SLWS245B May 2014 – February 2017 TRF3722
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Typical Characteristics
- 6.7 Typical Characteristics - Output Power
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics - Gain
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics - OIP3
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics - OIP2
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics - OP1dB
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics - Noise
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics - Unadjusted CF
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics - Unadjusted SBS
- 6.15 Typical Characteristics - LO Harmonic
- 6.16 Typical Characteristics - BB Harmonic
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics - RF Output Return Loss
- 6.18 Typical Characteristics - PLL/VCO
- 6.19 Typical Characteristics - Current Consumption
- 6.20 Typical Characteristics - Power Dissipation
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
TRF3722 integrates a high performance direct conversion quadrature modulator with exceptional linearity and low noise performance. The modulator which upconverts low frequency baseband signal to high frequency RF typically operates at 0.25 V common mode. It supports seamless interface with current source DACs. It also features high gain and low power operating modes. Additionally, TRF3722 integrates PLL and VCO to provide the local oscillator (LO) to the integrated modulator. The PLL and VCO provides excellent phase noise and extremely low spurious performance. The device also provides an LO output for driving another modulator or mixer. TRF3722 supports the use of an external VCO or LO signal.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram

8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 RF Output
The RF output is single ended and can drive a 50-Ω load. It can be tuned with the use of an output matching network to optimize the linearity and return loss performance within a selected band.
8.3.2 Baseband Inputs
The baseband inputs consist of the in-phase signal (I) and the quadrature-phase signals (Q). These I and Q signals are differential. The baseband lines are nominally biased at 0.25-V common-mode voltage (VCM); however, the device can operate with a VCM in the range of 0 V to 0.5 V. The baseband input lines are normally terminated externally 50 Ω on TRF3722 evaluation board, though it is possible to modify this value if necessary to match to an external filter load impedance requirement.
8.3.3 LO Output
The LO outputs are open collector differential outputs and are biased externally. These differential outputs can be tuned to optimized output power along with OUTBUF_BIAS register settings. It also is possible to use LO outputs in single ended mode.
8.3.4 PLL Architecture
Figure 132 illustrates a block diagram of the PLL architecture.
The VCO output frequency (fVCO) is given by Equation 1:
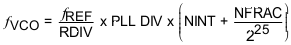
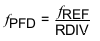
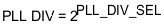
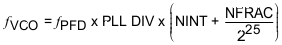
Where fREF is the reference input frequency, RDIV is the reference divider division ratio and the phase - frequency detector frequency is fPFD. PLL_DIV_SEL controls the division ratio of the programmable divider (PLL DIV) before the dual-modulus prescaler (DMP). NINT and NFRAC/225 is the integer and fractional part of the fractional divider (N.f), respectively. In Integer mode, the fractional setting is ignored and Equation 5 is applied.
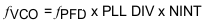
The complete feedback divider block consists of a PLL DIV, DMP, and N.f. The prescaler can be programmed as either a 4/5 or an 8/9. N.f includes an A and M digital counters.
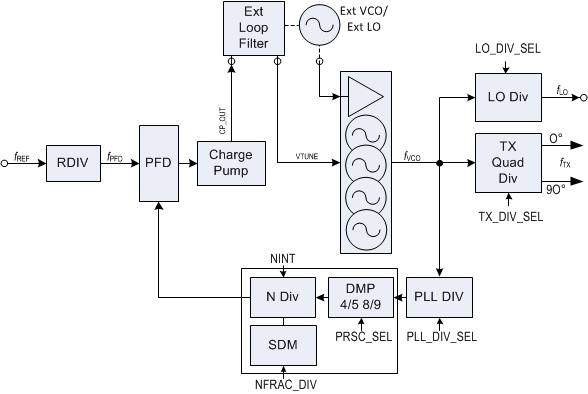 Figure 132. PLL Architecture
Figure 132. PLL Architecture
8.3.5 External VCO
An external LO or VCO signal may be applied. If an external LO is used the internal PLL can be powered down. Alternatively, dividers, phase-frequency detector, and charge pump can remain enabled and may be used to control the VTUNE of an external VCO. EN_EXTVCO is used to select the internal or external VCO.
8.3.6 Loop Filter
Loop filter design is critical for achieving low closed loop phase noise. Complete modulator performance data has been measured using integer mode loop filter. The integer mode loop filter was designed considering loop bandwidth 40 kHz and fPFD 2.56 MHz. Phase margin of 60 degrees was considered. Refer to TRF3722EVM User’s Guide to obtain the details on TRF3722 loop component calculations. Figure 133 shows integer loop filter.
