SLCS136V August 1999 – May 2025 LMV331 , LMV339 , LMV393
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics, VCC+ = 2.7V
- 5.6 Switching Characteristics, VCC+ = 2.7V
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics, VCC+ = 5V
- 5.8 Switching Characteristics, VCC+ = 5V
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Trademarks
- 12Electrostatic Discharge Caution
- 13Glossary
- 14Revision History
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
- DCK|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.9 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, VS = +5V, single supply, TA = 25°C
 Figure 5-1 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Output High
Figure 5-1 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Output High Figure 5-3 Output Voltage vs Output Current
Figure 5-3 Output Voltage vs Output Current Figure 5-5 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Negative Transition (VCC=5V)
Figure 5-5 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Negative Transition (VCC=5V) Figure 5-7 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Negative Transition (VCC = 2.7V)
Figure 5-7 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Negative Transition (VCC = 2.7V) Figure 5-2 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Output Low
Figure 5-2 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage Output Low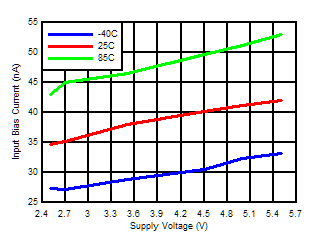 Figure 5-4 Input Bias Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-4 Input Bias Current vs Supply Voltage Figure 5-6 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Positive Transition (VCC = 5V)
Figure 5-6 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Positive Transition (VCC = 5V)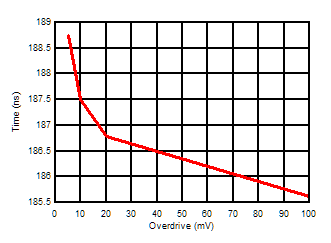 Figure 5-8 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Positive Transition (VCC = 2.7V)
Figure 5-8 Response Time vs Input Overdrives Positive Transition (VCC = 2.7V)