SNLS479B NOVEMBER 2014 – May 2020 DS90UB940-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 AC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements for the Serial ControlBus
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 Timing Diagrams and Test Circuits
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 High-Speed Forward Channel Data Transfer
- 7.3.2 Low-Speed Back Channel Data Transfer
- 7.3.3 FPD-Link III Port Register Access
- 7.3.4 Clock and Output Status
- 7.3.5 LVCMOS VDDIO Option
- 7.3.6 Power Down (PDB)
- 7.3.7 Interrupt Pin — Functional Description and Usage (INTB_IN)
- 7.3.8 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO)
- 7.3.9 SPI Communication
- 7.3.10 Backward Compatibility
- 7.3.11 Adaptive Equalizer
- 7.3.12 I2S Audio Interface
- 7.3.13 Built-In Self Test (BIST)
- 7.3.14 Internal Pattern Generation
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Configuration Select
- 7.4.1.1 1-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 4 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.2 1-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 2 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.3 2-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 4 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.4 2-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 2 MIPI® Lanes Output
- 7.4.1.5 1- or 2-Lane FPD-Link III Input, 2 or 4 MIPI® Lanes Output in Replicate
- 7.4.2 MODE_SEL[1:0]
- 7.4.3 CSI-2 Interface
- 7.4.4 Input Display Timing
- 7.4.5 MIPI® CSI-2 Output Data Formats
- 7.4.6 Non-Continuous / Continuous Clock
- 7.4.7 Ultra-Low-Power State (ULPS)
- 7.4.8 CSI-2 Data Identifier
- 7.4.1
Configuration Select
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1 Serial Control Bus
- 7.5.2 Multi-Master Arbitration Support
- 7.5.3 I2C Restrictions on Multi-Master Operation
- 7.5.4 Multi-Master Access to Device Registers for Newer FPD-Link III Devices
- 7.5.5 Multi-Master Access to Device Registers for Older FPD-Link III Devices
- 7.5.6 Restrictions on Control Channel Direction for Multi-Master Operation
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
DS90UB940N-Q1 Registers
- 7.6.1.1 I2C_Device_ID Register (Address = 0h) [reset = Strap]
- 7.6.1.2 Reset Register (Address = 1h) [reset = 4h]
- 7.6.1.3 General_Configuration_0 Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 80h]
- 7.6.1.4 General_Configuration_1 Register (Address = 3h) [reset = F0h]
- 7.6.1.5 BCC_Watchdog_Control Register (Address = 4h) [reset = FEh]
- 7.6.1.6 I2C_Control_1 Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 1Eh]
- 7.6.1.7 I2C_Control_2 Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.8 REMOTE_ID Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.9 SlaveID_0 Register (Address = 8h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.10 SlaveID_1 Register (Address = 9h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.11 SlaveID_2 Register (Address = Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.12 SlaveID_3 Register (Address = Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.13 SlaveID_4 Register (Address = Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.14 SlaveID_5 Register (Address = Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.15 SlaveID_6 Register (Address = Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.16 SlaveID_7 Register (Address = Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.17 SlaveAlias_0 Register (Address = 10h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.18 SlaveAlias_1 Register (Address = 11h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.19 SlaveAlias_2 Register (Address = 12h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.20 SlaveAlias_3 Register (Address = 13h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.21 SlaveAlias_4 Register (Address = 14h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.22 SlaveAlias_5 Register (Address = 15h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.23 SlaveAlias_6 Register (Address = 16h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.24 SlaveAlias_7 Register (Address = 17h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.25 MAILBOX_18 Register (Address = 18h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.26 MAILBOX_19 Register (Address = 19h) [reset = 1h]
- 7.6.1.27 GPIO_9_Global_GPIO_Config Register (Address = 1Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.28 Frequency_Counter Register (Address = 1Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.29 General_Status Register (Address = 1Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.30 GPIO0_Config Register (Address = 1Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.31 GPIO1_2_Config Register (Address = 1Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.32 GPIO_3_Config Register (Address = 1Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.33 GPIO_5_6_Config Register (Address = 20h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.34 GPIO_7_8_Config Register (Address = 21h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.35 Datapath_Control Register (Address = 22h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.36 RX_Mode_Status Register (Address = 23h) [reset = Strap]