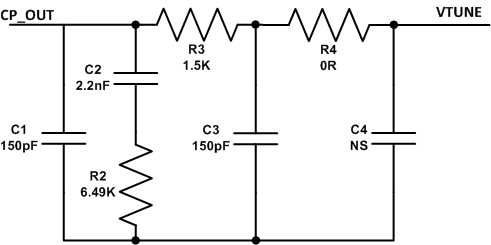 Figure 133. Integer Loop Filter
Figure 133. Integer Loop Filter
Frac-N performance data is obtained using the fractional loop filter shown in Figure 134. 40 kHz loop bandwidth and 15.36 MHz PFD was considered.
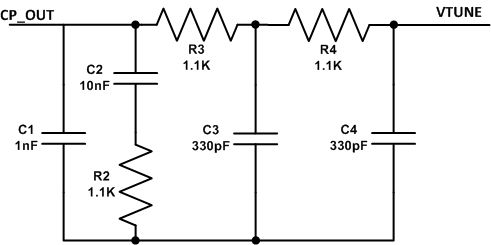 Figure 134. Fractional Loop Filter
Figure 134. Fractional Loop Filter
8.3.7 Lock Detect
The lock detect signal is generated in the phase frequency detector by comparing the two input signals. When the two compared phase signals remain aligned for several clock cycles, an internal signal goes high. The precision of this comparison is controlled through the LD_ANA_PREC bits. This internal signal is then averaged and compared against a reference voltage to generate the lock detect (LD) signal. The number of averages used is controlled through LD_DIG_PREC. Therefore, when the VCO is frequency locked, LD is high. When the VCO frequency is not locked, LD may pulse high or exhibit periodic behavior.
By default, the internal lock detect signal is made available on the LD terminal. Register bits MUX_CTRL can be used to control a multiplexer to output other diagnostic signals on the LD output.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Selecting PLL Divider Values
With reference to the PLL architecture illustrated in Figure 132, operation of the PLL requires TX_DIV_SEL / LO_DIV_SEL, PLL_DIV_SEL, RDIV, NINT, NFRAC and PRSC_SEL bits to be calculated.
- TX_DIV_SEL / LO_DIV_SEL
- PLL_DIV_SEL
- RDIV, NINT, NFRAC, PRSC_SEL
The LO to the integrated modulator (ƒTX) and additional LO output (ƒLO) frequency is related to fVCO according to the following:
ƒTX = fVCO / TX DIV
ƒLO = fVCO / LO DIV
Where TX DIV and LO DIV are related to TX_DIV_SEL and LO_DIV_SEL as:
| TX_DIV_SEL / LO_DIV_SEL | TX_DIV / LO_DIV | FREQUENCY RANGE |
|---|---|---|
| TX_DIV_SEL = 0 | TX DIV = 1 | 2050 MHz ≤ ƒTX ≤ 4100 MHz |
| TX_DIV_SEL = 1 | TX DIV = 2 | 1025 MHz ≤ ƒTX ≤ 2050 MHz |
| TX_DIV_SEL = 2 | TX DIV = 4 | 512.5 MHz ≤ ƒTX ≤ 1025 MHz |
| TX_DIV_SEL = 3 | TX DIV = 8 | 256.25 MHz ≤ ƒTX ≤ 512.5 MHz |
| LO_DIV_SEL = 0 | LO DIV = 1 | 2050 MHz ≤ ƒLO ≤ 4100 MHz |
| LO_DIV_SEL = 1 | LO DIV = 2 | 1025 MHz ≤ ƒLO ≤ 2050 MHz |
| LO_DIV_SEL = 2 | LO DIV = 4 | 512.5 MHz ≤ ƒLO ≤ 1025 MHz |
| LO_DIV_SEL = 3 | LO DIV = 8 | 256.25 MHz ≤ ƒLO ≤ 512.5 MHz |
Given fVCO, select PLL_DIV_SEL so that the division ratio PLL DIV limits the input frequency to the prescaler , fDMP, is limited to a maximum of 3000 MHz.
PLL DIV = min(1, 2, 4) such that fDMP ≤ 3000 MHz
PLL DIV is related to PLL_DIV_SEL according to the following equation:
PLL_DIV = 2PLL_DIV_SEL
This calculation can be restated as Equation 6.
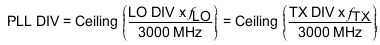
For both integer and fractional mode it is preferable to operate the fPFD at the highest possible frequency determined by the required frequency step of the RFOUT or LO_OUT. In Integer mode, select the maximum fPFD according to Equation 7.
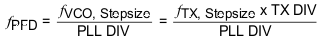
In Fractional mode, small RF stepsize can be obtained through the fractional divider. In this case, the highest fPFD frequency should be selected according to the reference clock and system requirements.
The remaing PLL parameters are calculated according to the following equations:
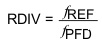

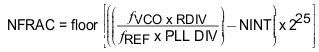
The DMP division ratio (P/P+1) can be set to 4/5 or 8/9 through the PRSC_SEL bit. To allow proper fractional operation, set PRSC_SEL according to:
PRSC_SEL = 0, (P/P+1) = 4/5 for 20 ≤ NINT < 72 in integer mode or 23 ≤ NINT < 75 in fractional mode.
