SBVS311A November 2019 – March 2020 TPS7A54
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.2 Soft Start and Inrush Current
- 8.1.3 Optimizing Noise and PSRR
- 8.1.4 Charge Pump Noise
- 8.1.5 Current Sharing
- 8.1.6 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.7 Power-Good Operation
- 8.1.8 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Operation
- 8.1.9 Dropout Voltage (VDO)
- 8.1.10 Device Behavior During Transition From Dropout Into Regulation
- 8.1.11 Load Transient Response
- 8.1.12 Reverse Current Protection Considerations
- 8.1.13 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.14 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 8.1.15 TPS7A54EVM Thermal Analysis
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPS|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2.2 Internal Sequencing
Controlling when a single power supply turns on can be difficult in a power distribution network (PDN) because of the high power levels inherent in a PDN, and the variations between all of the supplies. As shown in Figure 42 and Table 2, the LDO turnon and turnoff time is set by the enable circuit (EN) and undervoltage lockout circuits (UVLO1,2(IN) and UVLOBIAS).
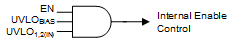 Figure 42. Simplified Turnon Control
Figure 42. Simplified Turnon Control Table 2. Internal Sequencing Functionality Table
| INPUT VOLTAGE | BIAS VOLTAGE | ENABLE STATUS | LDO STATUS | ACTIVE DISCHARGE | POWER GOOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN ≥ VUVLO_1,2(IN) | VBIAS ≥ VUVLO(BIAS) | EN = 1 | On | Off | PG = 1 when VOUT ≥ VIT(PG) |
| EN = 0 | Off | On | PG = 0 | ||
| VBIAS < VUVLO(BIAS) + VHYS(BIAS) | EN = don't care | Off | On(1) | ||
| VIN < VUVLO_1,2(IN) – VHYS1,2(IN) | BIAS = don't care | Off | |||
| IN = don't care | VBIAS ≥ VUVLO(BIAS) | Off |
(1) The active discharge remains on as long as VIN or VBIAS provide enough headroom for the discharge circuit to function.
VBIAS is not intended to be used dynamically when the IN rail is being powered up. If the BIAS rail is powered down when the IN rail is greater than 1.4 V, the PG output can trip. If the BIAS rail is powered up after the IN rail for VIN ≥ 1.4 V, a non-monotonic startup can occur.