- 7.6.1.37 BIST_Control Register (Address = 24h) [reset = 8h]
- 7.6.1.38 BIST_ERROR_COUNT Register (Address = 25h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.39 SCL_High_Time Register (Address = 26h) [reset = 83h]
- 7.6.1.40 SCL_Low_Time Register (Address = 27h) [reset = 84h]
- 7.6.1.41 Datapath_Control_2 Register (Address = 28h) [reset = Loaded from SER]
- 7.6.1.42 I2S_Control Register (Address = 2Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.43 PCLK_Test_Mode Register (Address = 2Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.44 DUAL_RX_CTL Register (Address = 34h) [reset = 1h]
- 7.6.1.45 AEQ_CTL1 Register (Address = 35h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.46 MODE_SEL Register (Address = 37h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.47 I2S_DIVSEL Register (Address = 3Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.48 Adaptive_EQ_Status Register (Address = 3Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.49 LINK_ERROR_COUNT Register (Address = 41h) [reset = 3h]
- 7.6.1.50 HSCC_CONTROL Register (Address = 43h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.51 ADAPTIVE_EQ_BYPASS Register (Address = 44h) [reset = 60h]
- 7.6.1.52 ADAPTIVE_EQ_MIN_MAX Register (Address = 45h) [reset = 88h]
- 7.6.1.53 CML_OUTPUT_CTL1 Register (Address = 52h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.54 CML_OUTPUT_ENABLE Register (Address = 56h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.55 CML_OUTPUT_CTL2 Register (Address = 57h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.56 CML_OUTPUT_CTL3 Register (Address = 63h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.57 PGCTL Register (Address = 64h) [reset = 10h]
- 7.6.1.58 PGCFG Register (Address = 65h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.59 PGIA Register (Address = 66h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.60 PGID Register (Address = 67h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.61 PGDBG Register (Address = 68h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.62 PGTSTDAT Register (Address = 69h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.63 CSICFG0 Register (Address = 6Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.64 CSICFG1 Register (Address = 6Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.65 CSIIA Register (Address = 6Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.66 CSIID Register (Address = 6Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.67 GPIO_Pin_Status_1 Register (Address = 6Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.68 GPIO_Pin_Status_2 Register (Address = 6Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1.69 ID0 Register (Address = F0h) [reset = 5Fh]
- 7.6.1.70 ID1 Register (Address = F1h) [reset = 55h]
- 7.6.1.71 ID2 Register (Address = F2h) [reset = 48h]
- 7.6.1.72 ID3 Register (Address = F3h) [reset = 39h]
- 7.6.1.73 ID4 Register (Address = F4h) [reset = 34h]
- 7.6.1.74 ID5 Register (Address = F5h) [reset = 30h]
- 7.6.2
CSI-2 Indirect Registers
- 7.6.2.1 CSI_TCK_PREP Register (Address = 0h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.2 CSI_TCK_ZERO Register (Address = 1h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.3 CSI_TCK_TRAIL Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.4 CSI_TCK_POST Register (Address = 3h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.5 CSI_THS_PREP Register (Address = 4h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.6 CSI_THS_ZERO Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.7 CSI_THS_TRAIL Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.8 CSI_THS_EXIT Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.9 CSI_TLPX Register (Address = 8h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.10 RAW_ALIGN Register (Address = 9h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.11 CSI_EN_PORT0 Register (Address = 13h) [reset = 3Fh]
- 7.6.2.12 CSI_EN_PORT1 Register (Address = 14h) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.2.13 CSIPASS Register (Address = 16h) [reset = 2h]
- 7.6.2.14 CSI_VC_ID Register (Address = 2Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 7.6.1
DS90UB940N-Q1 Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NKD|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- NKD|64
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
NKD Package
64-Pin WQFN
Top View
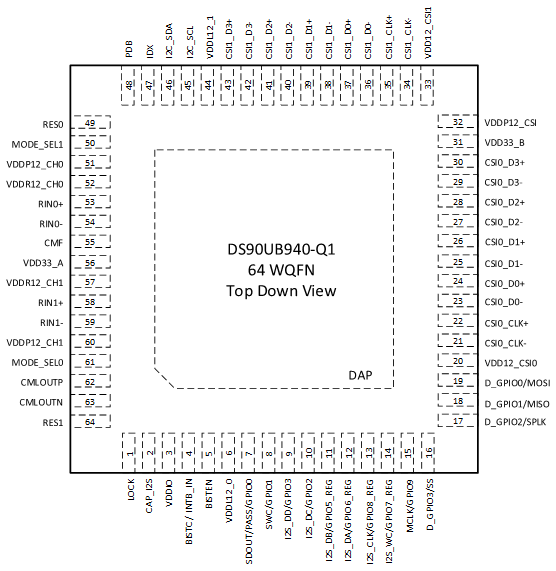
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O, TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NUMBER | ||
| MIPI DPHY / CSI-2 OUTPUT PINS | |||
| CSI0_CLK–
CSI0_CLK+ |
21
22 |
O | CSI-2 TX Port 0 differential clock output pins.