PRSC_SEL = 1, (P/P+1) = 8/9 for NINT ≥ 72 in integer mode or NINT ≥ 75 in fractional mode.
The PRSC_SEL limit at NINT < 75 applies to Fractional mode with third-order modulation. In Integer mode, the PRSC_SEL = 8/9 should be used with NINT as low as 72. The divider block accounts for either value of PRSC_SEL without requiring NINT or NFRAC to be adjusted. Then, calculate the maximum input frequency (fN) to the digital divider. Use the lower of the possible prescaler divide settings, P = (4,8), as shown by Equation 8.

Verify that the frequency into the digital divider, fN, is less than or equal to 375 MHz. If fN exceeds 375 MHz, choose a larger value for PLL_DIV_SEL and recalculate fPFD, RDIV, NINT, NFRAC, and PRSC_SEL.
8.4.2 Setup Example for Integer Mode
Suppose the following operating characteristics fractional example are desired for Integer mode operation:
- fREF = 61.44 MHz (reference input frequency)
- Step at RF = 2.56 MHz (RF channel spacing)
- fRF = 1799.68 MHz (RF frequency)
The VCO range is 2050 MHz to 4100 MHz. Therefore:
- LO DIV = 2 (LO_DIV_SEL = 1)
- fVCO = LO DIV × 1799.68 MHz = 3599.36 MHz
In order to keep the frequency of the prescaler below 3000 MHz:
- PLL_DIV = 2 (PLL_DIV_SEL = 1)
The desired stepsize at RF is 2.56 MHz, so:
- fPFD = 2.56 MHz
- fVCO, stepsize = PLL_DIV × fPFD = 5.12 MHz
Using the reference frequency along with the required fPFD gives:
- RDIV = 24
- NINT = 703
NINT ≥ 75; therefore, select the 8/9 prescaler.
where
This example shows that Integer mode operation gives sufficient resolution for the required stepsize.
8.4.3 Integer and Fractional Mode Selection
The PLL is designed to operate in either Integer mode or Fractional mode. If the desired local oscillator (LO) frequency is an integer multiple of fPFD, then select integer mode otherwise select fractional mode. In Integer mode, the feedback divider ratio is an integer, and the fraction is zero. Thus, bits corresponding to the fractional control in integer mode are don’t care and fractional divider functionality is disabled.
In Fractional mode, the accuracy of the final frequency is set by 25-bit resolution. The RF stepsize is fPFD/225 which is less than 1 Hz for fPFD up to 33 MHz. The appropriate fractional control bits in the serial register must be programmed. Optimal performance may require tuning the MOD_ORD, ISOURCE_SINK, and ISOURCE_TRIM values according to the chosen frequency band.
8.4.4 Selecting the VCO and VCO Frequency Control
To achieve a broad frequency tuning range, the TRF3722 integrates multiple VCOs. Each VCO tank uses a bank of coarse tuning capacitor to bring VCO frequency within a few MHz of the desired value. For a given LO frequency an appropriate VCO and capacitor array must be selected. The device integrates logic that automatically selects an appropriate VCO and capacitor array, such that in closed loop V(TUNE) is approximately equal to the open loop calibration reference voltage set by VCO_CAL_REF. An on-chip temperature sensor automatically adjusts this reference voltage so that proper lock can be maintained over the temperature range.
The calibration logic is driven by a CAL_CLK signal which is scaled version of the reference frequency according to CAL_CLK_SEL. For optimum accuracy It is recommended to limit the CAL_CLK frequency to 600 kHz.
When VCO_SEL_MODE is '0', the device automatically selects the VCO and the capacitor array. When VCO_SEL_MODE is '1', the VCO selected by VCO_SEL is used and the logic automatically selects the capacitor array. The VCO and capacitor array settings resulting from the calibration can be read from Register 0 - read back register.
