SLAAEF5 March 2024 MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1306-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Algorithm Introduction
- 3Gauge GUI Introduction
- 4MSPM0 Gauge Evaluation Steps
- 5MSPM0 Gauge Solutions
- 6References
2.2.2 CusRltSoc Calculation
For real applications, the wanted SOC by customer is not NomAbsSoc, because the current cannot be controlled at 0 when the battery full and battery empty state is reached, see in Figure 2-2.
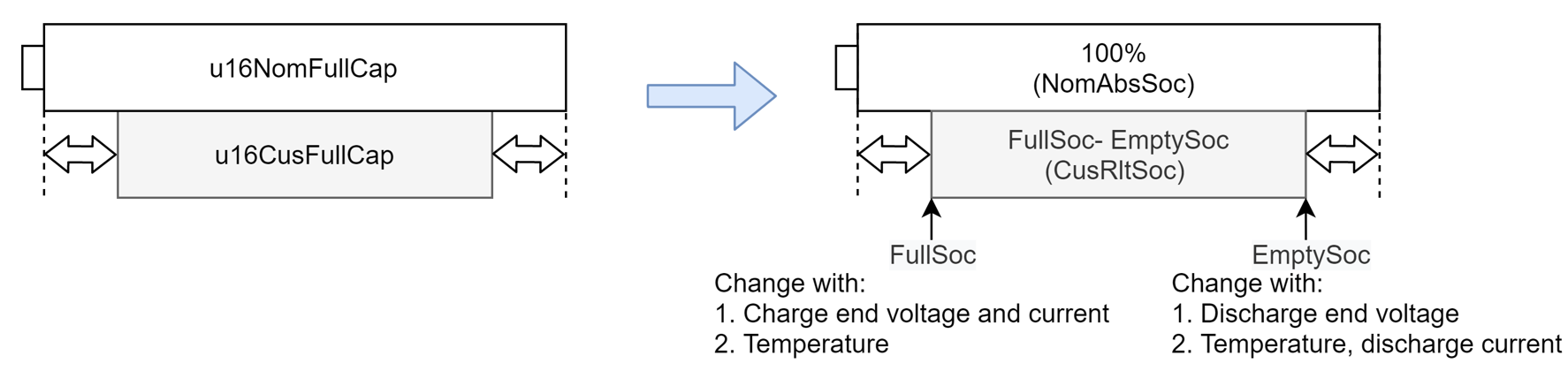 Figure 2-7 Capacity to SOC
Figure 2-7 Capacity to SOCBased on the normalization factor: NomFullCap, three new SOCs are gotten to represent the unchangeable capacity, see in Figure 2-7. FullSoc is used to represent the uncharged NomAbsSoc threshold and EmptySoc is used to represent the undischarged NomAbsSoc threshold. CusRltSoc is used to represent the relative SOC, which the normalization factor (FullSoc-EmptySoc) keeps changing with the battery conditions. The equations to calculate the CusRltSoc is shown in Equation 6.
The key point to get the CusRltSoc is to get FullSoc and EmptySoc under different conditions. In this gauge algorithm, FullSoc and EmptySoc are recorded and updated into a table under different battery conditions. For this part, refer to Section 2.3.4.