SGLS121E July 2002 – April 2025 UCC2800-Q1 , UCC2801-Q1 , UCC2802-Q1 , UCC2803-Q1 , UCC2804-Q1 , UCC2805-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Detailed Pin Description
- 7.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.3 Self-Biasing, Active Low Output
- 7.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 7.3.5 Oscillator
- 7.3.6 Synchronization
- 7.3.7 PWM Generator
- 7.3.8 Minimum Off-Time Setting (Dead-Time Control)
- 7.3.9 Leading Edge Blanking
- 7.3.10 Minimum Pulse Width
- 7.3.11 Current Limiting
- 7.3.12 Overcurrent Protection and Full Cycle Restart
- 7.3.13 Soft Start
- 7.3.14 Slope Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.3 Self-Biasing, Active Low Output
The self-biasing, active low clamp circuit shown in Figure 7-2 eliminates the potential for problematic MOSFET turnon. As the PWM output voltage rises while in UVLO, the P device drives the larger N type switch ON, which clamps the output voltage low. Power to this circuit is supplied by the externally rising gate voltage, so full protection is available regardless of the ICs supply voltage during undervoltage lockout.
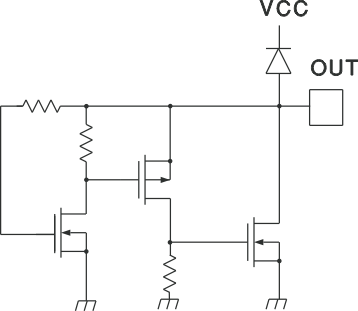 Figure 7-2 Internal Circuit Holding OUT Low During UVLO
Figure 7-2 Internal Circuit Holding OUT Low During UVLO Figure 7-3 OUT Voltage vs OUT Current During UVLO
Figure 7-3 OUT Voltage vs OUT Current During UVLO