Automatic calibration can be disabled by setting CAL_BYPASS to '1'. In this manual calibration mode, the VCO is selected through register bits VCO_SEL, while the capacitor array is selected through register bits VCO_TRIM. Calibration modes are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3. VCO Calibration Modes
| CAL_BYPASS | VCO_SEL_MODE | MAX CYCLES CAL_CLK | VCO | CAPACITOR ARRAY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 46 | Automatic | |
| 0 | 1 | 34 | VCO_SEL | Automatic |
| 1 | don't care | N/A | VCO_SEL | VCO_TRIM |
8.5 Register Maps
Table 4. Serial interface Register Summary
| Bit | Register 1 | Register 2 | Register 3 | Register 4 | Register 5 | Register 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | Register Address | Register Address | Register Address | Register Address | Register Address | Register Address | |
| Bit1 | |||||||
| Bit2 | |||||||
| Bit3 | |||||||
| Bit4 | |||||||
| Bit5 | RDIV | NINT | NFRAC | PWD_PLL | RSV | RSV | |
| Bit6 | PWD_CP | IB_MOD_GM | |||||
| Bit7 | PWD_VCO | VCO_TRIM | |||||
| Bit8 | PWD_VCO_MUX | IB_MOD_LO | |||||
| Bit9 | PWD _DIV124 | ||||||
| Bit10 | PWD_PRESC | VCO_BIAS | |||||
| Bit11 | RSV | ||||||
| Bit12 | PWD_OUTBUF | ||||||
| Bit13 | PWD_LO_DIV | EN_LOCKDET | |||||
| Bit14 | PWD_TX_DIV | VCOBUF_BIAS | VCO_TEST_MODE | ||||
| Bit15 | PWD_MOD | CAL_BYPASS | |||||
| Bit16 | EN_EXTVCO | VCOMUX_BIAS | MUX_CTRL | ||||
| Bit17 | RSV | ||||||
| Bit18 | RSV | EN_ISOURCE | OUTBUF_BIAS | ||||
| Bit19 | REF_INV | LD_ANA_PREC | ISOURCE_SINKB | ||||
| Bit20 | NEG_VCO | RSV | ISOURCE_TRIM | ||||
| Bit21 | ICP | PLL_DIV_SEL | CP_TRISTATE | ||||
| Bit22 | VCO_CAL_IB | ||||||
| Bit23 | PRSC_SEL | SPEEDUP | VCO_CAL_REF | LO_DIV_SEL | |||
| Bit24 | RSV | LD_DIG_PREC | |||||
| Bit25 | MOD_ORD | LO_DIV_BIAS | |||||
| Bit26 | ICPDOUBLE | VCO_SEL | VCO_AMPL_CTRL | ||||
| Bit27 | CAL_CLK_SEL | TX_DIV_SEL | |||||
| Bit28 | VCO_SEL_MODE | DITH_SEL | VCO_VB_CTRL | ||||
| Bit29 | CAL_ACC | DEL_SD_CLK | TX_DIV_BIAS | ||||
| Bit30 | RSV | RSV | |||||
| Bit31 | RSV | EN_CAL | EN_FRAC_MODE | EN_LD_ISOURCE | GAIN_CTRL | ||
8.5.1 Serial interface Register Definition
Table 5. Register 1
| Register 1 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 1 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 0 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 0 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | RDIV<0> | 1 | 13-bit Reference Divider Value (Rmin = 1, Rmax = 8191) |
| Bit6 | RDIV<1> | 0 | |
| Bit7 | RDIV<2> | 0 | |
| Bit8 | RDIV<3> | 0 | |
| Bit9 | RDIV<4> | 0 | |
| Bit10 | RDIV<5> | 0 | |
| Bit11 | RDIV<6> | 0 | |
| Bit12 | RDIV<7> | 0 | |
| Bit13 | RDIV<8> | 0 | |
| Bit14 | RDIV<9> | 0 | |
| Bit15 | RDIV<10> | 0 | |
| Bit16 | RDIV<11> | 0 | |
| Bit17 | RDIV<12> | 0 | |
| Bit18 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit19 | REF_INV | 0 | Invert Reference Clock Polarity; 1 = use falling edge |
| Bit20 | NEG_VCO | 1 | VCO polarity control; 1 = negative slope (negative Kv) |
| Bit21 | ICP<0> | 0 | Program charge pump DC current: [00000] = 1.94 mA [11111] = 0.47 mA [01010] = 0.97 mA |
| Bit22 | ICP<1> | 1 | |
| Bit23 | ICP<2> | 0 | |
| Bit24 | ICP<3> | 1 | |
| Bit25 | ICP<4> | 0 | |
| Bit26 | ICPDOUBLE | 0 | 1 = Set ICP to double the current |
| Bit27 | CAL_CLK_SEL<0> | 0 | Multiplication or division factor to create VCO calibration clock from the PFD frequency: [0000] = Fastest ( Rdiv / 128) [1111] = Slowest (Rdiv x 128), [1000] = Default (1x Rdiv) |
| Bit28 | CAL_CLK_SEL<1> | 0 | |
| Bit29 | CAL_CLK_SEL<2> | 0 | |
| Bit30 | CAL_CLK_SEL<3> | 1 | |
| Bit31 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
CAL_CLK_SEL[3..0]: Set the frequency divider value used to derive the VCO calibration clock from the reference frequency.
Table 6. CAL_CLK_SEL Scaling Factor Setting
| CAL_CLK_SEL | Scaling Factor | CAL_CLK_SEL | Scaling Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1111 | 1/128 | 0111 | NA |
| 1110 | 1/64 | 0110 | 2 |
| 1101 | 1/32 | 0101 | 4 |
| 1100 | 1/16 | 0100 | 8 |
| 1011 | 1/8 | 0011 | 16 |
| 1010 | 1/4 | 0010 | 32 |
| 1001 | 1/2 | 0001 | 64 |
| 1000 | 1 | 0000 | 128 |
ICP[4..0]: Set the charge pump current.
