I2C
- 6.3.5 I3C
- 6.3.6 MCAN
- 6.3.7 MCSPI
- 6.3.8 UART
- 6.3.9 MDIO
- 6.3.10 CPSW2G
- 6.3.11 CPSW5G
- 6.3.12 ECAP
- 6.3.13 EQEP
- 6.3.14 EPWM
- 6.3.15 USB
- 6.3.16 SERDES
- 6.3.17 OSPI
- 6.3.18 Hyperbus
- 6.3.19 GPMC
- 6.3.20 MMC
- 6.3.21 CPTS
- 6.3.22 MCASP
- 6.3.23 DMTIMER
- 6.3.24 Emulation and Debug
- 6.3.25 System and Miscellaneous
- 6.3.26 Power Supply
- 6.4 Pin Multiplexing
- 6.5 Connections for Unused Pins
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Power-On-Hours (POH)
- 7.5 Operating Performance Points
- 7.6
Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.1 I2C, Open-Drain, Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS Reset) Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.3 HFOSC Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.4 eMMCPHY Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.6 ADC12BT Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.7 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.8 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.9 SERDES Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6.10 DDR Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 7.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 7.9.2
Power Supply Sequencing
- 7.9.2.1 Power Supply Slew Rate Requirement
- 7.9.2.2 Combined MCU and Main Domains Power- Up Sequencing
- 7.9.2.3 Combined MCU and Main Domains Power- Down Sequencing
- 7.9.2.4 Independent MCU and Main Domains Power- Up Sequencing
- 7.9.2.5 Independent MCU and Main Domains Power- Down Sequencing
- 7.9.2.6 Independent MCU and Main Domains, Entry and Exit of MCU Only Sequencing
- 7.9.2.7 Independent MCU and Main Domains, Entry and Exit of DDR Retention State
- 7.9.2.8 Independent MCU and Main Domains, Entry and Exit of GPIO Retention Sequencing
- 7.9.3 System Timing
- 7.9.4
Clock Specifications
- 7.9.4.1
Input Clocks / Oscillators
- 7.9.4.1.1 WKUP_OSC0 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 7.9.4.1.2 WKUP_OSC0 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
- 7.9.4.1.3 Auxiliary OSC1 Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 7.9.4.1.4 Auxiliary OSC1 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
- 7.9.4.1.5 Auxiliary OSC1 Not Used
- 7.9.4.1.6 WKUP_LF_CLKIN Internal Oscillator Clock Source
- 7.9.4.1.7 WKUP_LF_CLKIN Not Used
- 7.9.4.2 Output Clocks
- 7.9.4.3 PLLs
- 7.9.4.4 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.9.4.5 Interface Clock Specifications
- 7.9.4.1
Input Clocks / Oscillators
- 7.9.5
Peripherals
- 7.9.5.1 ATL
- 7.9.5.2
CPSW2G
- 7.9.5.2.1 CPSW2G RMII Timings
- 7.9.5.2.2
CPSW2G RGMII Timings
- 7.9.5.2.2.1 Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RCLK – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.2.2.2 Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_RCTL – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.2.2.3 Switching Characteristics for RGMII[x]_TCLK – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.2.2.4 Switching Characteristics for RGMII[x]_TD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_TCTL – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.3
CPSW5G
- 7.9.5.3.1 CPSW5G MDIO Interface Timings
- 7.9.5.3.2 CPSW5G RMII Timings
- 7.9.5.3.3
CPSW5G RGMII Timings
- 7.9.5.3.3.1 Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RCLK – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.3.3.2 Timing Requirements for RGMII[x]_RD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_RCTL – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.3.3.3 Switching Characteristics for RGMII[x]_TCLK – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.3.3.4 Switching Characteristics for RGMII[x]_TD[3:0], and RGMII[x]_TCTL – RGMII Mode
- 7.9.5.4 DDRSS
- 7.9.5.5 ECAP
- 7.9.5.6 EPWM
- 7.9.5.7 EQEP
- 7.9.5.8 GPIO
- 7.9.5.9 GPMC
- 7.9.5.10 HyperBus
- 7.9.5.11 I2C
- 7.9.5.12 I3C
- 7.9.5.13 MCAN
- 7.9.5.14 MCASP
- 7.9.5.15 MCSPI
- 7.9.5.16 eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 7.9.5.17 NAVSS
- 7.9.5.18 OSPI
- 7.9.5.19 PCIE
- 7.9.5.20 Timers
- 7.9.5.21 UART
- 7.9.5.22 USB
- 7.9.6 Emulation and Debug
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Processor Subsystems
- 8.3
Other Subsystems
- 8.3.1 MSMC
- 8.3.2 NAVSS
- 8.3.3 PDMA Controller
- 8.3.4
Peripherals
- 8.3.4.1 ADC
- 8.3.4.2 ATL
- 8.3.4.3 CPSW2G
- 8.3.4.4 CPSW5G
- 8.3.4.5 DCC
- 8.3.4.6 DDRSS
- 8.3.4.7 ECAP
- 8.3.4.8 EPWM
- 8.3.4.9 ELM
- 8.3.4.10 ESM
- 8.3.4.11 EQEP
- 8.3.4.12 GPIO
- 8.3.4.13 GPMC
- 8.3.4.14 Hyperbus
- 8.3.4.15 I2C
- 8.3.4.16 I3C
- 8.3.4.17 MCAN
- 8.3.4.18 MCASP
- 8.3.4.19 MCRC Controller
- 8.3.4.20 MCSPI
- 8.3.4.21 MMC/SD
- 8.3.4.22 OSPI
- 8.3.4.23 PCIE
- 8.3.4.24 SerDes
- 8.3.4.25 WWDT
- 8.3.4.26 Timers
- 8.3.4.27 UART
- 8.3.4.28 USB
-
9 Applications,
Implementation, and Layout
- 9.1 Power Supply Mapping
- 9.2 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 9.3 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ALM|433
