SLVSE94F September 2018 – June 2021 TPS2663
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 9.3.2 PGOOD and PGTH
- 9.3.3 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.4 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.5 Input Reverse Polarity Protection (B_GATE, DRV)
- 9.3.6 Reverse Current Protection
- 9.3.7 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 9.3.8 Output Power Limiting, PLIM (TPS26632, TPS26633, TPS26635 and TPS26636 Only)
- 9.3.9 Current Monitoring Output (IMON)
- 9.3.10 FAULT Response ( FLT)
- 9.3.11 IN_SYS, IN, OUT and GND Pins
- 9.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 9.3.13 Low Current Shutdown Control (SHDN)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application: Power Path Protection in a PLC System
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 System Examples
- 10.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.7 Typical Characteristics
–40°C ≤ TA = TJ ≤ +125°C, V(IN_SYS) = V(IN) = 24 V, V( SHDN) = 2 V, R(ILIM) = 30 kΩ, IMON = PGOOD = FLT = OPEN, C(OUT) = 1 μF, C(dVdT) = OPEN. (Unless stated otherwise)
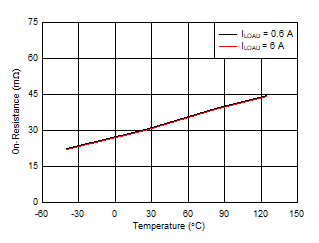 Figure 7-1 On-Resistance vs Temperature Across Load Current
Figure 7-1 On-Resistance vs Temperature Across Load Current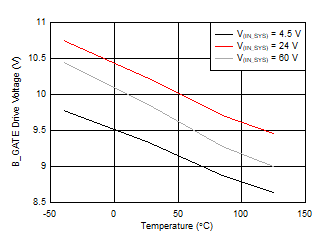 Figure 7-3 B_GATE Drive Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 7-3 B_GATE Drive Voltage vs Temperature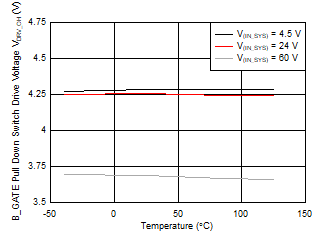 Figure 7-5 B_GATE Pull Down Drive Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 7-5 B_GATE Pull Down Drive Voltage vs Temperature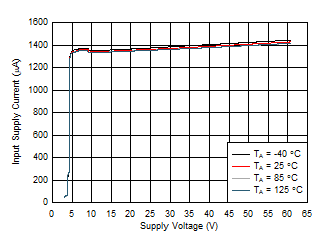 Figure 7-7 Input Supply Current vs Supply Voltage During Normal Operation
Figure 7-7 Input Supply Current vs Supply Voltage During Normal Operation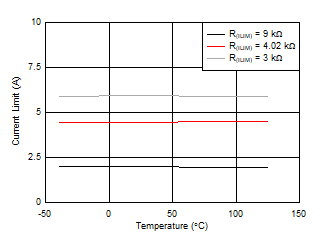 Figure 7-9 Overload Current Limit vs Temperature