Table 7. Charge Pump Current Set-Point
| ICP[4..0] | Current (mA) | ICP[4..0] | Current (mA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 000 | 1.94 | 10 000 | 0.75 |
| 00 001 | 1.76 | 10 001 | 0.72 |
| 00 010 | 1.62 | 10 010 | 0.69 |
| 00 011 | 1.49 | 10 011 | 0.67 |
| 00 100 | 1.38 | 10 100 | 0.65 |
| 00 101 | 1.29 | 10 101 | 0.63 |
| 00 110 | 1.21 | 10 110 | 0.61 |
| 00 111 | 1.14 | 10 111 | 0.59 |
| 01 000 | 1.08 | 11 000 | 0.57 |
| 01 001 | 1.02 | 11 001 | 0.55 |
| 01 010 | 0.97 | 11 010 | 0.54 |
| 01 011 | 0.92 | 11 011 | 0.52 |
| 01 100 | 0.88 | 11 100 | 0.51 |
| 01 101 | 0.84 | 11 101 | 0.50 |
| 01 110 | 0.81 | 11 110 | 0.48 |
| 01 111 | 0.78 | 11 111 | 0.47 |
Table 8. Register 2
| Register 2 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 0 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 1 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 0 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | NINT<0> | 0 | PLL N-Divider Value |
| Bit6 | NINT<1> | 0 | |
| Bit7 | NINT<2> | 0 | |
| Bit8 | NINT<3> | 0 | |
| Bit9 | NINT<4> | 0 | |
| Bit10 | NINT<5> | 0 | |
| Bit11 | NINT<6> | 0 | |
| Bit12 | NINT<7> | 1 | |
| Bit13 | NINT<8> | 0 | |
| Bit14 | NINT<9> | 0 | |
| Bit15 | NINT<10> | 0 | |
| Bit16 | NINT<11> | 0 | |
| Bit17 | NINT<12> | 0 | |
| Bit18 | NINT<13> | 0 | |
| Bit19 | NINT<14> | 0 | |
| Bit20 | NINT<15> | 0 | |
| Bit21 | PLL_DIV_SEL<0> | 1 | Select division ratio of divider in front of prescaler [00] = 1X, [01] = div2, [10] = div4 |
| Bit22 | PLL_DIV_SEL<1> | 0 | |
| Bit23 | PRSC_SEL | 1 | Select precaler modulus: [0] = 4/5, [1] =8/9 |
| Bit24 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit25 | RSV | 0 | |
| Bit26 | VCO_SEL<0> | 0 | Selects between the four integrated VCOs [00] = lowest frequency, [11] = highest frequency |
| Bit27 | VCO_SEL<1> | 1 | |
| Bit28 | VCO_SEL_MODE | 0 | Single VCO auto-calibration mode: [1] = active |
| Bit29 | CAL_ACC<0> | 0 | Error count during the cap array calibration [00] = 0, [01] = 1/32, [10] = 1/64, [11] =1/128) |
| Bit30 | CAL_ACC<1> | 0 | |
| Bit31 | EN_CAL | 0 | Initiate VCO auto-calibration, resets automatically |
Table 9. Register 3
| Register 3 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 1 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 1 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 0 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | NFRAC<0> | 0 | Fractional PLL N-Divider 0 to 0.99999 in fractional mode |
| Bit6 | NFRAC<1> | 0 | |
| Bit7 | NFRAC<2> | 0 | |
| Bit8 | NFRAC<3> | 0 | |
| Bit9 | NFRAC<4> | 0 | |
| Bit10 | NFRAC<5> | 0 | |
| Bit11 | NFRAC<6> | 0 | |
| Bit12 | NFRAC<7> | 0 | |
| Bit13 | NFRAC<8> | 0 | |
| Bit14 | NFRAC<9> | 0 | |
| Bit15 | NFRAC<10> | 0 | |
| Bit16 | NFRAC<11> | 0 | |
| Bit17 | NFRAC<12> | 0 | |
| Bit18 | NFRAC<13> | 0 | |
| Bit19 | NFRAC<14> | 0 | |
| Bit20 | NFRAC<15> | 0 | |
| Bit21 | NFRAC<16> | 0 | |
| Bit22 | NFRAC<17> | 0 | |
| Bit23 | NFRAC<18> | 0 | |
| Bit24 | NFRAC<19> | 0 | |
| Bit25 | NFRAC<20> | 0 | |
| Bit26 | NFRAC<21> | 0 | |
| Bit27 | NFRAC<22> | 0 | |
| Bit28 | NFRAC<23> | 0 | |
| Bit29 | NFRAC<24> | 0 | |
| Bit30 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit31 | RSV | 0 |
Table 10. Register 4
| Register 4 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 0 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 0 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 1 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | PWD_PLL | 0 | Power -down all PLL blocks: (1 = off) |
| Bit6 | PWD_CP | 0 | Power-down Charge Pump: (1=off) |
| Bit7 | PWD_VCO | 0 | Power-down VCO: (1=off) |
| Bit8 | PWD_VCO_MUX | 0 | Power-down VCO Mux blocks: (1=off) |
| Bit9 | PWD _DIV124 | 0 | Power-down the div 1,2,4 in the PLL f/b path: (1=off) |
| Bit10 | PWD_PRESC | 0 | Power-down Prescaler: (1=off) |
| Bit11 | RSV | 1 | Reserved |
| Bit12 | PWD_OUTBUF | 1 | Power-down Ouptut Buffer: (1=off) |
| Bit13 | PWD_LO_DIV | 1 | Power-down LO divider block: (1=off) |
| Bit14 | PWD_TX_DIV | 1 | Power-down TX divider block: (1=off) |
| Bit15 | PWD_MOD | 1 | Power-down modulator block: (1=off) |
| Bit16 | EN_EXTVCO | 0 | Enable external VCO input buffer: (1 = enabled) |
| Bit17 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit18 | EN_ISOURCE | 0 | Enable offset current at CP output (frac-n mode only). |
