SNVS726F July 2011 – March 2018 LM25118
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 R7 = RT
- 8.2.2.3 Inductor Selection – L1
- 8.2.2.4 R13 = RSENSE
- 8.2.2.5 C15 = CRAMP
- 8.2.2.6 Inductor Current Limit Calculation
- 8.2.2.7 C9 - C12 = Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.8 D1
- 8.2.2.9 D4
- 8.2.2.10 C1 – C5 = Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 C20
- 8.2.2.12 C8
- 8.2.2.13 C16 = CSS
- 8.2.2.14 R8, R9
- 8.2.2.15 R1, R3, C21
- 8.2.2.16 R2
- 8.2.2.17 Snubber
- 8.2.2.18 Error Amplifier Configuration
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
7.3.6 Maximum Duty Cycle
Each conduction cycle of the buck switch is followed by a forced minimum off-time of 400 ns to allow sufficient time for the recirculating diode current to be sampled. This forced off-time limits the maximum duty cycle of the controller. The actual maximum duty cycle will vary with the operating frequency of Equation 7.
where
- f is the oscillator frequency in Hz
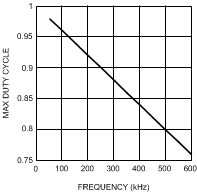 Figure 15. Maximum Duty Cycle vs Frequency
Figure 15. Maximum Duty Cycle vs Frequency
Limiting the maximum duty cycle will limit the maximum boost ratio (VOUT/VIN) while operating in buck-boost mode. For example, from Figure 15, at an operating frequency of 500 kHz, DMAX is 80%. Using the buck-boost transfer function.
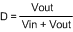
with
- D = 80%, solving for VOUT results in
- VOUT = 4 × VIN
With a minimum input voltage of 5 V, the maximum possible output voltage is 20 V at f = 500 kHz. The buck-boost step-up ratio can be increased by reducing the operating frequency which increases the maximum duty cycle.