SLUSD53G March 2018 – August 2020 TPS23880
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 I2C Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Complete Register Set
- 9.6.2
Detailed Register Descriptions
- 9.6.2.1 INTERRUPT Register
- 9.6.2.2 INTERRUPT MASK Register
- 9.6.2.3 POWER EVENT Register
- 9.6.2.4 DETECTION EVENT Register
- 9.6.2.5 FAULT EVENT Register
- 9.6.2.6 START/ILIM EVENT Register
- 9.6.2.7 SUPPLY and FAULT EVENT Register
- 9.6.2.8 CHANNEL 1 DISCOVERY Register
- 9.6.2.9 CHANNEL 2 DISCOVERY Register
- 9.6.2.10 CHANNEL 3 DISCOVERY Register
- 9.6.2.11 CHANNEL 4 DISCOVERY Register
- 9.6.2.12 POWER STATUS Register
- 9.6.2.13 PIN STATUS Register
- 9.6.2.14 OPERATING MODE Register
- 9.6.2.15 DISCONNECT ENABLE Register
- 9.6.2.16 DETECT/CLASS ENABLE Register
- 9.6.2.17 Power Priority / 2Pair PCUT Disable Register Name
- 9.6.2.18 TIMING CONFIGURATION Register
- 9.6.2.19 GENERAL MASK Register
- 9.6.2.20 DETECT/CLASS RESTART Register
- 9.6.2.21 POWER ENABLE Register
- 9.6.2.22 RESET Register
- 9.6.2.23 ID Register
- 9.6.2.24 Connection Check and Auto Class Status Register
- 9.6.2.25 2-Pair Police Ch-1 Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.26 2-Pair Police Ch-2 Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.27 2-Pair Police Ch-3 Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.28 2-Pair Police Ch-4 Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.29 Power-on Fault Register
- 9.6.2.30 PORT RE-MAPPING Register
- 9.6.2.31 Channels 1 and 2 Multi Bit Priority Register
- 9.6.2.32 Channels 3 and 4 Multi Bit Priority Register
- 9.6.2.33 4-Pair Wired and Port Power Allocation Register
- 9.6.2.34 4-Pair Police Ch-1 and 2 Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.35 4-Pair Police Ch-3 and 4 Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.36 TEMPERATURE Register
- 9.6.2.37 4-Pair Fault Configuration Register
- 9.6.2.38 INPUT VOLTAGE Register
- 9.6.2.39 CHANNEL 1 CURRENT Register
- 9.6.2.40 CHANNEL 2 CURRENT Register
- 9.6.2.41 CHANNEL 3 CURRENT Register
- 9.6.2.42 CHANNEL 4 CURRENT Register
- 9.6.2.43 CHANNEL 1 VOLTAGE Register
- 9.6.2.44 CHANNEL 2 VOLTAGE Register
- 9.6.2.45 CHANNEL 3 VOLTAGE Register
- 9.6.2.46 CHANNEL 4 VOLTAGE Register
- 9.6.2.47 2x FOLDBACK SELECTION Register
- 95
- 9.6.2.48 FIRMWARE REVISION Register
- 9.6.2.49 I2C WATCHDOG Register
- 9.6.2.50 DEVICE ID Register
- 9.6.2.51 CHANNEL 1 DETECT RESISTANCE Register
- 9.6.2.52 CHANNEL 2 DETECT RESISTANCE Register
- 9.6.2.53 CHANNEL 3 DETECT RESISTANCE Register
- 9.6.2.54 CHANNEL 4 DETECT RESISTANCE Register
- 9.6.2.55 CHANNEL 1 ASSIGNED CLASS Register
- 9.6.2.56 CHANNEL 2 ASSIGNED CLASS Register
- 9.6.2.57 CHANNEL 3 ASSIGNED CLASS Register
- 9.6.2.58 CHANNEL 4 ASSIGNED CLASS Register
- 9.6.2.59 AUTO CLASS CONTROL Register
- 9.6.2.60 CHANNEL 1 AUTO CLASS POWER Register
- 9.6.2.61 CHANNEL 2 AUTO CLASS POWER Register
- 9.6.2.62 CHANNEL 3 AUTO CLASS POWER Register
- 9.6.2.63 CHANNEL 4 AUTO CLASS POWER Register
- 9.6.2.64 ALTERNATIVE FOLDBACK Register
- 9.6.2.65 SRAM CONTROL Register
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTQ|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTQ|56
Orderable Information
9.3.2 Port Power Priority
The TPS23880 supports 1- and 3-bit shutdown priority, which are selected with the MbitPrty bit of General Mask register (0x17).
The 1-bit shutdown priority works with the Port Power Priority (0x15) register. An OSSn bit with a value of 1 indicates that the corresponding port is treated as low priority, while a value of 0 corresponds to a high priority. As soon as the OSS input goes high, the low-priority ports are turned off.
The 3-bit shutdown priority works with the Multi Bit Power Priority (0x27/28) register, which holds the priority settings. A port with “000” code in this register has highest priority. Port priority reduces as the 3-bit value increases, with up to 8 priority levels. See Figure 9-1.
The multi bit port priority implementation is defined as the following:
- OSS code ≤ Priority setting (0x27/28 register): Port is disabled
- OSS code > Priority setting (0x27/28 register): Port remains active
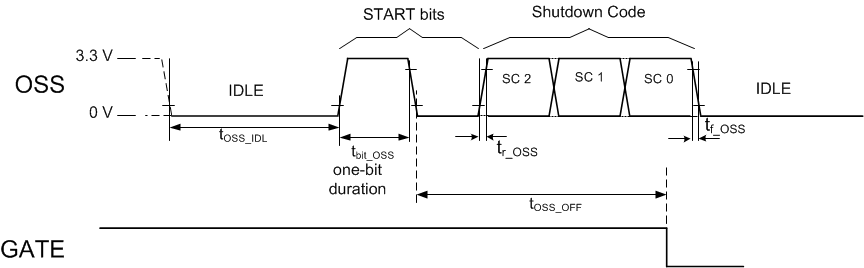 Figure 9-1 Multi Bit Priority Port Shutdown if Lower-Priority Port
Figure 9-1 Multi Bit Priority Port Shutdown if Lower-Priority PortPrior to setting the MbitPrty bit from 0 to 1, make sure the OSS input is in the idle (low) state for a minimum of 200 µs, to avoid any port misbehavior related to loss of synchronization with the OSS bit stream.
The OSS input has an internal 1-µs to 5-µs deglitch filter. From the idle state, a pulse with a longer duration is interpreted as a valid start bit. Ensure that the OSS signal is noise free.
To ensure both channels of a 4-pair port are disabled during and OSS event, make sure both channel have the same configurations in the 0x15 or 0x27/28 registers.