| Bit19 | LD_ANA_PREC<0> | 0 | Control precision of Analog Lock Detector: [00] = H/H (High), [01] = L/L (Low), [10] = H/L , [11] = L/L |
| Bit20 | LD_ANA_PREC<1> | 0 | |
| Bit21 | CP_TRISTATE<0> | 0 | Set the charge pump output in Tristate mode: [00] = Off, [01] = Down, [10] = Up, [11] = Tristate |
| Bit22 | CP_TRISTATE<1> | 0 | |
| Bit23 | SPEEDUP | 0 | Enable fast turn on/off time of bias blocks. |
| Bit24 | LD_DIG_PREC | 0 | Lock detector precision (increases sampling time if set to 1) |
| Bit25 | MOD_ORD<0> | 1 | Modulator order (1-4). Not used in integer mode (defaul 3rd order + dither) |
| Bit26 | MOD_ORD<1> | 0 | |
| Bit27 | MOD_ORD<2> | 1 | |
| Bit28 | DITH_SEL | 0 | Dither Mode: [0] = pseudo-random, [1] = constant |
| Bit29 | DEL_SD_CLK<0> | 0 | DS modulator clock delay. Frac-n mode only. [00] = Min delay, [11] = max delay |
| Bit30 | DEL_SD_CLK<1> | 1 | |
| Bit31 | EN_FRAC_MODE | 0 | Enable Frac-n mode when set to 1 |
Table 11. Register 5
| Register 5 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 1 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 0 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 1 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit6 | IB_MOD_GM<0> | 0 | Adjust modulator bias current gm |
| Bit7 | IB_MOD_GM<1> | 1 | |
| Bit8 | IB_MOD_LO<0> | 0 | Adjust modulator BB and LO bias current |
| Bit9 | IB_MOD_LO<1> | 1 | |
| Bit10 | VCO_BIAS<0> | 0 | Adjust VCO bias reference current |
| Bit11 | VCO_BIAS<1> | 0 | |
| Bit12 | VCO_BIAS<2> | 0 | |
| Bit13 | VCO_BIAS<3> | 1 | |
| Bit14 | VCOBUF_BIAS<0> | 0 | Adjust VCO buffer reference current |
| Bit15 | VCOBUF_BIAS<1> | 1 | |
| Bit16 | VCOMUX_BIAS<0> | 0 | Adjust VCO Mux reference current |
| Bit17 | VCOMUX_BIAS<1> | 1 | |
| Bit18 | OUTBUF_BIAS<0> | 0 | Adjust output buffer current |
| Bit19 | OUTBUF_BIAS<1> | 1 | |
| Bit20 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit21 | RSV | 1 | |
| Bit22 | VCO_CAL_IB | 0 | Bias current for CAL reference voltage: [0] = PTAT, [1] = Constant |
| Bit23 | VCO_CAL_REF<0> | 0 | VCO calibration reference voltage adjustment [000] = 0.9 V, [111] = 1.4 V [011] = recommended = 1.11 V |
| Bit24 | VCO_CAL_REF<1> | 0 | |
| Bit25 | VCO_CAL_REF<2> | 1 | |
| Bit26 | VCO_AMPL_CTRL<0> | 0 | Adjusts the signal level at the VCO_MUX input: [00] =max, [11] = min |
| Bit27 | VCO_AMPL_CTRL<1> | 1 | |
| Bit28 | VCO_VB_CTRL<0> | 0 | Adjusts the VCO core bias voltage: [00] = 1.2 V, [01] = 1.35 V, [10] = 1.5 V, [11] = 1.65 V |
| Bit29 | VCO_VB_CTRL<1> | 1 | |
| Bit30 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit31 | EN_LD_MON_ISOURCE | 1 | Enable monitoring of LD to turn on Isource; recommend [0] = Isource ctrl |
Table 12. Register 6
| Register 6 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 0 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 1 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 1 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | RSV | 0 | Reserved |
| Bit6 | RSV | 0 | |
| Bit7 | VCO_TRIM<0> | 0 | VCO capacitor array control bits; used in manual cal mode |
| Bit8 | VCO_TRIM<1> | 0 | |
| Bit9 | VCO_TRIM<2> | 0 | |
| Bit10 | VCO_TRIM<3> | 0 | |
| Bit11 | VCO_TRIM<4> | 0 | |
| Bit12 | VCO_TRIM<5> | 1 | |
| Bit13 | EN_LOCKDET | 0 | Enable monitor of lock detector output for autocal mode |
| Bit14 | VCO_TEST_MODE | 0 | Counter mode, measure max and min freq for each VCO |
| Bit15 | CAL_BYPASS | 0 | Bypass auto-cal; sets VCO_SEL and VCO_TRIM from Serial interface |
| Bit16 | MUX_CTRL<0> | 1 | Select signal for test output: [001] = LD, [010] = NDIV, [100] = RDIV, [110] = A_counter |
| Bit17 | MUX_CTRL<1> | 0 | |
| Bit18 | MUX_CTRL<2> | 0 | |
| Bit19 | ISOURCE_SINKB | 0 | Offset current polarity |
| Bit20 | ISOURCE_TRIM<0> | 0 | Adjust Isource bias current in frac-n mode. |
| Bit21 | ISOURCE_TRIM<1> | 0 | |
| Bit22 | ISOURCE_TRIM<2> | 1 | |
| Bit23 | LO_DIV_SEL<0> | 0 | Adjust LO path divider: [00] = Div/1, [01] = Div/2, [10] = Div/4. [11] = Div/8 |
| Bit24 | LO_DIV_SEL<1> | 0 | |
| Bit25 | LO_DIV_BIAS<0> | 0 | Adjust LO divider bias current: [00] = 25 uA, [01] = 37.5 uA, [10] = 50 uA, [11] = 62.5 uA |
| Bit26 | LO_DIV_BIAS<1> | 1 | |
| Bit27 | TX_DIV_SEL<0> | 0 | Adjust TX path divider. |
| Bit28 | TX_DIV_SEL<1> | 1 | [00] = Div/1, [01] = Div/2, [10] = Div/4. [11] = Div/8 |