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD_CORE | MAIN domain core supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDD_MCU | MCUSS core supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDD_CPU | CPU core supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDD_MCU_WAKE1 | Core supply for MCU WAKE function | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDD_WAKE0 | Core supply for MAIN domain WAKE function which includes all "CANUART" IO. | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDA_0P8_DLL_MMC0 | MMC0 DLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDAR_CORE | MAIN domain RAM supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDAR_MCU | MCUSS RAM supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDAR_CPU | CPU RAM supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDA_0P8_SERDES0 | SERDES0 analog supply low | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDA_0P8_SERDES0_C | SERDES0 clock supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDA_0P8_USB | USB0 0.8 V analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDA_0P8_PLL_DDR | DDR PLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | |
| VDDA_1P8_USB | USB0 1.8 V analog supply | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_1P8_SERDES0 | SERDES0 analog supply high | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_3P3_USB | USB0 3.3 V analog supply | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDA_MCU_PLLGRP0 | Analog supply for MCU PLL Group 0 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_PLLGRP0 | Analog supply for MAIN PLL Group 0 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_PLLGRP4 | Analog supply for MAIN PLL Group 4 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_PLLGRP6 | Analog supply for MAIN PLL Group 6 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_PLLGRP8 | Analog supply for MAIN PLL Group 8 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_WKUP | Oscillator supply for WKUP domain | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_ADC_MCU | ADC analog supply | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_MCU_TEMP | Analog supply for temperature sensor 0 in MCU domain | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_POR_WKUP | WKUP domain analog supply | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_TEMP0 | Analog supply for temperature sensor 0 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_TEMP1 | Analog supply for temperature sensor 1 | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDS_DDR(10) | DDR inteface power supply | -0.3 | 1.2 | V | |
| VDDS_DDR_BIAS(10) | Bias supply for LPDDR4 | -0.3 | 1.2 | V | |
| VDDS_DDR_C(10) | IO power for DDR Memory Clock Bit (MCB) macro | -0.3 | 1.2 | V | |
| VDDS_MMC0 | MMC0 IO supply | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDA_OSC1 | HFOSC1 supply | -0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDSHV0_MCU | IO supply MCUSS general IO group, and MCU and MAIN domain warm reset pins | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV0 | IO supply for MAIN domain general | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV1_MCU | IO supply for MCUSS IO group 1 | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV2_MCU | IO supply for MCUSS IO group 2 | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV2 | IO supply for MAIN domain IO group 2 | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV5 | IO supply for MAIN domain IO group 5 | -0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VPP_CORE | Supply voltage range for CORE EFUSE domain | -0.3 | 1.89 | V | |
| VPP_MCU | Supply voltage range for MCU EFUSE domain | -0.3 | 1.89 | V | |
| USB0_VBUS(9) | Voltage range for USB VBUS comparator input | -0.3 | 3.6 | V | |
| Steady State Max. Voltage at all fail-safe IO pins | I2C0_SCL, I2C0_SDA, WKUP_I2C0_SCL, WKUP_I2C0_SDA, MCU_I2C0_SCL, MCU_I2C0_SDA, EXTINTn | –0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| MCU_PORz, PORz | –0.3 | 3.8 | V | ||
| VMON2_IR_VCPU | -0.3 | 1.05 | V | ||
| VMON3_IR_VEXT1P8, VMON4_IR_VEXT1P8, VMON1_ER_VSYS(8) | –0.3 | 2.2 | V | ||
| VMON5_IR_VEXT3P3 | –0.3 | 3.8 | V | ||
| Steady State Max. Voltage at all other IO pins(3) | All other IO pins | –0.3 | IO supply voltage + 0.3 | V | |
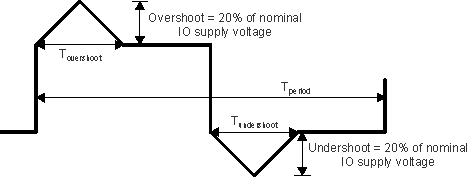
| Transient Overshoot and Undershoot specification at IO pin | 20% of IO supply voltage for up to 20% of signal period
(see Figure 7-1, IO Transient Voltage Ranges) |
0.2 × VDD(6) | V | ||
| Latch-up Performance, Class II (125°C)(4) | I-Test | –100 | 100 | mA | |
| Over-Voltage (OV) Test | NA | 1.5 × VDD(7) | V | ||
| TSTG(5) | Storage temperature | -55 | +150 | °C | |
Pins stressed per JEDEC JESD78E (Class II) and passed with specified I/O pin injection current and clamp voltage of 1.5 times maximum recommended I/O voltage and negative 0.5 times maximum recommended I/O voltage.
For overvoltage performance:
Supplies stressed per JEDEC JESD78E (Class II) and passed specified voltage injection.
Fail-safe IO terminals are designed such they do not have dependencies on the respective IO power supply voltage. This allows external voltage sources to be connected to these IO terminals when the respective IO power supplies are turned off. The I2C0_SCL, I2C0_SDA, WKUP_I2C0_SCL, WKUP_I2C0_SDA, MCU_I2C0_SCL, MCU_I2C0_SDA, EXTINTn, MCU_PORz, PORz, VMON1_ER_VSYS, VMON2_IR_VCPU, VMON3_IR_VEXT1P8, VMON4_IR_VEXT1P8, VMON5_ER_VEXT3P3 are the only fail-safe IO terminals. All other IO terminals are not fail-safe and the voltage applied to them should be limited to the value defined by the Steady State Max. Voltage at all IO pins parameter in Section 7.1.