SLVSES8A October 2020 – December 2020 LM5127-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Enable (EN, VCC_HOLD)
- 8.3.2 Dual Input VCC Regulator (BIAS, VCCX, VCC)
- 8.3.3 Dual Input VDD Switch (VDD, VDDX)
- 8.3.4 Device Configuration and Light Load Switching Mode Selection (CFG/MODE)
- 8.3.5 Fixed or Adjustable Output Regulation Target (VOUT, FB)
- 8.3.6 Overvoltage Protection (VOUT, FB)
- 8.3.7 Power Good Indicator (PGOOD)
- 8.3.8 Programmable Switching Frequency (RT)
- 8.3.9 External Clock Synchronization (SYNC)
- 8.3.10 Programmable Spread Spectrum (DITHER)
- 8.3.11 Programmable Soft Start (SS)
- 8.3.12 Fast Re-start using VCC_HOLD (VCC_HOLD)
- 8.3.13 Transconductance Error Amplifier and PWM (COMP)
- 8.3.14 Current Sensing and Slope Compensation (CSA, CSB)
- 8.3.15 Constant Peak Current Limit (CSA, CSB)
- 8.3.16 Maximum Duty Cycle and Minimum Controllable On-time Limits (Boost)
- 8.3.17 Bypass Mode (Boost)
- 8.3.18 Minimum Controllable On-time and Minimum Controllable Off-time Limits (Buck)
- 8.3.19 Low Dropout Mode for Extended Minimum Input Voltage (Buck)
- 8.3.20 Programmable Hiccup Mode Overload Protection (RES)
- 8.3.21 MOSFET Drivers and Hiccup Mode Fault Protection (LO, HO, HB)
- 8.3.22 Battery Monitor (BMOUT, BMIN_FIX, BMIN_PRG)
- 8.3.23 Dual-phase Interleaved Configuration for High Current Supply (CFG)
- 8.3.24 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.25 External VCCX Supply Reduces Power Dissipation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGZ|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGZ|48
発注情報
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
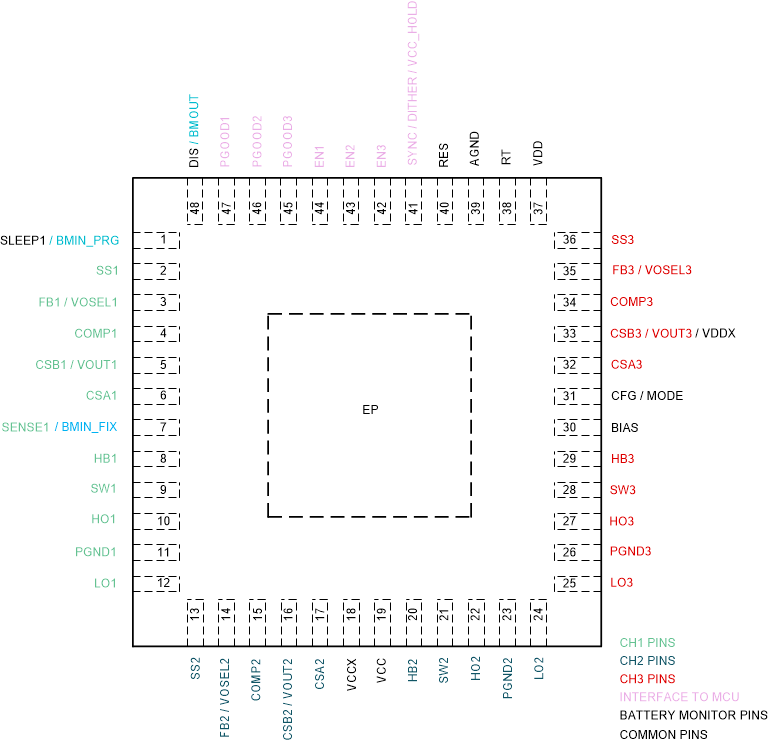 Figure 6-1 48-pin QFN with Wettable
Flanks RGZ Package (Top View)
Figure 6-1 48-pin QFN with Wettable
Flanks RGZ Package (Top View)Table 6-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O(3) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 39 | AGND | G | Analog ground pin. Connect to the analog ground plane through a wide and short path. |
| 30 | BIAS | P | Supply voltage input to the VCC regulator. Connect a 1-μF local BIAS capacitor from the pin to ground. |
| 31 | CFG/MODE | I | Device configuration (boost or buck, single-phase or dual-phase) and switching mode (FPWM or Skip mode) selection pin. Diode emulation mode is enabled by connecting 57.6 kΩ between SS and AGND in FPWM mode. |
| 4 | COMP1 | O | Output of the internal trans-conductance error amplifier. Connect the loop compensation components between the pin and AGND. |
| 15 | COMP2 | ||
| 34 | COMP3 | ||
| 6 | CSA1 | I | Current sense amplifier input pin. In boost configuration, the pin works as a negative input pin. In buck configuration, the pin works as a positive input pin. |
| 17 | CSA2 | ||
| 32 | CSA3 | ||
| 5 | CSB1/VOUT1 | I | Current sense amplifier input pin. In boost configuration, the pin works as a positive input pin. In buck configuration, the pin works as a negative input pin and senses output voltage for fixed output voltage options. VDDX is an optional input for the VDD supply. If the VOUT3 regulation target is 3.3 V and the device is in deep sleep mode, VDDX is internally connected to VDD when VDD is less than 3.4 V (typical). |
| 16 | CSB2/VOUT2 | ||
| 33 | CSB3/VOUT3/VDDX | ||
| 48 | DIS/BMOUT | O | When CH1 is configured as a pre-boost, the DIS pin works as a resistor divider disconnection pin. The pin is pulled low when at least one channel is in active mode. In order to minimize leak current through the resistor dividers, the pin opens during shutdown and during deep sleep mode when all enabled channels are in sleep, SLEEP1 > 1.02 V and SENSE1 > 6.0 V. When CH1 is configured as a buck, the pin works as a battery monitor output. The pin is pulled low when BMIN_FIX is less than 5.7 V or BMIN_PRG is less than 1.0 V. The pin opens when BMIN_FIX is greater than 6.0 V. |
| 44 | EN1 | I | Enable pin. If EN is less than 0.4, the channel is in shutdown mode. The pin must be raised above 2.0 V to enable the channel. Connect to BIAS if not used. |
| 43 | EN2 | ||
| 42 | EN3 | ||
| 3 | FB1/VOSEL1 | I | Error amplifier negative feedback input or fixed output voltage selection pin. In buck configuration, connect the pin to AGND for a 3.3-V output, connect the pin to VDD for a 5-V output, or connect feedback resistors to the pin to program the output regulation target. In boost configuration, always connect feedback resistors to the pin to program the output regulation target. |
| 14 | FB2/VOSEL2 | ||
| 35 | FB3/VOSEL3 | ||
