SLVSDY7B October 2017 – January 2021 DRV8873-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|24
Orderable Information
7.4.1.4 nSLEEP Reset Pulse
In addition to the CLR_FLT bit in the SPI register, a latched fault can be cleared through a quick nSLEEP pulse. This pulse must be greater than the nSLEEP deglitch time of 5 µs and shorter than 20 µs. If nSLEEP is low for longer than 20 µs, the faults are cleared and the device may or may not shutdown, as shown in the timing diagram (see Figure 7-14). This reset pulse resets any SPI faults and does not affect the status of the charge pump or other functional blocks.
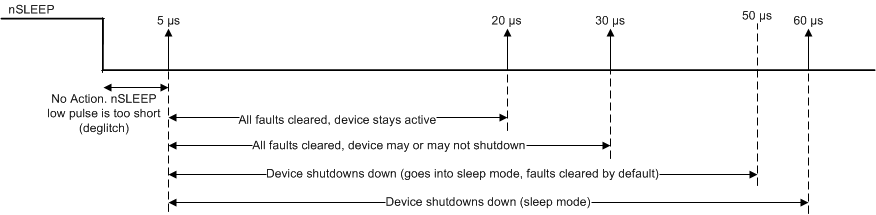 Figure 7-14 nSLEEP Reset Pulse
Figure 7-14 nSLEEP Reset Pulse