SBOU187A april 2017 – april 2023
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
- 2INA233EVM Hardware
- 3INA233EVM Hardware Setup
-
4INA233EVM Software Overview
- 4.1 Starting the INA233EVM Software
- 4.2 Configuring the INA233EVM Software
- 4.3 Using the INA233EVM Software
- 5INA233EVM Documentation
- 6Revision History
3.3 Configuration of INA233EVM Jumper Settings
Figure 3-2 shows the default jumper configuration for the INA233EVM. In general, the jumper settings of the SM-USB-DIG Platform do not need to be changed. Change the jumpers on the INA233EVM board to match your specific configuration. For example, set a specific I2C address by configuring J1 and J2.
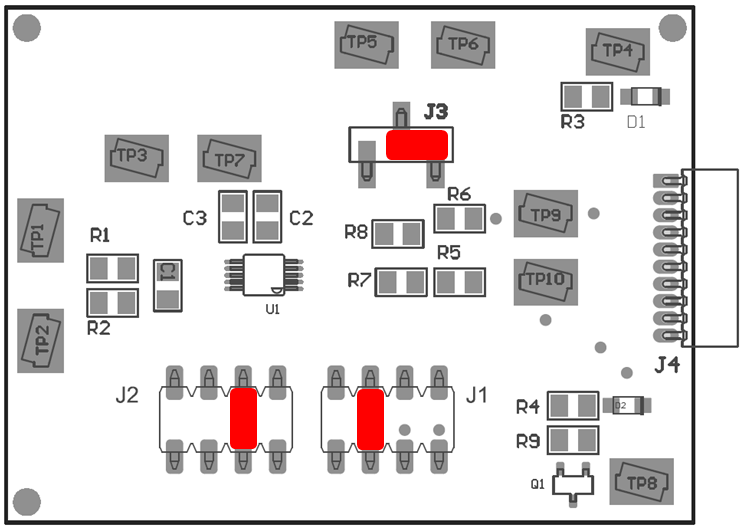 Figure 3-2 INA233EVM
Default Jumper Settings
Figure 3-2 INA233EVM
Default Jumper SettingsTypically, jumper 3 (J3) on the INA233EVM is always set to the INT position. When set to the INT position, the SM-USB-DIG Platform provides the supply for the INA233. When this jumper is set to the EXT position, an external supply voltage can be connected to test point VS_EXT to provide the supply for the INA233.
Jumper 1 (J1) and jumper 2 (J2) control the I2C address pins for the INA233. These jumpers can set the address for A0 and A1 to either supply, ground, SCL, or SDA. Make sure to only connect one jumper at a time for each address control. Failure to properly connect jumpers can cause shorts or interruptions in the communication lines. For more information on the INA233 addressing, refer to the INA233 product data sheet.
Table 3-1 summarizes the function of the INA233 Test Board jumpers. For most applications, all jumpers must be left in the respective default configurations.
| Jumper | Default | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| J3 | INT | This jumper selects whether the VS pin on the INA233 is connected to the VDUT signal generated from the SM-USB-DIG Platform or whether the digital supply pin is connected to test point VS_EXT, allowing for an external supply to power the device. The default INT position connects the VS pin to the VDUT control signal. |
| J1 | GND | This jumper selects the I2C A0 address selection for A0. |
| J2 | GND | This jumper selects the I2C A1 address selection for A1. |