Figure 7-9 Overload Current Limit vs Temperature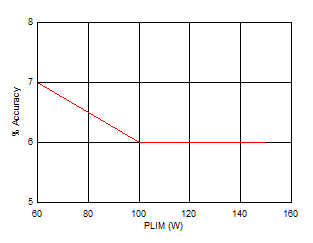 Figure 7-11 Output Power Limiting Accuracy vs PLIM
Figure 7-11 Output Power Limiting Accuracy vs PLIM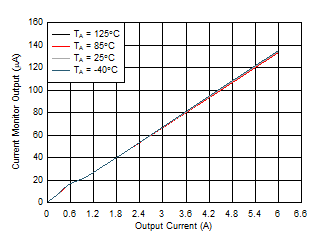 Figure 7-13 Current Monitor Output vs Output Current
Figure 7-13 Current Monitor Output vs Output Current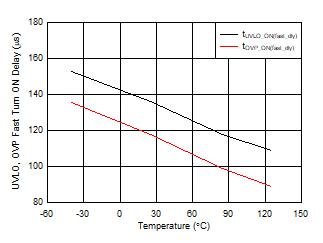
| V(PGTH) > V(PGTHF) |
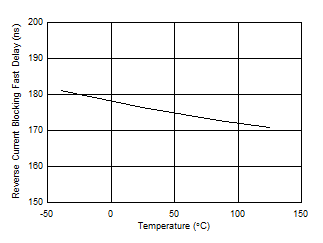 Figure 7-17 Reverse Current Blocking Response vs Temperature
Figure 7-17 Reverse Current Blocking Response vs Temperature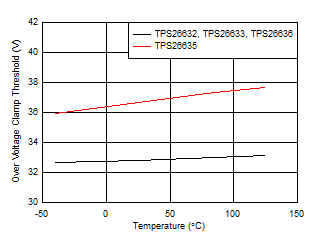 Figure 7-2 Overvoltage Clamp Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 7-2 Overvoltage Clamp Threshold vs Temperature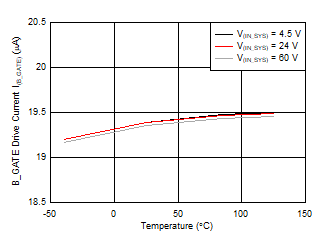 Figure 7-4 B_GATE Drive Current vs Temperature
Figure 7-4 B_GATE Drive Current vs Temperature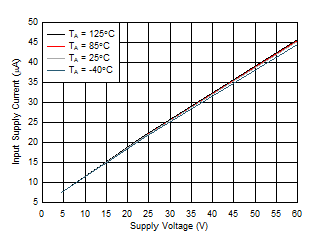 Figure 7-6 Input Supply Current vs Supply Voltage in Shutdown
Figure 7-6 Input Supply Current vs Supply Voltage in Shutdown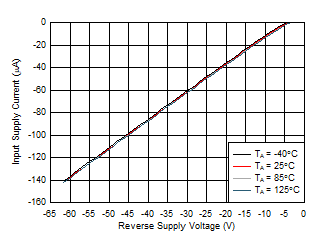
| V(OUT) = 0 V |
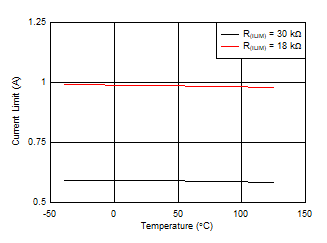 Figure 7-10 Overload Current Limit vs Temperature
Figure 7-10 Overload Current Limit vs Temperature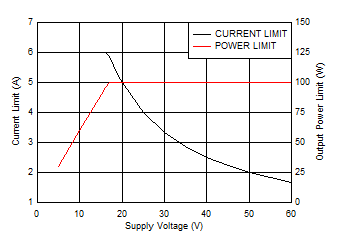
| TPS26632 | R(PLIM) = 100 kΩ | R(ILIM) = 3 kΩ |
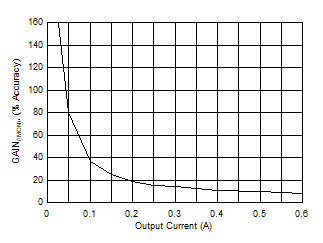 Figure 7-14 IMON Gain Accuracy at < 0.6-A Output Current
Figure 7-14 IMON Gain Accuracy at < 0.6-A Output Current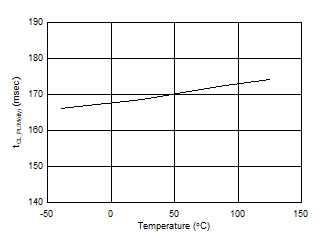 Figure 7-16 Maximum Duration in Current and Power Limiting vs Temperature
Figure 7-16 Maximum Duration in Current and Power Limiting vs Temperature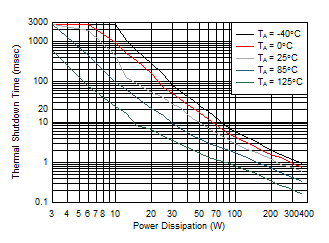
| Taken on VQFN device on EVM Board |