| 8 | HB1 | P | High-side driver supply for bootstrap gate drive. In boost configuration, boot diode is internally connected from VCC to the pin. Connect external boot diode from the pin to VCC in buck topology. Connect a 0.1-μF capacitor between the pin and SW. Connect HB to VCC directly for non-synchronous boost operation. |
| 20 | HB2 | ||
| 29 | HB3 | ||
| 10 | HO1 | O | High-side gate driver output. Connect to the gate of the N-channel MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| 22 | HO2 | ||
| 27 | HO3 | ||
| 12 | LO1 | O | Low-side gate driver output. Connect directly to the gate of the N-channel MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| 24 | LO2 | ||
| 25 | LO3 | ||
| 11 | PGND1 | G | Power ground pin. Connect directly to the source of the N-channel MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| 23 | PGND2 | ||
| 26 | PGND3 | ||
| 47 | PGOOD1 | O | Power-good indicator with open-drain output. In buck configuration, the pin is pulled low when VOUT is out of the regulation window. In boost configuration, the pin is pulled low when VOUT is less than the regulation target. |
| 46 | PGOOD2 | ||
| 45 | PGOOD3 | ||
| 40 | RES | O | Restart timer pin. A capacitor between RES and AGND determines the time the channel remains off before automatically restarting in hiccup mode. If the pin is connected to AGND, the channel never restarts after the hiccup mode off-time until EN is toggled. If the pin is connected to VDD during initial power-on, the hiccup mode fault counter is disabled and the device operates with non-hiccup mode cycle-by-cycle current limit. The fault counter of each channel operates independently. One channel can operate in normal mode while the other is in hiccup mode overload protection. |
| 38 | RT | I/O | Switching frequency setting pin. If no external clock is applied to SYNC, the switching frequency is programmed by a single resistor between RT and AGND. |
| 7 | SENSE1/BMIN_FIX | I | When CH1 is configured as a synchronous boost, SENSE1 senses the output voltage. The pin should be connected to the drain connection of the high side MOSFET as close as possible in boost configuration. When CH1 is configured as a buck, BMIN_FIX works as a fixed threshold battery monitor input pin. |
| 1 | SLEEP1/BMIN_PRG | I | When CH1 is configured as a boost, it is allowed to enter sleep mode when SLEEP1 is greater than 1.0 V. When CH1 is configured as a buck, BMIN_PRG works as a programmable threshold battery monitor input pin. |
| 2 | SS1 | I/O | Soft-start time programming pin. The device forces diode emulation during soft-start time. By connecting 57.6 kΩ to ground in FPWM mode, the device works in diode emulation without entering sleep mode. Switching stops when SS is grounded. |
| 13 | SS2 | ||
| 36 | SS3 | ||
| 9 | SW1 | P | Switching node. Connect directly to the source of the high-side MOSFET and the drain of the low-side MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. Connect SW to PGND directly for non-synchronous boost operation. |
| 21 | SW2 | ||
| 28 | SW3 | ||
| 41 | SYNC/DITHER /VCC_HOLD | I/O | External synchronization clock input or dithering frequency programming pin. The internal oscillator can be synchronized to an external clock during the operation. If VCC_HOLD > 2.0 V, the device holds the VCC pin voltage higher than VCC UVLO threshold when all EN pins are grounded, which helps to restart switching immediately without reconfiguration. If a capacitor is connected between the pin and AGND, dithering is enabled. In this mode, the capacitor is charged and discharged with a 20-μA current source/sink. As the voltage on the pin ramps up and down, the oscillator frequency is modulated between –7% and +7% of the nominal frequency set by the RT resistor. Dithering can be disabled during the operation by pulling down the pin to ground. Connect the pin to AGND if the pin is not used. |
| 19 | VCC | P | VCC bias supply pin. Connect a 10-μF VCC capacitor between the pin and power ground. |
| 18 | VCCX | P | Optional input for an external VCC supply. If VCCX > 4.5 V, VCCX is internally connected to VCC. Connect a 0.47-μF local VCCX capacitor between the pin and PGND. If VCCX is unused, the pin must be connected to ground. |
| 37 | VDD | P | VDD bias supply pin. Connect a 0.1-μF VDD capacitor between the pin and AGND. |
| - | EP | Exposed pad of the package. EP is internally connected to AGND. EP must be soldered to the large analog ground plane to reduce thermal resistance. | |
(3) G = Ground, I = Input, O = Output, P = Power