Leave unused pins as No Connect. Do not connect to an external pullup or pulldown. |
| CSI0_D0–
CSI0_D0+ |
23
24 |
O | CSI-2 TX Port 0 differential data output pins.
Leave unused pins as No Connect. Do not connect to an external pullup or pulldown. |
| CSI0_D1–
CSI0_D1+ |
25
26 |
O | |
| CSI0_D2–
CSI0_D2+ |
27
28 |
O | |
| CSI0_D3–
CSI0_D3+ |
29
30 |
O | |
| CSI1_CLK–
CSI1_CLK+ |
34
35 |
O | CSI-2 TX Port 1 differential clock output pins.
Leave unused pins as No Connect. Do not connect to an external pullup or pulldown. |
| CSI1_D0–
CSI1_D0+ |
36
37 |
O | CSI-2 TX Port 1 differential data output pins.
Leave unused pins as No Connect. Do not connect to an external pullup or pulldown. |
| CSI1_D1–
CSI1_D1+ |
38
39 |
O | |
| CSI1_D2–
CSI1_D2+ |
40
41 |
O | |
| CSI1_D3–
CSI1_D3+ |
42
43 |
O | |
| FPD-LINK III INTERFACE | |||
| RIN0– | 54 | I/O | FPD-Link III RX Port 0 pins. The port receives FPD-Link III high-speed forward channel video and control data and transmits back channel control data. It can interface with a compatible FPD-Link III serializer TX through a STP or coaxial cable (see Figure 40 and Figure 41). It must be AC-coupled per Table 101.
Leave unused pins as No Connect. Do not connect to an external pullup or pulldown. |
| RIN0+ | 53 | I/O | |
| RIN1– | 59 | I/O | FPD-Link III RX Port 1 pins. The port receives FPD-Link III high-speed forward channel video and control data and transmits back channel control data. It can interface with a compatible FPD-Link III serializer TX through a STP or coaxial cable (see Figure 40 and Figure 41). It must be AC-coupled per Table 101.
Leave unused pins as No Connect. Do not connect to an external pullup or pulldown. |
| RIN1+ | 58 | I/O | |
| CMF | 55 | I/O | Common mode filter – connect 0.1-µF capacitor to GND |
| I2C PINS | |||
| I2C_SDA | 46 | I/O, OD | I2C Data Input / Output Interface pin. See Serial Control Bus.
Recommend a 2.2 kΩ to 4.7 kΩ pullup to 1.8 V or 3.3 V. See I2C Bus Pullup Resistor Calculation (SLVA689). |
| I2C_SCL | 45 | I/O, OD | I2C Cock Input / Output Interface pin. See Serial Control Bus.
