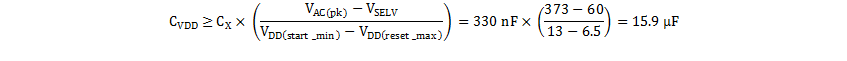SLUSBW3D March 2014 – December 2017 UCC28630 , UCC28631 , UCC28632 , UCC28633 , UCC28634
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 High-Voltage Current Source Start-Up Operation
- 8.3.2 AC Input UVLO / Brownout Protection
- 8.3.3 Active X-Capacitor Discharge (UCC28630 and UCC28633 only)
- 8.3.4 Magnetic Input and Output Voltage Sensing
- 8.3.5 Fixed-Point Magnetic Sense Sampling Error Sources
- 8.3.6 Magnetic Sense Resistor Network Calculations
- 8.3.7 Magnetic Sensing: Power Stage Design Constraints
- 8.3.8 Magnetic Sense Voltage Control Loop
- 8.3.9 Peak Current Mode Control
- 8.3.10 IPEAK Adjust vs. Line
- 8.3.11 Primary-Side Constant-Current Limit (CC Mode)
- 8.3.12 Primary-Side Overload Timer (UCC28630 only)
- 8.3.13 Overload Timer Adjustment (UCC28630 only)
- 8.3.14 CC-Mode IOUT(lim) Adjustment
- 8.3.15 Fault Protections
- 8.3.16 Pin-Fault Detection and Protection
- 8.3.17 Over-Temperature Protection
- 8.3.18 External Fault Input
- 8.3.19 External SD Pin Wake Input (except UCC28633)
- 8.3.20 External Wake Input at VSENSE Pin (UCC28633 Only)
- 8.3.21 Mode Control and Switching Frequency Modulation
- 8.3.22 Frequency Dither For EMI (except UCC28632)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Applications and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Notebook Adapter, 19.5 V, 65 W
- 9.2.2 UCC28630 Application Schematic
- 9.2.3 Design Requirements
- 9.2.4
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.4.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.4.2 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 9.2.4.3 Transformer Turn Ratio
- 9.2.4.4 Transformer Magnetizing Inductance
- 9.2.4.5 Current Sense Resistor RCS
- 9.2.4.6 Transformer Constraint Verification
- 9.2.4.7 Transformer Selection and Design
- 9.2.4.8 Slope Compensation Verification
- 9.2.4.9 Power MOSFET and Output Rectifier Selection
- 9.2.4.10 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.4.11 Calculation of CC Mode Limit Point
- 9.2.4.12 VDD Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.4.13 Magnetic Sense Resistor Network Selection
- 9.2.4.14 Output LED Pre-Load Resistor Calculation
- 9.2.5 External Wake Pulse Calculation at VSENSE Pin (UCC28633 Only)
- 9.2.6 Energy Star Average Efficiency and Standby Power
- 9.2.7 Application Performance Plots
- 9.3 Dos and Don'ts
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|7
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.4.12 VDD Capacitor Selection
Size the VDD capacitor to supply sufficient IDD(run) current to the device during initial start-up, and also during the charging phase of the main output capacitors. During the charging phase the bias winding on the transformer must supply the bias power. When VDD reaches the VDD(start) threshold, the device consumes IDD(run) for tSTART(del) before the PWM switching commences. Thereafter, the bias current is the device current plus the MOSFET gate current. The VDD capacitor must support this higher level of current until the output is sufficiently charged that the bias winding rail has increased above the VDD(stop) level.
Calculate the required bias capacitance from the total bias charge associated with the device run current during the tSTART(del) phase, plus the device run current during the output charge phase, plus the primary MOSFET gate charge current during the output charge phase. The time taken for the output charge phase to reach a sufficient level to supply the bias can be calculated from the size of the output capacitor, target output regulation voltage, and the difference between the available CC mode current limit and the maximum load current (assuming that the output capacitor has to be charged whilst also supplying full rated load current). Assume that the MOSFET is switched at 60 kHz throughout the charging phase.
Combining these into one equation, the required VDD capacitor can be calculated as shown in Equation 57.
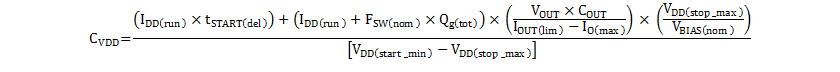
This can be re-written with the explicit device values substituted:
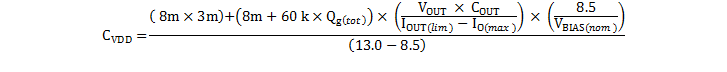
For this EVM design, the MOSFET Qg(tot) is 30 nC, VBIAS(nom) is 12.6 V. IO(max) is 3.35 A, so this equates to:
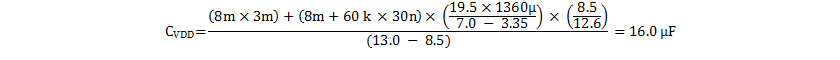
Choose the next higher standard value, 22 μF.
Verify that the bias capacitance is sufficient to absorb all the X-capacitor energy when it has to be discharged, per Equation 3. From Figure 44, the value of X-capacitor is 330 nF.