| Bit29 | TX_DIV_BIAS<0> | 0 | Adjust TX divider bias current: [00] = 25 uA, [01] = 37.5 uA, [10] = 50 uA, [11] = 62.5 uA |
| Bit30 | TX_DIV_BIAS<1> | 1 | |
| Bit31 | GAIN_CTRL | 0 | Modulator gain control: [0] = Default, [1] = High Gain |
Table 13. READBACK Mode Summary Serial interface Map
| Bit | Register 0 | RDBK | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | Register Address | Register Address | |
| Bit1 | |||
| Bit2 | |||
| Bit3 | |||
| Bit4 | |||
| Bit5 | CHIP_ID | N/C | |
| Bit6 | |||
| Bit7 | NU | ||
| Bit8 | |||
| Bit9 | |||
| Bit10 | |||
| Bit11 | |||
| Bit12 | R_SAT_ERR | ||
| Bit13 | COUNT | VCO_TRIM | |
| Bit14 | |||
| Bit15 | |||
| Bit16 | |||
| Bit17 | |||
| Bit18 | |||
| Bit19 | |||
| Bit20 | |||
| Bit21 | VCO_SEL | ||
| Bit22 | |||
| Bit23 | |||
| Bit24 | |||
| Bit25 | |||
| Bit26 | |||
| Bit27 | MUX_COUNT | ||
| Bit28 | RB_REG | ||
| Bit29 | |||
| Bit30 | |||
| Bit31 | MUX_COUNT | RB_ENABLE | |
Table 14. Register 0 (Readback Only)
| Register 0 | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 0 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 0 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 0 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | CHIP_ID<0> | 1 | Chip ID |
| Bit6 | CHIP_ID<1> | 0 | |
| Bit7 | NU | x | Not Used |
| Bit8 | NU | x | |
| Bit9 | NU | x | |
| Bit10 | NU | x | |
| Bit11 | NU | x | |
| Bit12 | R_SAT_ERR | x | R-div saturation error for cal |
| Bit13 | COUNT<0>/NU | x | VCO frequency counter high when MUX_COUNT = 0 and VCO_TEST_MODE = 1 VCO frequency counter low when MUX_COUNT = 1 and VCO_TEST_MODE = 1 Autocal results for VCO_TRIM and VCO_SEL when VCO_TEST_MODE = 0 |
| Bit14 | COUNT<1>/NU | x | |
| Bit15 | COUNT<2>/VCO_TRIM<0> | x | |
| Bit16 | COUNT<3>/VCO_TRIM<1> | x | |
| Bit17 | COUNT<4>/VCO_TRIM<2> | x | |
| Bit18 | COUNT<5>/VCO_TRIM<3> | x | |
| Bit19 | COUNT<6>/VCO_TRIM<4> | x | |
| Bit20 | COUNT<7>/VCO_TRIM<5> | x | |
| Bit21 | COUNT<8>/VCO_SEL<0> | x | |
| Bit22 | COUNT<9>/VCO_SEL<1> | x | |
| Bit23 | COUNT<10>/VCO_SEL<2> | x | |
| Bit24 | COUNT<11> | x | |
| Bit25 | COUNT<12> | x | |
| Bit26 | COUNT<13> | x | |
| Bit27 | COUNT<14> | x | |
| Bit28 | COUNT<15> | x | |
| Bit29 | COUNT<16> | x | |
| Bit30 | COUNT<17> | x | |
| Bit31 | MUX_COUNT | x | [0] = max freq count, [1] = min freq count |
Table 15. Register RDBK (Write Register for Readback)
| RDBK | Bit Name | Reset Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit0 | ADDR<0> | 0 | Register Address Bits |
| Bit1 | ADDR<1> | 0 | |
| Bit2 | ADDR<2> | 0 | |
| Bit3 | ADDR<3> | 1 | |
| Bit4 | ADDR<4> | 0 | |
| Bit5 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit6 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit7 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit8 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit9 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit10 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit11 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit12 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit13 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit14 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit15 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit16 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit17 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit18 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit19 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit20 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit21 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit22 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit23 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit24 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit25 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit26 | N/C | 0 | |
| Bit27 | MUX_COUNT | 0 | [0] = max freq count, [1] = min freq count |
| Bit28 | RB_REG<0> | x | Three LSBs of the address for the register that is being read: [001] = Register 1 [110] = Register 6 |
| Bit29 | RB_REG<1> | x | |
| Bit30 | RB_REG<2> | x | |
| Bit31 | RB_ENABLE | 1 | Puts device in Readback mode |
8.5.1.1 BIAS SETTINGS
Optimum TRF7322 bias settings used in the performance measurements are shown in Table 16.