Recommend a 2.2 kΩ to 4.7 kΩ pullup to 1.8 V or 3.3 V. See I2C Bus Pullup Resistor Calculation (SLVA689). |
| IDx | 47 | I, S | I2C Serial Control Bus Device ID Address Select configuration pin
Connect to an external pullup to VDD33 and a pulldown to GND to create a voltage divider. See Table 10. |
| SPI PINS | |||
| MOSI
(D_GPIO0) |
19 | I/O, PD | SPI Master Output, Slave Input pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with D_GPIO0) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See SPI Mode Configuration. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| MISO
(D_GPIO1) |
18 | I/O, PD | SPI Master Input, Slave Output pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with D_GPIO1) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See SPI Mode Configuration. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| SPLK
(D_GPIO2) |
17 | I/O, PD | SPI Clock pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with D_GPIO2) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See SPI Mode Configuration. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| SS
(D_GPIO3) |
16 | I/O, PD | SPI Slave Select pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with D_GPIO0) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See SPI Mode Configuration. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| CONTROL PINS | |||
| MODE_SEL0 | 61 | I, S | Mode Select 0 configuration pin
Connect to an external pullup to VDD33 and pulldown to GND to create a voltage divider. See Table 7. |
| MODE_SEL1 | 50 | I, S | Mode Select 1 configuration pin
Connect to external pullup to VDD33 and pulldown to GND to create a voltage divider. See Table 8. |
| PDB | 48 | I, PD | Inverted Power-Down input pin
Typically connected to a processor GPIO with a pulldown. When PDB input is brought HIGH, the device is enabled and internal registers and state machines are reset to default values. Asserting PDB signal low will power down the device and consume minimum power. The default function of this pin is PDB = LOW; POWER DOWN with a weak (3 µA) internal pulldown enabled. PDB should remain low until after power supplies are applied and reach minimum required levels. PDB = 1, device is enabled (normal operation) PDB = 0, device is powered down When the device is in the POWER DOWN state, the LVCMOS outputs are in tri-state, the PLL is shut down, and IDD is minimized. |
| BISTEN | 5 | I, PD | BIST Enable pin
0: BIST mode is disabled 1: BIST mode is enabled It is a configuration pin with a weak (3 µA) internal pulldown. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. See Built-In Self Test (BIST) for more information. |
| BISTC
(INTB_IN) |
4 | I, PD | BIST Clock Select pin (function set by BISTEN pin)
0: PCLK 1: 33 MHz It is a multifunction pin (shared with INTB_IN) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is only enabled when in BIST mode. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| INTB_IN
(BISTC) |
4 | I, PD | Interrupt Input pin (default function)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with BISTC) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). See Interrupt Pin — Functional Description and Usage (INTB_IN). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO PINS | |||
| GPIO0
(SDOUT) |
7 | I/O, PD | General Purpose Input / Output 0 pin (default function)
default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with SDOUT) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO1
(SWC) |
8 | I/O, PD | General Purpose Input / Output 1 pin (default function)
default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with SWC) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO2
(I2S_DC) |
10 | I/O, PD | General Purpose Input / Output 2 pin (default function)
default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with I2S_DC) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO3
(I2S_DD) |
9 | I/O, PD | General Purpose Input / Output 3 pin (default function)
default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with I2S_DD) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO9
(MCLK) |
15 | I/O, PD | General Purpose Input / Output 9 pin (default function)
default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with MCLK) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| HIGH-SPEED GPIO PINS | |||
| D_GPIO0
(MOSI) |
19 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 0 pin (default function)
default state: tri-state Only available in Dual Link Mode. It is a multifunction pin (shared with MOSI) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| D_GPIO1
(MISO) |
18 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 1 pin (default function)
default state: tri-state Only available in Dual Link Mode. It is a multifunction pin (shared with MISO) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| D_GPIO2
(SPLK) |
17 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 2 pin (default function)
default state: tri-state Only available in Dual Link Mode. It is a multifunction pin (shared with SPLK) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| D_GPIO3
(SS) |
16 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 3 pin (default function)
