SPRACP3C November 2019 – December 2021 AWR6843 , AWR6843AOP , IWR1443 , IWR1642 , IWR6443 , IWR6843 , IWR6843AOP
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Typical Certification Procedure
- 3Regulatory Compliance Overview
- 4Tools and Setup
- 5Common Issues and Resolutions
- 6References
- 7Revision History
3.1.1 Efficient Use of the Radio Spectrum (EN 305 550)
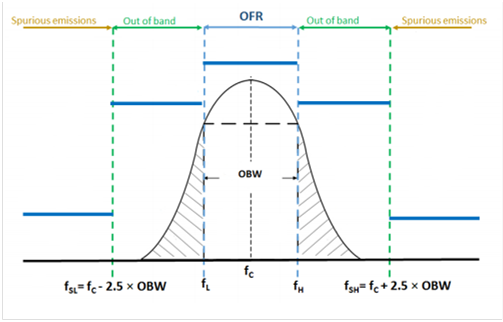 Figure 3-1 OFR, Out of Band and Spurious Emission Frequency Limit
Figure 3-1 OFR, Out of Band and Spurious Emission Frequency LimitThe following limits and tests apply:
- Duty Cycle: The duty cycle is factored into mean power measurement when using a power meter; see section on duty cycle Section 3.3.1.
- Permitted range of operating frequencies: See section 4.3.1 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 ( section 7.3 EN 305 550-1 V1.2.1). This is the authorized frequency range devices are permitted to operate.
- Operating frequency range (OFR): See section 4.3.2 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 . This is the intentional operating frequency range of the device. The IWR6843 mmWave device falls in the 57 to 64 GHz band and can also be operated in the 61.0 GHz to 61.5 GHz bandwidth. The occupied bandwidth (OBW) is measured as the bandwidth occupying 99% of the total power in the operating frequency range.
Table 3-1 Operating Frequency Range
| Bandwidth (GHz) | FL (GHz) | FH (GHz) |
|---|---|---|
| 57 - 64 | > 57 | < 64 |
| 61.0 – 61.5 | > 61 | < 61.5 |
| 122 - 123 | > 122 | < 123 |
| 244 - 246 | > 244 | < 246 |
- Mean Power: See section 4.3.3 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 ( section 7.2 EN 305 550-1 V1.2.1) . Mean power is a measure of radiated power or mean equivalent isotropic Radiated power (EIRP); it refers to the highest transmitted power level during the transmission cycle. The limit for 57 to 64 GHz is 100 mW EIRP (20 dBm EIRP), same limit applies to 61.0 GHz to 61.5 GHz. When taking measurement using a signal analyzer the channel power function is used:
Equation 1.
- Mean Power spectral density: See section 4.3.4 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 ( section 7.1 EN 305 550-1 V1.2.1). This is defined as the emitted power spectral density over the transmission bandwidth in the direction of maximum antenna gain. Limit for 57 GHz to 64 GHz is 13 dBm/MHz EIRP. No limit is defined for 61.0 GHz to 61.5 GHz.
- Out of band (OOB) emissions: See section 4.3.5 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 ( section 7.4 EN 305 550-1 V1.2.1). The OOB bandwidth is calculated as in Equation 2.
Equation 2.
Equation 3.
Table 3-2 shows the limits and bandwidth for out of band and spurious emissions for the mmWave device operating at both the full 4-GHz bandwidth and 500-MHz bandwidth.
The occupied bandwidth (OBW) is the width of the intentional signal mean power containing 99% of the total mean power, power below and above this limit (the out of band emission) should be equal to 0.5% of the mean power. This equates to -23dBc bandwidth of the signal.
Table 3-2 Out of Band and Spurious Emissions Bandwidth
| OBW/OFR | Permitted operating frequency range | fsl | fl | fc | fh | fsh | OOB limit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 GHz | 57 GHz to 64 GHz | 52 | 60 | 62 | 64 | 72 | -20 dBm/Mhz | |
| 500 MHz(similar limits to 4 Ghz applies if operating outside of the 61 to 6.15 range ) | 61.0 GHz to 61.5 GHz | 60 | 61 | 61.25 | 61.5 | 62.5 | -10 dBm/Mhz |
- Radiated spurious emissions: See section 4.3.6 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 ( section 7.5 EN 305 550-1 V1.2.1). The spurious emission frequency range includes frequency beyond the OOB limit. The spurious emission is measured up to the 2nd harmonic of the fundamental frequency; the IWR6843 operates from 60-64 GHz, with second harmonic at 128 GHz.
- Receiver spurious: See section 4.4.2 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0 (section 8 EN 305 550-1 V1.2.1). Per clause 4.4.2.1 the receiver spurious is only applicable when the equipment can work in receive-only mode. The test does not apply to mmWave devices as it operate in simultaneous transmit/receive mode.
- Receiver interference signal handling: See section 4.4.3 of EN 305 550 V2.1.0. This measures the capability of the device to coexist with other radio applications transmitting within the in-band, OOB, and remote band frequency limit. The interference source should transmit at 10-dBm equivalent EIRP for in band frequency and 20-dBm equivalent EIRP for OOB and remote band frequency.
Equation 4.Equation 5.Equation 6.