Table 16. Register Settings With Optimized Bias Set Used in the Performance Measurement.
| REGISTER | BITS | TYPICAL OPERATING MODE [256MHz-2GHz], INT MODE | TYPICAL OPERATING MODE [2GHz - 3GHz], INT MODE | TYPICAL OPERATING MODE [3GHz - 4.1GHz], INT MODE | LOW POWER MODE, INT MODE | FRACTIONAL MODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REGISTER 1 | RDIV | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 1 | REF_INV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 1 | NEG_VCO | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| REGISTER 1 | ICP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 1 | ICPDOUBLE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 1 | CAL_CLK_SEL | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 15 |
| REGISTER 2 | NINT | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 2 | PLL_DIV_SEL | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 2 | PRSC_SEL | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 2 | VCO_SEL | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 2 | VCO_SEL_MODE | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 2 | CAL_ACC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 2 | EN_CAL | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| REGISTER 3 | NFRAC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | x |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_PLL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_CP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_VCO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_VCO_MUX | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD _DIV124 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_PRESC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_OUTBUF | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_LO_DIV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_TX_DIV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | PWD_MOD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | EN_EXTVCO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | EN_ISOURCE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| REGISTER 4 | LD_ANA_PREC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| REGISTER 4 | CP_TRISTATE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | SPEEDUP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | LD_DIG_PREC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | MOD_ORD | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| REGISTER 4 | DITH_SEL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | DEL_SD_CLK | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| REGISTER 4 | EN_FRAC_MODE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| REGISTER 5 | IB_MOD_GM | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| REGISTER 5 | IB_MOD_LO | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCO_BIAS | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCOBUF_BIAS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| REGISTER 5 | OUTBUF_BIAS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCOMUX_BIAS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCO_CAL_IB | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCO_CAL_REF | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCO_AMPL_CTRL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 5 | VCO_VB_CTRL | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| REGISTER 5 | EN_LD_ISOURCE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 6 | VCO_TRIM | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 6 | EN_LOCKDET | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 6 | VCO_TEST_MODE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 6 | CAL_BYPASS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 6 | MUX_CTRL | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| REGISTER 6 | ISOURCE_SINKB | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REGISTER 6 | ISOURCE_TRIM | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 7 |
| REGISTER 6 | LO_DIV_SEL | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 6 | LO_DIV_BIAS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| REGISTER 6 | TX_DIV_SEL | x | x | x | x | x |
| REGISTER 6 | TX_DIV_BIAS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| REGISTER 6 | GAIN_CTRL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |