SLUS719H MARCH 2007 – May 2019 TPS40192 , TPS40193
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection (C8)
- 8.2.2.4 Peak Current Rating of the Inductor
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection (C7)
- 8.2.2.6 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1, Q2)
- 8.2.2.7 Boot Strap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Input Bypass Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.9 BP5 Bypass Capacitor (C5)
- 8.2.2.10 Input Voltage Filter Resistor (R11)
- 8.2.2.11 Short Circuit Protection (R9)
- 8.2.2.12 Feedback Compensation (Modeling the Power Stage)
- 8.2.2.13 Feedback Divider (R7, R8)
- 8.2.2.14 Error Amplifier Compensation (R6, R10, C1, C2, C3)
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
7.3.7 5-V Regulator
An on board 5-V regulator that allows the parts to operate from a single voltage feed. No separate 5-V feed to the part is required. This regulator needs to have a minimum of 1-μF of capacitance on the BP5 pin for stability. A ceramic capacitor is suggested for this purpose.
This regulator can also be used to supply power to nearby circuitry, eliminating the need for a separate LDO in some cases. If this pin is used for external loads, be aware that this is the power supply for the internals of the TPS40192 and TPS40193 devices . While efforts have been made to reduce sensitivity, any noise induced on this line has an adverse effect on the overall performance of the internal circuitry and shows up as increased pulse jitter, or skewed reference voltage. Also, when the device is disabled by pulling the EN pin low, this regulator is turned off and cannot supply power.
The amount of power available from this pin varies with the size of the power MOSFETs that the drivers must operate. Larger MOSFETs require more gate drive current and reduce the amount of power available on this pin for other tasks. The total current that this pin can draw from both the gate drive and external loads cannot exceed 50 mA. The device uses up to 4 mA from the regulator and the total gate drive current can be found from Equation 5.
For regulator stability, a 1-μF capacitor is required to be connected from BP5 to GND. In some applications using higher gate charge MOSFETs, a larger capacitor is required for noise suppression. For a total gate charge of both the high and low-side MOSFETs greater than 20 nC, a 2.2-μF or larger capacitor is recommended.
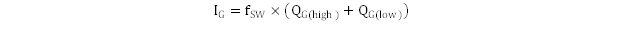
where
- IG is the required gate drive current
- fSW is the switching frequency (600 kHz for TPS40192, and 300 kHz for TPS40193)
- QG(high) is the gate charge requirement for the high-side MOSFET when VGS= 5 V
- QG(low) is the gate charge requirement for the low-side MOSFET when VGS= 5 V