SNLS693B December 2021 – December 2023 SN75LVPE5412
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUA|42
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUA|42
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
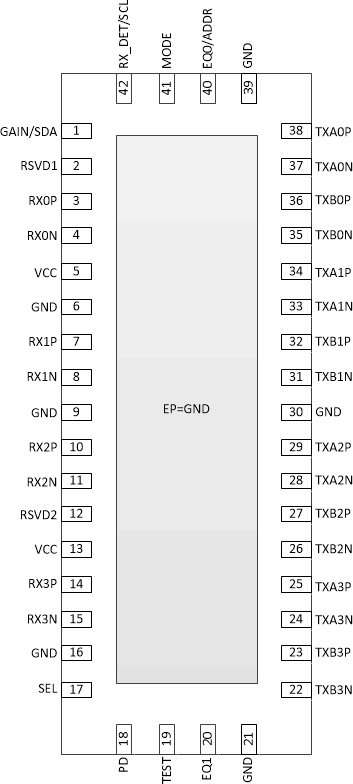 Figure 4-1 RUA Package, 42-Pin
WQFN (Top View)
Figure 4-1 RUA Package, 42-Pin
WQFN (Top View)Table 4-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| MODE | 41 | I, 5-level | Sets device control configuration modes. The 5-level IO pin is
defined in Table 6-1. The pin can be exercised at device power up or in normal
operation mode. L0: Pin Mode – device control configuration is done solely by strap pins. L1 or L2: SMBus/I2C Mode – device control configuration is done by an external controller with SMBus/I2C primary. This pin along with ADDR pin sets devices secondary address. L3 and L4 (Float): RESERVED – TI internal test modes. |
| EQ0 /ADDR | 40 | I, 5-level | In Pin Mode:
The EQ0 and EQ1 pins sets receiver linear equalization CTLE (AC gain) for all channels according to Table 6-2. These pins are sampled at device power-up only. In SMBus/I2C Mode: The ADDR pin in conjunction with MODE pin sets SMBus / I2C secondary address according to Table 6-5. The pin is sampled at device power-up only. |
| EQ1 | 20 | I, 5-level | |
| GAIN /SDA | 1 | I, 5-level / IO | In Pin Mode: Flat gain (broadband gain – DC and AC) from the input to the output of the device for all channels. Note: the device also provides AC (high frequency) gain in the form of equalization controlled by EQ pins or SMBus/I2C registers. The pin is sampled at device power-up only. In SMBus/I2C Mode: 3.3V SMBus/I2C data. External pullup resistor such as 4.7 kΩ required for operation. |
| GND | EP, 6, 9, 16, 21, 30, 39 | P | Ground reference for the device. EP: the Exposed Pad at the bottom of the QFN package. It is used as the GND return for the device. The EP should be connected to one or more ground planes through the low resistance path. A via array provides a low impedance path to GND. The EP also improves thermal dissipation. |
| PD | 18 | I, 3.3V LVCMOS | 2-level logic controlling the operating state of the redriver.
Active in both Pin Mode and SMBus/I2C Mode.
The pin is used part of PCIe RX_DET state machine as outlined in
Table 6-4. High: power down for all channels Low: power up, normal operation for all channels |
| RSVD1, 2 | 2, 12 | — | Reserved pins – for best signal integrity performance connect the pins to GND. Alternate option would be 0 Ω resistors from pins to GND. |
| RX_DET /SCL | 42 | I, 5-level / IO | In Pin Mode:
Sets receiver detect state machine options according to Table 6-4. The pin is sampled at device power-up only. In SMBus/I2C Mode: 3.3V SMBus/I2C clock. External pullup resistor such as 4.7 kΩ required for operation. |
| RX0N | 4 | I | Inverting differential RX inputs. Channel 0. |
| RX0P | 3 | I | Noninverting differential RX inputs. Channel 0. |
| RX1N | 8 | I | Inverting differential RX inputs. Channel 1. |
| RX1P | 7 | I | Noninverting differential RX inputs. Channel 0. |
| RX2N | 11 | I | Inverting differential RX inputs. Channel 2. |
| RX2P | 10 | I | Noninverting differential RX inputs. Channel 2. |
| RX3N | 15 | I | Inverting differential RX inputs. Channel 3. |
| RX3P | 14 | I | Noninverting differential RX inputs. Channel 3. |
| SEL | 17 | I, 3.3V LVCMOS | Selects the mux path. Active in both Pin Mode and
SMBus/I2C Mode. The pin has a weak
internal pull-down resistor. Note: the SEL pin must be exercised in
system implementations for mux selection between Port A vs Port B.
The pin is used for PCIe RX_DET state machine as outlined in
Table 6-4. L: Port A selected. H: Port B selected. |
| TXA0N | 37 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 0. |
| TXA0P | 38 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 0. |
| TXA1N | 33 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 1. |
| TXA1P | 34 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 1. |
| TXA2N | 28 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 2. |
| TXA2P | 29 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 2. |
| TXA3N | 24 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 3. |
| TXA3P | 25 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port A, Channel 3. |
| TXB0N | 35 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 0. |
| TXB0P | 36 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 0. |
| TXB1N | 31 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 1. |
| TXB1P | 32 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 1. |
| TXB2N | 26 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 2. |
| TXB2P | 27 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 2. |
| TXB3N | 22 | O | Inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 3. |
| TXB3P | 23 | O | Non-inverting differential TX output – Port B, Channel 3. |
| TEST | 19 | O | TI internal test pin. Keep no connect. |
| VCC | 5, 13 | P | Power supply, VCC = 3.3V ± 10%. The VCC pins on this device should be connected through a low-resistance path to the board VCC plane. |
(1) I = input, O = output, P = power, GND = ground