default state: tri-state Only available in Dual Link Mode. It is a multifunction pin (shared with SS) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| REGISTER ONLY GPIO PINS | |||
| GPIO5_REG
(I2S_DB) |
11 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 5 pin (default function)
I2C register control only default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with I2S_DB) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO6_REG
(I2S_DA) |
12 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 6 pin (default function)
I2C register control only default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with I2S_DA) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO7_REG
(I2S_WC) |
14 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 7 pin (default function)
I2C register control only default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with I2S_WC) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| GPIO8_REG
(I2S_CLK) |
13 | I/O, PD | High-Speed General Purpose Input / Output 8 pin (default function)
I2C register control only default state: logic LOW It is a multifunction pin (shared with I2S_CLK) with a weak internal pulldown (3 µA). Pin function is programmed through registers. See General-Purpose I/O (GPIO). If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| SLAVE MODE LOCAL I2S CHANNEL PINS | |||
| I2S_WC
(GPIO7_REG) |
14 | O | Slave Mode I2S Word Clock Output pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO7_REG). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| I2S_CLK
(GPIO8_REG) |
13 | O | Slave Mode I2S Clock Output pin (function programmed through register)
NOTE: Disable I2S data jitter cleaner, when using these pins, through the register bit I2S Control: 0x2B[7]=1 It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO8_REG). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| I2S_DA
(GPIO6_REG) |
12 | O | Slave Mode I2S Data Output pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO6_REG). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| I2S_DB
(GPIO5_REG) |
11 | O | Slave Mode I2S Data Output pin (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO5_REG). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| I2S_DC
(GPIO2) |
10 | O | Slave Mode I2S Data Output (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO2). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| I2S_DD
(GPIO3) |
9 | O | Slave Mode I2S Data Output (function programmed through register)
It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO3). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| MASTER MODE LOCAL I2S CHANNEL PINS | |||
| SWC
(GPIO1) |
8 | O | Master Mode I2S Word Clock Output pin (function is programmed through registers)
(Pin is shared with GPIO1) It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO1). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| SDOUT
(GPIO0) |
7 | O | Master Mode I2S Data Output pin (function is programmed through registers)
(Pin is shared with GPIO0) It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO0). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| MCLK
(GPIO9) |
15 | O | Master Mode I2S System Clock Output pin (function is programmed through registers)
(Pin is shared with GPIO9) It is a multifunction pin (shared with GPIO9). Pin function is programmed through registers. See I2S Audio Interface. If unused, tie to an external pulldown. |
| STATUS PINS | |||
| LOCK | 1 | O | Lock Status Output pin
LOCK = 1: PLL acquired lock to the reference clock input; DPHY outputs are active LOCK = 0: PLL is unlocked |
| PASS | 7 | O | Normal mode status output pin (BISTEN = 0)
PASS = 1: No fault detected on input display timing PASS = 0: Indicates an error condition or corruption in display timing. Fault condition occurs:
PASS = 1: No error detected PASS = 0: Error detected |
| POWER and GROUND | |||
| VDD33_A,
VDD33_B |
56
31 |
P | 3.3-V (±10%) supply. Power to on-chip regulator. Recommend to connect with 10-µF, 1-µF, 0.1-µF, and 0.01-µF capacitors to GND. |
| VDDIO | 3 | P | LVCMOS I/O power supply: 1.8 V (±5%) OR 3.3 V (±10%). Recommend to connect with 10-µF, 1-µF, 0.1-µF, and 0.01-µF capacitors to GND. |
| VDD12_CSI0
VDDP12_CSI VDD12_CSI1 VDDL12_0 VDDL12_1 VDDP12_CH0 VDDR12_CH0 VDDP12_CH1 VDDR12_CH1 |
20
32 33 6 44 51 52 60 57 |
P | 1.2-V (±5%) supply. Recommend to connect with 10-µF, 1-µF, 0.1-µF, and 0.01-µF capacitors to GND at each VDD pin. |
| CAP_I2S | 2 | D | Decoupling capacitor connection for on-chip regulator. Recommend to connect with a 0.1-µF decoupling capacitor to GND. |
| VSS | DAP | G | DAP is the large metal contact at the bottom side, located at the center of the WQFN package. Connect to the ground plane (GND) with at least 32 vias. |
| OTHER PINS | |||
| CMLOUTP
CMLOUTN |
62
63 |
O | Channel Monitor Loop-through Driver differential output pins
Route to a test point or a pad with 100-Ω termination resistor between pins for channel monitoring (recommended). See Figure 37 or Figure 38. |
| RES0
RES1 |
49
64 |
- | Reserved pins. May be left as No Connect pin or connected to ground through a 0.1- µF capacitor. |